* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Host Microbe Relationship
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
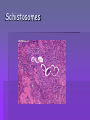
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
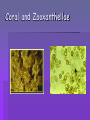
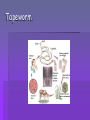
Host Microbe Relationship Patricia Sidelsky 2007 Microbe host relationships Symbiosis – Coexistence of two or more organisms to the success of the other in the environment. Can evolve specific mechanisms to maintain this relationship 1. Mutualism 2. Commensalism 3. Parasitism Mutualism Both partners in a relationship are dependent upon each other Each contributes to the success of the other organism in a particular environmemt Rhizobium and legumes Coral and Zooxanthellae Coral Bleaching can lead to death of the reef Leaf cutter ants Ruminants - Gut reactions: Sequencing ruminal bacteria Commensalism Microbes that share space on the skin as well as the metabolic products Coexist – the partners in the relationship do not contribute to the success of their fellow microbes, but neither are they harmed E. Coli in the gut E. coli lives in an enriched environment high in nutrients In return E. coli produces Vitamin K for blood clotting Parasitism and Pathogens Pathogens are disease producing organisms The parasite benefits from the relationship The host is harmed +/- relationship Flat worms - Platyhelminthes Cestodes Trematodes Schistosomiasis Schistosomes Clinorchis senensis - Liver Tapeworm Tapeworm Protozoan parasites – Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum Giardia lamblia Entamoeba histolytica Key terms Infection refers to the presence or a parasitic organism or pathogen( implies that they are established and reproducing) Infestation – A word usually limited to larger parasites like helminths or worms Contamination – refers to the presence of microbes( can be on the surface of an inanimate object ) Disease Disturbance in the state of health that may result in the infection of human tissue by microbes Changes in the host that interfere with normal function Fever, diarrhea, inflammation, irreparable damage Pathogenicity Ability to produce disease Invasion of pathogen Release of molecules by pathogen Host response to invader Relationships Normal flora – normal microbiota – Many organisms have well established associations with humans Resident microbiota – microbes that are always present – skin, orifices, interior of nose and throat – Tend to colonize mucous membranes Transient microbes Present under certain conditions May require special nutrients Not as adaptive OPPORTUNISTIC ORGANISMS MAY BE TRANSIENT Opportunistic organisms Able to penetrate the immune defenses if there is another infectious agent present Immunocompromised due to malnutrion or other extennuating factor Introduced at an innapropriate body site Imbalance of the normal flora due to antibiotic therapy Imbalance of the normal flora due to chemotherapy