* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
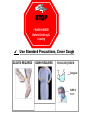
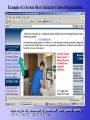
INFECTION CONTROL – IT’S IN YOUR HANDS Infection Prevention & Control THE BASICS HAND HYGIENE - NO ARTIFICIAL NAILS - CLEANSING HANDS - THE MOST IMPORTANT MEANS OF PREVENTING THE SPREAD OF INFECTION Germs don’t have a chance with the proper use of these weapons. Soap / Water Alcohol-based hand hygiene products Hand Hygiene Two different ways to keep your hands germ free Soap and water for 15 seconds. (Make bubbles while applying friction). Alcohol hand rub if no visible soiling present on hands. Hand Hygiene is JCAHO’s # 7 Patient Safety Goal Speak-up Campaign for Patients Encouraging patients to ask the Healthcare Worker (HCW) about handwashing! STANDARD PRECAUTIONS Healthcare workers must treat all blood & body fluids as infectious. Standard Precautions also include: • Hand Hygiene • Personal Protective Equipment shields,goggles (PPE) gloves,gowns,masks,face- • Anticipate Your Exposure • Use Sharp-Safety Devices • Clean Surfaces Regularly • Appropriate Waste Disposal (Red bags, regulated medical waste) PPEs Wear them proudly. BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS “The Big 3” HIV, HEPATITIS B AND HEPATITS C SPREAD THROUGH CONTACT WITH BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS HIGH RISK BEHAVIORS: Sharing Needles or other sharp objects Unprotected Sexual Contact Unclean Tattoo Parlors Accidental puncture from contaminated needles and other sharps can result in transmission of Bloodborne pathogens. Safety Needles, Devices and PPEs = Protection. Hepatitis B Vaccinated: If you have received the vaccine (all 3 shots) and have developed immunity, virtually no risk for infection. Unvaccinated: Risk from single needlestick or cut 6-30% Depends on the Hepatitis (antigen of sources blood). Hepatitis C Limited studies available but risk seems to be about 1.8%. HIV Average risk for HIV infection to develop after needlestick or cut exposure to HIV blood is 0.3% Risk after exposure to HIV blood through splashes to eyes, mouth or nose is 0.1% RESPIRATORY ETIQUETTE A.K.A. Good Health Manners Cover coughs and sneezes with tissue or your upper sleeve, NOT your hand. Put used tissues in trash ASAP. Patients who can’t cover their coughs might be asked to wear a mask. Don’t forget to: wash wash wash Keep your germs to yourself Make Respiratory Etiquette your “Modus Operandi.” RESPIRATORY ETIQUETTE Simple Steps Help Infections What Healthcare workers can do: • Encourage patients to wash hands • Wear mask/eye protection if close to coughing patient (within 3ft) • Place patient in private room or away from other patients if cough & fever are present and suspect contagious disease • Provide patients with tissues; teach them to cover their coughs Sample Sign Might see this sign in facilities Lets now put the “Spotlight” on Tuberculosis (a.k.a. TB) TB is an airborne disease “ the germ is in the air” Certain procedures must be followed when caring for a patient with known or suspect TB •HCWs wear a N-95mask or PAPR for any room entry •Keep the patient’s room door closed at all times (special air handling room, negative air pressure) •When in the patient room: - Encourage patients to Cover Coughs with a tissue - Encourage patients to wash hands •When patients leave their rooms, make sure they are wearing a surgical mask (e.g. during any transport) After Standard Precautions & Respiratory Etiquette comes, Transmission-based PRECAUTIONS Standard Precautions & Respiratory Etiquette use doesn’t control all communicable diseases. Organisms (a.k.a. germs) can be spread in different ways. Respiratory droplets: Influenza, Rubella, Bacterial Meningitis Inhaled airborne: Tuberculosis (TB), Smallpox, Chickenpox Direct contact: Diarrhea (e.g. C. difficile), skin infections, & multidrug resistant organisms (e.g. MRSA, VRE) Transmission-based PRECAUTIONS Always Communicate to others when patients are in isolation For any room entry don appropriate PPE Clean ANY shared equipment between Patients Although Isolation Signs May Appear Different, ALL Will Have: - a STOP Sign - List of Room Entry PPE Transmission-based Precautions = isolation. STOP WASH HANDS! Before Entering & Leaving Use Standard Precautions, Cover Cough GLOVES REQUIRED GOWN REQUIRED MASK REQUIRED ___Surgical ___ N-95 or PAPR IMMUNIZATIONS, INJURIES & Employee Health -HEPATITIS B VACCINE -ANNUAL TB RISK ASSESSMENT -Other vaccinations - REPORT ALL INJURIES If you have a work related injury, including needlestick or blood exposure, immediately notify your supervisor, & report the injury to Employee Health. Infection Control Most facilities will have the following on their intranet: Regional policies & procedures Facility specific policies & procedures (Infection Control Manual) Links, Resource Center Educational material Lots of valuable information Example of a Screen Shot: Infection Control Regional Site. Links on the left allow user to “check out” their specific facility Add to “Favorite” web sites folder. - Compassion -Excellence - Respect - Justice -Stewardship