* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ambulatory Care Lecture: Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
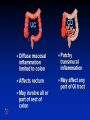
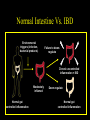
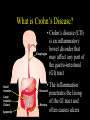
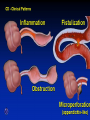
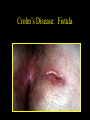
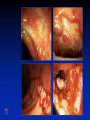
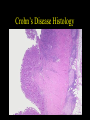
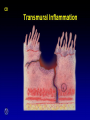
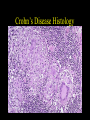
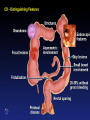
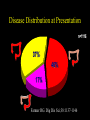
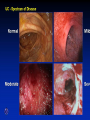
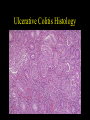
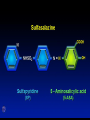
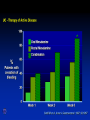
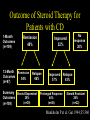
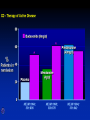
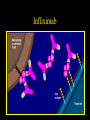
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Kimberly Persley, MD Digestive Disease Associates of Dallas Presbyterian Hospital of Dallas What is IBD? • • • • Chronic Inflammation of the bowel Idiopathic Relapsing course IBD Spectrum Ulcerative colitis Crohn’s Disease Indeterminant colitis Epidemiology IBD Facts • Approx 1,000,000 Americans have IBD • men and women affected equally • first peak occurs between the ages of 15-30 a later peak occurs in the 7th decade Normal Intestine Vs. IBD Environmental triggers (infection, bacterial products) Failure to downregulate Chronic uncontrolled inflammation = IBD Moderately inflamed Normal gut controlled inflammation Down-regulate Normal gut controlled inflammation Proportion of Patients with Family History of IBD by Age of Diagnosis % Patients with Positive Family History of IBD 30% 25% * 20% * 15% 10% <20 20-39 >40 5% 0% Age at Diagnosis *p<0.005 Polito JM et al. Gastro.1996;111:580 Diagnosis Diagnosis • • • • • • Clinical history Physical examination Laboratory tests Endoscopic findings Radiographic findings Histology Differential Diagnosis • • • • • • • • Lymphoma Infectious etiologies Appendicitis Diverticulitis Carcinoma Celiac Disease Ischemic colitis Irritable Bowel Syndrome Crohn’s Disease History • In 1932, Drs. Crohn, Oppenheimer and Ginzburg at Mount Sinai Medical Center described a subacute inflammatory process affecting the distal ileum – “terminal ileitis” – “granulomatous ileitis” • In 1952, Dr. Wells reported colonic involvement What is Crohn’s Disease? • Crohn’s disease (CD) is an inflammatory bowel disorder that Esophagus may affect any part of the gastro-intestinal (GI) tract Small Intestine Large Intestine (Colon) Appendix • The inflammation Stomach penetrates the lining of the GI tract and Rectum often causes ulcers Crohn’s Disease: Fistula Fibrostenotic Crohn’s Disease Crohn’s Disease Histology Crohn’s Disease Histology Ulcerative Colitis History • 1859, Samuel Wilks described “simple idiopathic colitis” • 1909 – Hawkins described the natural history of UC – Hurst describe the sigmoidoscopic appearance Disease Distribution at Presentation n=1116 37% 46% 17% Farmer RG. Dig Dis Sci;38:1137-1146 Ulcerative Colitis Histology Medical Treatment Goals of Therapy • • • • • • • Relieve symptoms Prevent recurrence of symptoms Prevent or cure complications Control inflammation of the GI tract Improve quality of life Steroid sparing Reduce the need for surgery Disease Activity • • • • • • • • Number of bowel movements a day presence of blood in stool abdominal exam (tenderness) Weight loss Extraintestinal manifestation Overall well-being Vitals: fever, tachycardia Labs: anemia, Medications for Mild-Moderate Disease • Aminosalicylates – Sulfasalazine – Mesalamine (Pentasa, Asacol, Colazal, Rowasa enema and Canasa Suppositories) • Antibiotics – Metronidazole (Flagyl) – Quinolones (Cipro) Medications for Moderate-Severe Disease • Steroids – Prednisone – Solumedrol – Budesonide (Entocort) • Immunosuppressives – – – – Azathioprine (Imuran) 6-mercaptopurine (Purinethol) Methotrexate Cyclosporin Medications for Moderate-Severe Disease • Biologics – Infliximab (Remicade) Side Effects of Sulfasalazine • • • • • • Fever Headache Rash Nausea/vomiting Diarrhea Loss of appetite Oral 5-ASA Release Sites Pentasa® Asacol® Olsalazine Sulfasalazine COLAZAL™ Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Mesalamine in microgranules Mesalamine w/ eudragit-S Azo bond Mesalamine Side Effects • • • • • Nausea/vomiting Heartburn Diarrhea Headache Allergic Reaction Antibiotic Side Effects • Flagyl – – – – – – metallic taste headache nausea/vomiting dizziness diarrhea peripheral neuropathy • Cipro – – – – – headache rash nausea/vomiting dizziness Achilles tendon rupture Steroid Side Effects • • • • • • • • GI upset Acne Moon face Fluid Retention Diabetes HTN Striae Weight gain • • • • • • Cataracts Glaucoma Depression Osteoporosis Infection Growth retardation Outcome of Steroid Therapy for Patients with CD 1-Month Outcomes (n=109) 12-Month Outcomes (n=87) Remission 48% Remission 54% Improved 32% Relapse 46% Summary Steroid Dependent Outcomes 36% (n=39) (n=109) Improved 57% Prolonged Response 44% (n=48) No response 20% Relapse 43% Steroid Resistant 20% (n=22) Munkholm P et al. Gut 1994;35:360 Purine Metabolism 6Methyl Mercaptopurine TPMT AZA HPRT 6MP Xanthine oxidase 6Thiouric Acid 6TGN Immunosuppressant Side Effects • AZA/6MP – Bone marrow suppression – pancreatitis – hepatitis – allergic reaction – lymphoma – infections • MTX – – – – – hepatotoxicity pneumonitis teratogenic alopecia allergic reaction Infliximab Infliximab Side Effects • • • • • • • Reactivation of TB Headache Nausea Upper respiratory tract infection Other serious infections Fatigue Fever Referral to Surgeon • Symptoms not relieved by medications • Serious complications – – – – abscesses fistula intestinal blockage uncontrolled bleeding Conclusion • Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis are the two major types of IBD • The inflammatory bowel diseases are chronic diseases the are caused by genetic, environmental factors and immunologic abnormalities • Medical treatment options should be tailored based of disease type, distribution and pattern Conclusion • Medical treatment will usually relieve symptoms but relapse is common and therefore treatment is lifelong