* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L Bjerrum
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Acute pancreatitis wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
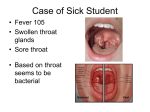
Health Alliance for Prudent Prescribing, Yield And Use of anti-microbial Drugs In the Treatment of Respiratory Tract Infections Proposal for EU DG Research, March 2006 Coordinator: Research Unit of General Practice, Odense, Denmark Prevalence of penicillin resistant pneumococci in Europe 0-5 % 0-2 % 20-30 % 0-5 % 0-5 % 35-40% 15-20 % 40-65 % 40-45% 2 Use of antibiotics in Europa 2002 DDD/1000 persons/day Gossens et al: Outpatient antibiotic use in Europe and association with resistance: a cross-national database study. The Lancet 2005 Penicillin-resistance in pneumococci Linear correlation between use of antibiotics and resistance From: Emerging Infectious Diseases 2004;19(3):514 Selection for Antibiotic Resistance Resistant Strains Rare Antimicrobial Exposure Resistant Strains Dominant HAPPY AUDIT Objective to reduce the occurrence of bacterial resistance by reducing prescribing of unnecessary antibiotics for respiratory tract infections by improving the use of appropriate antibiotics in suspected bacterial infections by improving the quality of diagnostic procedures for RTIs in general practice 60 77 31 102 39 - - - - Nordic region - Denmark 102 GPs - Sweden 77 GPs Balticum region - Lithuania 31 GPs - Kaliningrad 39 GPs Region Hispano-America: - Spain 309 GPs - Argentina 60GPs TOTAL 618 GPs 309 Kick-off meeting April 2007 Project time schedule 2007 2008 X X 2009 2010 Analysis and conference Second registration of Patients Intervention: GPs and patients First registration of Patients First invitation of GPs Total project period: 3 years (April 2007 – March 2010) Kaliningrad Sweden Lithuania Spain Denmark Argentina Intervention material for professionals Report with aggregated and individual results Happy Audit Guidelines Laboratory test instructions Reports in national language including individual results were sent to all paticipating GPs Respiratory infections in general practice Results from 6 countries My Practice My Practice My Practice Centor criteria*: 1. 2. 3. 4. Fever Tender angular glands Tonsil Coatings Absence of cough *Described by dr. Robert Centor of the University of Alabama Centor criteria and probability of Streptococci Number of Centor Criteria Probability of Streptococci Recommandation 0 2% No test – no treatment 1 3% No test – no treatment 2 8% Test and treat 3 19% Test and treat 4 41% Test and treat Patients with 0-1 Centor criteria should not be tested with Strep A Use of Strep A in patients with odinophagia (painful swallowing) Patients StrepA performed Percentage with Strep A Argentina 1500 33 2.2% Denmark 1061 822 77.5% Lithuania 803 0 0.0% Russia 764 4 0.5% Spain 7052 96 1.4% Sweden 501 319 63.7% 11681 1274 10.9% Total Strep A test in Denmark Strep A test in Sweden Carriers of Streptococci 5-10% of individuals are asymptomatic carriers of streptococci A Strep A test will show that carriers have streptococci even though they are not causing symptoms. Generally, carriers should not be treated with antibiotics Overuse of Strep A may lead to inappropriate antibiotic treatments Generally, Strep A should not be performed in: Asymptomatic carriers of Streptococci Patients with sore throat and less than 2 Centor criteria 100 80 60 40 20 0 1 2 EAPs/Facultatiu 3 4 5 Objectiu >70% Conclusion Denmark, Sweden: Overuse of Strep may lead to inappropriate antibiotic treatment and initiatives should be taken to reduce overuse of Strep A testing in general practice Spain, Argentina, Lithuania, Russia: Introduction of Strep A may leed to a lower prescribing in patients with sore thorat and initiatives should be taken to introduce Strep A in general practice ”The more you use it, - the faster you lose it” Burke JP, Lancet 1995;345:977 www.happyaudit.org Collaboration in Europe about rational prescribing of antibiotics CHAMP Changing behaviour of Health care professionals And the general public towards a More Prudent use of antimicrobial agents. Thank you [email protected] Validation study of Strep A in general practice in Barcelona Inclusded 182 patients with sore throat and ≥ 2 Centor criteria Tests: Throat Culture Strep A 44 Amigdalitis La validez de la prueba de Strep A pare diagnosticar Estrep betahem gr A Cult + Cult - Total Strep A pos. 38 10 48 Strep A neg. 2 132 134 40 142 182 Sensitivity: 38/40 = 95% Pos predictive value PPV = 38/48 = 79% Neg predictive value NPV = 132/134 = 98% Specificity: 132/142 = 93% Llor et al. Validación de una técnica antigénica rápida en el diagnóstico de la faringitis por esptreptococo betahemolitico del grupo A, Aten Primaria 2008 Nycocard CRP single test Axis-Shield, Norway Training through local distributors Instrument free during test period Development of quality indicators for diagnosis and treatment of respiratory tract infections in general practice Tonsillitis/pharyngitis Number of patients with a positive StrepA test -------------------------------------------------------------------------Number of patients with acute tonsillitis/pharyngitis treated with antibiotics Number of patients treated with narrow-spectrum penicillin (J01CE) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Number of patients with acute tonsillitis/pharyngitis treated with antibiotics Experts – to do Rate to what extent they agree with the relevance of the 59 quality indicators – according to: A. Reducing antimicrobial resistance B. Clinical relevance for the patient* * Reducing symptoms and/or shortening duration of the actual course of the disease Consensus The item should be retained: ≥ 75 % of participants scored the item ≥ 5 The item should be excluded: ≥ 75 % of participants scored the item ≤ 3 No consensus: items which failed to meet either of the above criteria The final set of indicators 6 acute sinusitis 9 acute otitis media 6 acute tonsillitis/pharyngitis 7 acute lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) 1 acute respiratory tract infection (RTI) 1 penicillin allergy 1 acute bronchitis 5 pneumonia 5 exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Number of doctors Number of patients registered Number of patients treated with antibiotics Argentina 60 4374 1780 Denmark 102 3904 1351 Lithauen 31 2706 1152 Russia 39 3685 1215 Spain 309 16751 4675 77 1853 764 618 33273 10937 Sweden Total Conclusion Participating GPs Estimated: 400 Real number 618 Number of consultations registered Estimated 20-25.000 Real number: 33.273 Written material completed for all partners Guidelines, Patient brochures, Reports etc Days with symptoms