* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy - Tripod
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
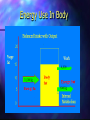
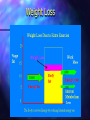
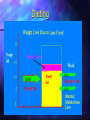
http://barry-b.tripod.com/nutl2.html Nutrients and Energy in Food Macronutrients Micronutrients Energy Nutrients Micronutrients Vitamins and Minerals – are need to effectively extract energy from the macronutrients via catabolism Macronutrients – Protein, Carbohydrate and Lipids –Contain stored energy Energy Content Carbohydrate contain 16 kj/gram Protein contain 17 kj/gram Fat contains 37 kj/gram Alcohol contains 29 kj/gram How is energy content of food measured? – Bomb calorimeter Measures the energy released when the food is burnt. This includes energy from indigestible foods as well as digestible food . The energy content of this "fibre" must be subtracted from the bomb calorimeter measurement. Bomb Calorimeter Stirrer Ignition fuse Water Thermometer Food Sample Bomb Water Tank The extraction of energy from food Catabolism Repackaging energy in ATP packets – Glucose = approx 100 ATP – But catabolism maximum yield is 38 ATP / glucose – as little as 0 ATP as in Brown Adipose Tissue The rest is lost as heat Energy Needs of the Body Total Kilojoule Requirements The average day can be dived into three stages: • Rest, Work and Play Energy need for each stage are about: • Rest, 2000kj Work 3-4000kj Play 3-4000kj • Over all per day = from 6000kj for total bed rest to 14,000 for a very active individual • The need depend on body mass and sex Basal Metabolism – The energy needs of the body at complete rest Used for all Internal energy needs Recycle tissue Immunity Body warmth Reduced by Tissue decrease Is not really “basal” as it can change due to: temperature • and diet. Measure of energy needs of the body Indirect Calorimetry measuring the amount of CO2 breathed out . People can have a respirometer attached while moving Whole body: people can be housed in a room connected to CO2 monitors for air In and out Which nutrients are used first for energy? Actually all macronutrients are used for energy all the time. Different material in different tissues eg.: The brain needs glucose Aerobic Muscles use fat The liver uses mainly excess protein. • Ideal Body Weight Obese Calculate Body Mass Index (BMI) From % Body fat – Measured with Skinfold thickness buoyancy Electrical conduction Desire % Body Fat Body Condition Female Unhealthy <15% Lean 17-22% Normal 22-25% Above Average 25-29% Over weight 29-35% Obese 35+% Male <10% 10-15 15-18% 18-20% 20-25% 25+% Dangers of Under and Over weight Framington study – indicated obesity increased chance of early death cardiovascular disease diabetes Framington Study From Kennel and Gordon 1974 Underweight Framington study indicated underweight increased – chance of early death – infectious disease – cancer Anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa Energy Use In Body Weight Loss Dieting Fat distribution Effect of fat distribution type Andomorphs – More likely to suffer cardiovascular disease Gynomorphs – Less likely to suffer cardiovascular disease Benefits of Obesity Obese people do not get osteoporosis. This may be due to their higher insulin secretion reducing calcium lost in the urine. Causes of Obesity – Nurture versus Nature Nurture Theories Obesity may be caused by phycology • Eating to satisfy : Boredom • Parents • • Stress • Culture • Effect of age • Ego Most obese adults were slim when young Nature Theories Obesity caused by physiology Dieting does not help Muscle tone Diet induced Thermogenesis Glycogen storage variations Ageing Need large food intake to maintain Nitrogen Balance Benefits of Obesity Obese people do not get osteoporosis. This may be due to their higher insulin secretion reducing calcium lost in the urine. Causes of Obesity – Nurture versus Nature Why Dieting Doesn't Work Reduced energy intake causes the body to adapt: lowers “basal metabolism” burns up fat reduces energy using tissue – lean body mass When you go off the diet use less energy get fatter than before