* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Immune and Nervous System
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
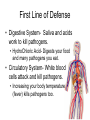
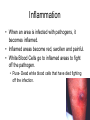
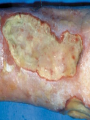
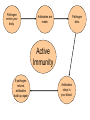
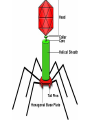
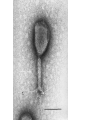
The Immune System What is the Immune System? • A group of defenses that protects the body against disease-causing organisms. • Pathogen- Any disease causing organism. First Line of Defense • Skin- The skin keeps most pathogens from entering into the body. • If the skin is cut or torn, pathogens can get in. • Respiratory System- Mucous and cilia in your windpipe trap pathogens. • Sneezing and coughing gets rid of these trapped pathogens. First Line of Defense • Digestive System- Saliva and acids work to kill pathogens. • HydroChloric Acid- Digests your food and many pathogens you eat. • Circulatory System- White blood cells attack and kill pathogens. • Increasing your body temperature (fever) kills pathogens too. Inflammation • When an area is infected with pathogens, it becomes inflamed. • Inflamed areas become red, swollen and painful. • White Blood Cells go to inflamed areas to fight off the pathogen. • Puss- Dead white blood cells that have died fighting off the infection. Active Immunity • 1. A pathogen (bacteria, virus) enters your body, and you get sick. • 2. White Blood Cells produce AntibodiesSpecific proteins that attack the pathogen. • 3. The pathogen dies, and you get better. • 4. That Antibody stays in your blood incase the pathogen comes back later. • 5. If the pathogen comes back, white blood cells make more Antibodies to fight off the attack, keeping you from getting sick. Pathogen enters your body. Antibodies are made. Pathogen dies. Active Immunity If pathogen returns, antibodies build up again Antibodies stays in your blood. Vaccination • Process of giving a vaccine to help give active immunity. • Vaccine- Preparation of dead or damaged pathogens. -After you get the vaccine, your body will begin making antibodies to fight off the pathogen. -If you ever get the real pathogen, your body will know how to kill it quickly with antibodies. -Your body REMEMBERS which antibodies attack which pathogens! Passive Immunity • When antibodies are made in another person or animal, and then given to you. • Newborn babies have Passive Immunity from antibodies in their mother’s blood. • This Passive Immunity only last for a few months, so the baby will need vaccines to build up their own Active Immunity. Disease-Causing Organisms • Bacteria- Tetanus, strep throat, and pneumonia. • Virus- A small piece of DNA surrounded by a protein coat. • A virus “Tricks” your cells into making more viruses. • Can cause the flu, AIDS, measles, mumps and chickenpox. Disease-Causing Organisms • Protist – Malaria is spread by mosquitoes and African Sleeping Sickness is spread by Tsetse fly. • Fungi – Ringworm and Athletes foot. Infectious Disease • Any disease that is caused by a virus, bacterium, protist or fungus and is easily spread. • Infectious Disease can be spread by contact, water, air or food. • Biological Vector- Any organism that is carrying the disease. Infectious Disease Bacteria Strep Throat Viruses Pneumonia AIDS Protists Fungi Ringworm Athletes Foot Chickenpox Malaria Sleeping Sickness