* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CDC Update on the 2007 TB Technical Instructions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
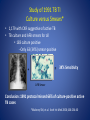
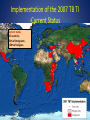
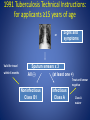
CDC Update on the 2007 TB Technical Instructions Sharmila Shetty, MD Immigrant, Refugee & Migrant Health Branch Division of Global Migration and Quarantine Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Summary • Overview of Immigrant, Refugee, Migrant Health Branch • Epidemiology and trends of TB in the US • Changes in 2007 TB Technical Instructions (TI) Annual Estimate of Migrants Entering the U.S. Total: ~60 million Source: U.S. Department of Homeland Security Refugee admissions: 61,498 (2008) Immigrant, Refugee, and Migrant Health Branch (IRMH) Role • Track and report diseases in these populations • Respond to disease outbreaks in the US and overseas • Advise U.S. partners on health care for refugee groups • Educate and communicate with immigrant and refugee groups and partners. • Provide medical screening and treatment guidelines (technical instructions) Technical Instructions (TIs) Consist of medical screening guidelines Used by overseas panel physicians who conduct medical examinations for U.S.-bound refugees and immigrants Identify applicants with medical conditions of public health concern Inadmissible communicable diseases of public health significance Tuberculosis, active Syphilis, untreated Chancroid, untreated Gonorrhea, untreated Granuloma Inguinale, untreated Lymphogranuloma Venereum, untreated Hansen’s disease (Leprosy) Panel Physician Program: Basics • Statistics 670 panel sites (1 or more panel physicians) > 1,000 laboratory and radiology facilities • Contracted through Dept. of State TB=disease of greatest public health concern Estimated TB Incidence Rate, 2007 Estimated new TB cases (all forms) per 100 000 population No estimate 0-24 25-49 50-99 100-299 300 or more 1/3 of world infected 9.3 million cases of active TB 1.8 million deaths TB Cases, United States, 19932008 TB rate: FB 20.6/100K US 2.1/100K MDR TB Cases, United States 1993-2007 XDR TB (’00-’06): 76% XDR TB (’00-’06): 76% Simplified TB Screening Algorithm CDC required TB screening overseas medical exam: panel physicians Abnormal CXR Normal CXR Sputum work-up to identify active TB TB follow-up exam requested + Post-arrival medical exam 1991 Tuberculosis Technical Instructions • CXR if ≥ 15 years old; no screening for <15 yr • If chest x-ray abnormal • Serial AFB smears • If AFB+ • treat until smear negative • complete therapy in US • No cultures, no DST Study of 1991 TB TI Culture versus Smears* • 1,179 with CXR suggestive of active TB • TB culture and AFB smears for all • 183 culture positive --Only 63 (34%) smear-positive = + 34% Sensitivity AFB Smear Conclusion: 1991 protocol missed 66% of culture-positive active TB cases *Maloney SM, et al. Arch Int Med 2006;166:234-40 Hmong Refugee Resettlement, 2004—2005 • 16,000 Laotian Hmong in Wat Tham Krabok, Thailand • Five states identified 48 TB Cases (7 MDR) in newly arrived Hmong refugees •TB culture added to screening TB in US-bound Hmong Refugees TB Cases # of Refugees Location Cases Identified N Rate/100,000 9482 Wat Tham Krabok 24 126 US 48 506 *Screened with 1991 TB TI TB in US-bound Hmong Refugees TB Cases # of Refugees Location Cases Identified N Rate/100,000 9482 Wat Tham Krabok 24 126 US 48 506 •TB culture added to screening algorithm 5801 Wat Tham Krabok 24 420 US 5 86 Recommendations • Overseas: Expand screening, treatment, and overall TB control • Focus on high-prevalence countries • Improve TB screening • To include culture • To screen persons <15 years esp. highprevalence countries • Domestic: Support timely and complete post-arrival follow-up of immigrants and refugees with overseas TB classifications 2007 TB TI • CDC process to revise Technical Instructions began in 2005 • Scientific literature reviewed • Input from U.S. Tuberculosis Community : • Advisory Council for the Elimination of Tuberculosis (ACET) • National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) • National Coalition for the Elimination of Tuberculosis (NCET) 2007—TB TI • Chest x-ray for persons ≥15 years of age and for persons 2-14 years with a TST>10 mm* or positive IGRA • If chest x-ray abnormal, serial AFB smears and cultures Drug susceptibility testing (DST) for all TB isolates Treatment to completion of therapy according to ATS/CDC/IDSA guidelines, delivered as DOT + + *countries with WHO-estimated incidence rate ≥20 per 100,000 Saint Luke’s Extension Clinic, Philippines FY 2007 (52,530 applicants, 1991 TB TI) vs. FY 2008 (41,793 applicants, 2007 TB TI) 505 Number of Applicants with Pulmonary TB 291 102 95 Smear + / Culture + 93 Smear + / Culture – 75 306 Smear – / Culture + 4 Smear – / Culture – 2007 Technical Instruction Smear – / No Culture Done 1991 Technical Instruction 121 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 TB case detection rate 1991 vs 2007 TB TI: 554 vs. 1,208 (per 100,000) 450 500 550 Implementation • TB culture facilities built -liquid culture w/ Bactec MGIT 960 • Training of panel physicians • Rollout in countries according to: • #s of applicants • TB rates • In-country resources As of January, 2010 • Populations from 27 countries on three continents are being screening according to the 2007 TB TI • 53% immigrants • >50% refugees Implementation of the 2007 TB TI -Current Status Current status 27 countries 53% of immigrants >50% of refugees Implementation of the 2007 TB TI -2010 Implementation South Korea Ghana Panel physician training India: January 13-15 Ghana: March 16-18 Dominican Republic: May 3-5 Summer/Fall Spring Nepal Spring ACET/NTCA Vietnam India Summer/Fall Guatemala Summer/Fall Thailand Nigeria Summer/Fall Spring Malaysia Indonesia Summer/Fall Spring 2007 Technical Instructions: Impact on Prevention of Disease • Improve detection of tuberculosis overseas • More refugees that need treatment will receive it • Improve stateside follow-up • Decrease importation of tuberculosis • Assist in global tuberculosis control efforts • Improve tuberculosis expertise and infrastructure overseas 2007 TB Technical Instructions Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/immigrantrefugeehealth/exams/ti/pane l/tuberculosis-panel-technical-instructions.html Acknowledgments International Organization for Migration (IOM) •Tom O’Rourke •Warren Jones •Raz Wali •Dr. Yen Dept. of State •Bureau of Population, Refugees, and Migration CDC •Drew Posey •Marty Cetron •John Painter •Greg Armstrong •Luis Ortega •Susan Maloney Thank you!! 1991 Tuberculosis Technical Instructions: for applicants ≥15 years of age or Valid for travel within 6 months Signs and symptoms Sputum smears x 3 All (-) (at least one +) Treat until smear negative Noninfectious Class B1 Infectious Class A Class A waiver 2007 TB TI If TB rate ≥20/100,000 2-14 years of age: TST ≥10 mm or Positive IGRA Valid for travel within 6 months HIV or Signs and symptoms Sputum smears x 3 All (-) + cultures (at least one +) DOT Treat until smear negative 3 Noninfectious Class B1 Infectious Class A cured Class A waiver 2007 Technical Instructions: Classifications Class 1991 Technical Instructions 2007 Technical Instructions No classification Normal evaluation Normal evaluation Class A Tuberculosis disease Tuberculosis disease Class B1Pulmonary Abnormal CXR, sputum smears negative Abnormal CXR, sputum smears and cultures negative Class B1 – Extrapulmonary Extrapulmonary tuberculosis Extrapulmonary tuberculosis Class B2 Inactive tuberculosis on CXR LTBI evaluation Class B3 Old or healed tuberculosis Contact evaluation Waivers for Medical Conditions Basic Points • IRMH/CDC is involved in the waiver process for immigrants based on the following medical conditions: HIV Infection Mental/Physical Disorders with associated harmful behavior Tuberculosis Class A Medical Conditions Inadmissible Treatment or waiver required for admission Examples • • • • TB (laboratory positive) HIV STIs (untreated) Mental Disorders with Harmful Behavior (including Alcohol Abuse) • Substance Abuse (no waiver for immigrants) Class B Medical Conditions Admissible Substantial departure from normal health Examples: • • • • TB (laboratory negative) STIs (treated), Mental Disorders without Harmful Behavior Substance Abuse (in remission) Stateside notifications for TB