* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neutropenia Febril
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Surround optical-fiber immunoassay wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
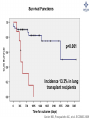
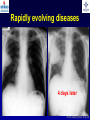
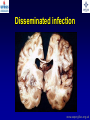
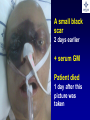
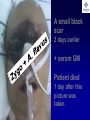
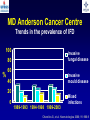
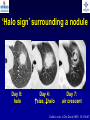
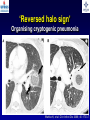
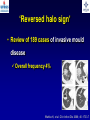
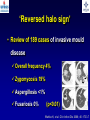
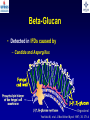
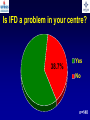
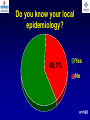
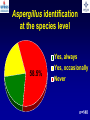
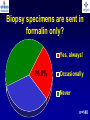
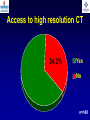
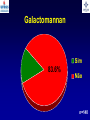
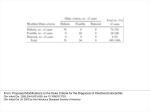
What are we looking at? Challenges in the diagnosis of Invasive Mould Diseases Alessandro C. Pasqualotto [email protected] Porto Alegre, Brazil Potential conflicts of interest • Research Grants Myconostica, Pfizer, Merck, Sigma-Tau, CAPES, CNPq, Fungal Research Trust • Travel Grants Pfizer, United Medical, Schering (now Merck), Bagó, Merck • Speaker honoraria Pfizer, United Medical, Merck, Schering (now Merck), Biometrix First assumption: IFD are highly lethal diseases p<0.001 Incidence 13.3% in lung transplant recipients Xavier MO, Pasqualotto AC, et al. ECCMID 2009 Rapidly evolving diseases 4 days later www.aspergillus.org.uk Disseminated infection www.aspergillus.org.uk Second assumption: We need to intervene asap Early versus late intervention Mortality rate (%) 100 80 60 40 20 0 Within 10 days Von Eiff, et al. Respiration 1995; 62: 241-7 Early versus late intervention Mortality rate (%) 100 80 60 40 20 0 Within 10 days > 11 days Von Eiff, et al. Respiration 1995; 62: 241-7 But how can we achieve such an early diagnosis? A small black scar 2 days earlier + serum GM Patient died 1 day after this picture was taken A small black scar 2 days earlier + serum GM Patient died 1 day after this picture was taken MD Anderson Cancer Centre Necropsy study over a 15-years period • IFD detected in 31% over 1,017 necropsies • Antemortem diagnosis in only 25% Chamilos G, et al. Haematologica 2006; 91: 986-9 MD Anderson Cancer Centre Necropsy rate has reduced over time 100 80 % 60 40 20 0 1989-1993 1994-1998 1999-2003 Chamilos G, et al. Haematologica 2006; 91: 986-9 By the way, what is the necropsy rate in your institution? 1. >40% 2. 10-39% 3. 1-10% 4. <1% 5. Are you kidding? MD Anderson Cancer Centre Trends in the prevalence of IFD 100 Invasive fungal disease 80 % 60 Invasive mould disease 40 20 0 1989-1993 1994-1998 1999-2003 Mixed infections Chamilos G, et al. Haematologica 2006; 91: 986-9 No need to worry! CT scan and galactomannan are there to help us out! ‘Halo sign’ surrounding a nodule Day 0: halo Day 4: size, halo Day 7: air crescent Caillot, et al. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 139-47 The sign is not specific for IA • Vasculitis • Metastasis • Pseudomonas infections • Zygomycosis and other angio-invasive infections Greene RE, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: 373-9 Absence of typical findings at chest CT scan • COPD • Steroids • Other non-neutropenic patients / ICU • Lung transplant recipients • ? Monoclonal antibodies ‘Reversed halo sign’ Organising cryptogenic pneumonia Wahba H, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1733-7 ‘Reversed halo sign’ • Review of 189 cases of invasive mould disease Overall frequency 4% Wahba H, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1733-7 ‘Reversed halo sign’ • Review of 189 cases of invasive mould disease Overall frequency 4% Zygomycosis 19% Aspergillosis <1% Fusariosis 0% (p<0.01) Wahba H, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1733-7 Other predictors of zygomycosis • >10 nodules • Pleural effusion • Concomitant sinusitis • Treatment with voriconazole Chamilos G, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41: 60-6 Meta-analysis of GM testing Low PPV High NPV Pfeiffer CD, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2006; 42: 1417-27 Reproducibility Caution with low +ve indexes! Upton A, et al. J Clin Microbiol 2005; 43: 4796-800 GM release by non-Aspergillus fungi • Penicillium marneffei • Paecilomyces variotii • Geotricum capitatum • Botrytis tulipae • Acremonium species • Cladosporium species • Alternaria alternata • Exophiala dermatitidis • Rhodotorula rubra • Trichophyton species Aquino VR, Goldani LZ, Pasqualotto AC. Mycopathologia 2007; 163: 191-202 Cross-reaction with GM testing 100 90 80 70 60 % 50 40 30 20 10 0 Paracocci Histo Crypto neoformans C gattii Xavier MO, Pasqualotto AC, Severo LC. Clin Vaccin Immunol 2009; 16: 132-3 Clinical case • 19 year-old man, refractory leukaemia • Febrile neutropenia • Amox-clav for E. Coli bacteremia Maertens J, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 289-90 Clinical case • 19 year-old man, refractory leukaemia • Febrile neutropenia • Amox-clav for E. Coli bacteremia • Daily GM determination – D1 after antibiotic: GM index of >1.5 – 5 +ve tests afterwards Maertens J, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 289-90 Clinical case • 19 year-old man, refractory leukaemia • Febrile neutropenia • Amox-clav for E. Coli bacteremia • Daily GM determination – D1 after antibiotic: GM index of >1.5 – 5 +ve tests afterwards • Fluoroquinolone: gradual reduction in GM index Maertens J, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 289-90 Clinical case • 1 wk later – Pipe-tazo for appendicitis – GM >2.5; bilateral nodular infiltrate Maertens J, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 289-90 Clinical case • 1 wk later – Pipe-tazo for appendicitis – GM >2.5; bilateral nodular infiltrate • Probable IA (EORTC / MSG) – Antifungal therapy + meropenem – Gradual ↓ in GM index Maertens J, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 289-90 Clinical case • 1 wk later – Pipe-tazo for appendicitis – GM >2.5; bilateral nodular infiltrate • Probable IA (EORTC / MSG) – Antifungal therapy + meropenem – Gradual ↓ in GM index • Necropsy: leukaemia infiltrate – Absence of IA Maertens J, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2004; 39: 289-90 Meta-analysis of GM testing Proven or probable IA Haematological malignancies Solid organ transplantation Sensitivity Specificity 0.58 (52-64) 0.95 (94-96) 0.41 (21-64) 0.85 (80-89) Pfeiffer CD, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2006; 42: 1417-27 Specificity 94% BAL PCR testing Sensitivity 79% Marked heterogeneity (particularly for sensitivity) Tuon FF. Rev Iberoam Micol 2007; 24: 89-94 PCR Critical points • Variable sensitivity / specificity • Lack of standardised targets / reagents • Extraction method • Platform (conventional PCR vs Real time) • Poor understanding of DNA kinetics • Not yet part of the EORTC/MSG criteria De Pauw B, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2008; 46: 1813-21 Beta-Glucan • Detected in IFDs caused by – Candida and Aspergillus Ergosterol Yoshida M, et al. J Med Veter Mycol 1997; 35: 371-4 Beta-Glucan • Detected in IFDs caused by – Candida and Aspergillus – Trichosporon – Fusarium – Acremonium – Saccharomyces – Pneumocystis Yoshida M, et al. J Med Veter Mycol 1997; 35: 371-4 There he is again, speaking about a test that nobody uses in Brazil … The reality in Brazil • A survey performed in collaboration with ANVISA 140 hospitals >42,000 beds 65% teaching hospitals 90% belonging to the Sentinel Network B eu M ro T su rg er y N A eo na IDS t H ae al c ar m od e ya lis is B ur n N T % SO nc H ea olo gy rt su rg er y O Complexity in hospital care 100 80 60 40 20 0 Is IFD a problem in your centre? 38.7% Yes No n=140 Do you know your local epidemiology? 40.1% Yes No n=140 Specialised media for fungi Yes 19.7% No n=140 Aspergillus identification at the species level 58.5% Yes, always Yes, occasionally Never n=140 Fungal staining - biopsies Yes, always 51.1% Yes, occasionally No n=140 Biopsy specimens are sent in formalin only? Yes, always! 26.0% Occasionally Never n=140 Access to high resolution CT 34.3% Yes No n=140 Galactomannan Sim 83.6% Não n=140 The appropriateness or inappropriateness of feelings is relative to the ground and to the circumstances of those feelings Aristotle The Doctrine of the Mean, 384-322 BC Fight fire with fire Metallica Ride the Lightning, 1984 AD Invasive diagnostic interventions • CT-guided percutaneous lung biopsy: yield of 70-100% Nosari A, et al. Haematologica 2003; 88: 1405-9 Crawford SW, et al. Transplantation 1989; 48: 266-71 Hoffer FA, et al. Pediatr Radiol 2001; 31: 144-52 Lass-Florl C, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45: e1001-4 Invasive diagnostic interventions • CT-guided percutaneous lung biopsy: yield of 70-100% Platelets >60,000/ml are required Pneumothorax 18% Haemoptysis 3% Nosari A, et al. Haematologica 2003; 88: 1405-9 Crawford SW, et al. Transplantation 1989; 48: 266-71 Hoffer FA, et al. Pediatr Radiol 2001; 31: 144-52 Lass-Florl C, et al. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45: e1001-4 Invasive diagnostic interventions • Transbronchial biopsies: False-negative results are frequently seen Lass-Florl C, Freund MC. In: Aspergillosis: from diagnosis to prevention. Pasqulaotto AC, ed. Springer, 2009 Invasive diagnostic interventions • Open lung biopsies: Provide larger samples of tissue with improved accuracy and specificity Lass-Florl C, Freund MC. In: Aspergillosis: from diagnosis to prevention. Pasqulaotto AC, ed. Springer, 2009 Invasive diagnostic interventions • Open lung biopsies: Provide larger samples of tissue with improved accuracy and specificity Contradictory results Complication rate of 10-15% Lass-Florl C, Freund MC. In: Aspergillosis: from diagnosis to prevention. Pasqulaotto AC, ed. Springer, 2009 Invasive diagnostic interventions Peripheral lesions Bilateral / multifocal disease Focal lesions near the hilum / great vessels Needle biopsy / Surgical resection BAL Urgent thoracotomy and resection Lass-Florl C, Freund MC. In: Aspergillosis: from diagnosis to prevention. Pasqulaotto AC, ed. Springer, 2009 Conclusion • It is mostly but not all about IA Invasive mould diseases have to be differentiated from each other Conclusion • It is mostly but not all about IA Invasive mould diseases have to be differentiated from each other • Diagnosis is the most challenging step in infectious diseases Conclusion • It is mostly but not all about IA Invasive mould diseases have to be differentiated from each other • Diagnosis is the most challenging step in infectious diseases • We need a better understanding on the performance of the available tests Acknowledgments • Mycology team Luiz Carlos Severo Valerio R Aquino Cecilia B Severo Luciana Guazelli Melissa Xavier • Infection Control Dept Teresa Sukiennik

















































![Jones Handouts [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004198564_1-64893a1a1dcde6f69f39c96314d64c08-150x150.png)




