* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Sodium hypochlorite wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
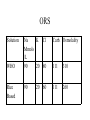
Diarrhea Dr.K.S.Sunil MBBS, MD, PGDGM • Increase in frequency, size or loosening of bowel movements. • Differentiate from fecal incontinence or functional bowel disease- normal stool weight • With western diet- less than 200g/day Pathophysiology • Increased active anion secretion • Decreased absorption of water and electrolytes Types • Transmissible agents • Noninfectious - abnormal mucosa – Inflammatory Bowel disease – Celiac disease, microscopic colitis, eosinophilic and allergic gastroenteritis, radiation enteritis • Noninfectious - normal mucosa – Osmotic diarrhea – Mal-absorption – Rapid intestinal transit- IBS Infectious diarrhea • Mostly feco-oral route • Bacterial • Viral • Parasitic Bacterial • Watery – Enterotoxigenic• Vibrio cholera • Enterotoxigenic E.coli – Food borne toxins• Bacillus cereus • Clostridium perfringens – Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex Bacterial • Bloody – Invasive • Campylobacter jejuni – Destructive • Shigella • Enteropathogenic E.coli • Clostridium difficile Viral • Rotavirus – Children less than 2 years – Most common cause of diarrhea in children all over the world • Norwalk – Older children and adults • These viruses injure the small intestinal mucosa • Watery diarrhea • CMV – Immunocompromised Parasitic • Protozoa – Giardia lamblia – Entamoeba histolytica – Cryptosporidium • Helminths – – – – – Ascaris lumbricoides Ancylostoma Strongyloides stercoralis Trichinella spiralis Capillaria philippensis Opportunistic pathogens • Clostridium difficile – Nosocomial pathogens in healthcare and long term care facility – Poor handwashing – Clindamycin, cephalosporins, ampicillin – Exotoxin mediated In immunocomromised Hosts • Besides the common pathogens, – – – – – – Giardia Legionella Candida albicans Cryptosporidium species Mycobacterium avium-intralcellulare CMV Others • Tropical sprue – In those who live or travel to the tropics – Overgrowth of predominantly coliform bacteria in the small intestine • Whipple’s Disease – Infection by Tropheryma whippelii – HLA B27 History • Is it truly diarrhea? • Duration– acute <3 weeks – Chronic >4 weeks • Texture • Frequency • Blood? History • • • • • • • • Fever Vomiting Abdominal pain Fainting or dizzyness Travel Drug use Diet Weight loss History • • • • • • Alcohol Abdominal operations Chemotherapy Radiation Immune status Comorbidities Physical • Vital signs – Orthostatic signs – Hyperventilation- acidosis • Volume status – – – – – – Skin tenting Dry mucous membranes Resting tachycardia Hypotension Sunken eyeballs Scaphoid abdomen Physical • Abdominal and rectal exam. – – – – Distension Bowel sounds Tenderness Masses • Stool swab- culture Physical • Chronic diarrhea – Malnutrition • • • • • • • Weight loss Muscle wasting Tetany Oral and skin lesions Peripheral neuropathy Ataxia Edema Labs • Stool tests for inflammation – Pus cells- specific but low sensitivity( about 50%) – Lactoferrin • Released from leucocytes during an inflammatory reaction • Sensitivity is 90% but less specific Labs • Stool culture – Positive in only 40 to 60% • • • • Stool for ova and parasites Stool for Clostridium difficile toxin Stool Sudan test for fat Stool Electrolytes-differentiates secretory diarrhea from osmotic diarrhea • Stool pH-<7 indicates carbohydrate malabsorption Other investigations • Flexible sigmoidoscopy – Pseudomembranes – Inflammation – Melanosis coli • Blood Hormone levels – Serum gastrin, VIP, somatostatin, cortisol, neurokinins, calcitonin – Carcinoid- serotonin, urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid Management • Fluid therapy • Persons with moderate to severe diarrhea lose large amounts of Na, CL, K, HCO3 & H20 • Pre renal azotemia, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis – ORS – IV Fluids ORS-principle • Saline solution (water plus Na+) by mouth - no beneficial effect – Na+ absorption is impaired in the diarrhoeal state – if the Na+ is not absorbed water cannot be absorbed. – Excess Na+ in the lumen of the intestine causes increased secretion of water and the diarrhoea worsens. ORS • Glucose - absorbed through the intestinal wall unaffected by the diarrhoeal disease state - sodium is carried in conjunction through by a co-transport coupling mechanism. This occurs in a 1:1 ratio, one molecule of glucose co-transporting one sodium ion (Na+). • Starch – – metabolized in the intestine to glucose and therefore it has the same properties of enhancing sodium absorption – less osmotic effect in the lumen of the intestine. • Citrate, a base precursor, corrects acidosis and enhances the absorption of water and electrolytes ORS-History • First developed in the early 1950’s and was formulated to mirror ions lost in stool. • In the early 1960’s the mechanism by which ORT works, the coupled transport of sodium and glucose, was discovered.6 • In 1971, the efficacy of ORT demonstrated during an epidemic of cholera in a refugee camp in Bangladesh. – ORT reduced the death rate from more than 50% to only 5%.7 By the early 1970’s a consensus was reached about the effectiveness of ORT. ORS • Lancet- "potentially the most important medical advance this century" • World Health Organization estimates that 90% of diarrheal deaths worldwide could be prevented with appropriate treatment with ORS ORS • Start early • Rice based ones ( Glucose polymers) increase intestinal fluid absorption • In adults – use urine output for monitoring ORS • • • • Sodium Chloride 3.5 grams Sodium Bicarbonate 2.5 grams Potassium Chloride 1.5 grams Glucose 20 grams ORS Solution WHO Rice Based Na K Cl Mmols /L 90 20 80 Carb. Osmolality 111 310 90 111 260 20 60 ORS- caution • A number of studies have addressed the concern that ORT can lead to hypernatremia in neonates and infants. • These studies show that administration of breast milk or plain water after rehydration prevents this problem.1 IV Fluids • Must contain Potassium and a base – Ringer’s lactate Chronic Diarrheas • Zn and Magnesium replacement Antibiotics • Invasive bacterial Enteritis- esp.Shigellae – Quinilone orally twice daily for 3 days • Cholera • Traveler's diarrhea – Prophylactic- not recommended – A single dose of oral Quinilone at onset • Clostridium difficile – Metronidazole – Oral Vancomycin Antimotility agents • Should be avoided • Concern for promoting bacterial invasion or prolonging the infection Food • Do not withhold – Withholding food, even for one or two days, greatly exacerbates the malnutrition – Coupled with anorexia, caused partly by chronic potassium depletion, causes a vicious circle – It is this diarrhoea/malnutrition cycle rather than acute dehydration that causes almost half of the five million deaths a year in under five year old children that are associated with diarrhoeal disease. Good nutrition and hygiene can prevent most diarrhea. Thank You!