* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DEFINISI ZOONOSIS
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
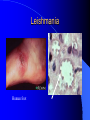
LECTURE NOTES ON ZOONOSIS DEFINITION AND TERMINOLOGY CLASSIFICATION EXAMPLE OF ZOONOSIS PARASITIC Departement of Parasitology DEFINITION OF ZOONOSIS Zoonosis is a group of diseases commonly found among vertebrate animal capable of infecting human, and vice-versa. Based on this definition, 2 group of classification are known: zooanthroponosis and anthropozoonosis. Zoonotic Parasitology Copyright 2010. PEER.tamu.edu In simple term A zoonotic disease is any disease which may be passed from animals to people or from people to animals (According to the CDC*) CDC: U.S. Communicable Disease Center Some Facts about Zoonotic Diseases Approximately 60% of all human pathogens are zoonotic 75% of emerging infectious diseases have an animal origin Growing need for veterinarians and physicians to work together Parasites and Animals Many methods of parasite transmission to people involve animals Classification of zoonosis by Cause CLASSIFICATION OF ZOONOSIS BASED ON ITS CAUSE Viral Zoonosis – Bacterial Zoonosis –fungal/mycotic Zoonosis • Parasitic Zoonosis Causes of Zoonotic Disease Bacteria Fungi Virus Parasites ZOONOSIS CAUSED VIRUS EBOLA JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS CRIMEAN-CONGO HEMORRHAGIC FEVER NIPAH FEVER MARBURG DISEASE KOREAN HEMORRHAGIC FEVER (SONG-GO) RABIES WEST NILE ENCEPHALITIS RIFT VALLEY FEVER BACTERIAL ZOONOSIS ANTHRAX LYME DISEASE Q FEVER BRUCELLOSIS LEPTOSPIROSIS BARTONELLOSIS PORCINE ERYSIPELAS LISTERIOSIS PSITTACOSIS SALMONELLOSIS STREPTOCOCCOSIS MELIOIDOSIS CLASSIFICATION OF PARASITIC ZOONOSIS ZOONOSIS BY PARASITIC PROTOZOA ZOONOSIS BY PARASITIC HELMINTHES ZOONOSIS BY ECTOPARASITES ZOONOSIS BY PARASITIC PROTOZOA BALANTIDIASIS CRYPTOSPORIDIASIS GIARDIASIS PNEUMOCYSTOSIS SARCOSPORIDIOSIS TOXOPLASMOSIS ZOONOSIS BY HELMINTHES ANGYOSTRONGYLIASIS ASCARIASIS SUUM DIPYLIDIASIS DIROFILARIASIS FASCIOLIASIS HYDATIDOSIS HYMENOLEPIASIS LARVA MIGRANS LINGUATULIASIS PHYSALOPTERIASIS SCHISTOSOMIASIS SPARGANOSIS STRONGYLOIDIASIS TAENIASIS SAGINATA TRICHINOSIS TRICHSTRONGYLIDIASIS ZOONOSIS BY ECTOPARASITES ACARIASIS MYIASIS SCABIES INFESTATION BY TICKS DAN MITES Vector-borne Parasites A vector is an agent which transfers a parasite from one host to another Typical parasite vectors: fleas, ticks, mites, mosquitoes, flies, and other insects People become infected when a vector picks up the parasite from an infected animal and infects a human CONTACT BETWEEN EPIZOOTIC CYCLE AMONG PRIMATES AND MAN Epizootic Cycle Zoonotic Cycles Parasites carried by Vectors Many parasites that are carried by vectors are often found in the blood of humans and animals Trypanosoma Cruzi Causes Chagas disease. Damage to heart, digestive tract, and brain (in children). Spread by the “Kissing Bug,” native to South America and the southern US The bug bites the human then defecates next to the wound. Rubbing bite wound spreads parasite into the wound. Parasite can cycle from animals like armadillos, raccoons, opossums, and foxes to bugs to humans. Chagas Disease & The “Kissing Don’t Kiss ME!!! Bug” Trypanosoma cruzi in the blood Kissing Bug found in Texas Babesia Intracellular protozoa found in red blood cells If you play around trees, check your Spread by infected Ticks head and body for me!! Leishmania Unlike Babesia and Chagas Disease, Leishmania live in tissue and not the blood Spread through the bite of an infected Sandfly* *common on Caribbean beaches Leishmania Human foot Waterborne Parasites Spread when humans come into contact with water that has been contaminated by an infected animal Common waterborne parasites include – Giardia – Cryptosporidium Giardia & Cryptosporidium Giardia & Cryptosporidium Get from swallowing water contaminated by another infected human or animal Giardia is the 2nd most common parasitic disease in people Cryptosporidium is the most common cause of diarrhea from swimming Both can cause severe diarrhea Gross!!! Don’t drink the water your swimming in!!! How Do People Get Parasites Methods of Parasite I need to WASH MY Transmission HANDS!!! Insect bites Animal feces Handling raw meat and fish Handling cat litter boxes Contaminated fruits and vegetables Infected food handlers Contaminated water Contact with an infected person Broad Categories of Transmission Vectorborne (insects) Waterborne Fecal Oral Transmission Contaminated Meat Fecal-Oral Transmission Most common way people become infected with zoonotic parasites Parasites are spread to humans when they ingest the eggs from the feces of an infected I don’t animal feel so Parasites spread by fecal oral transmissiongood generally live in the intestinal tract Spread by Fecal Oral Transmission Hookworms Roundworms Hydatid Disease Toxoplasmosis Hookworms & Roundworms They are like monsters!!!! Hookworms & Roundworms Carried by dogs and cats Kids often get infected from playing in sand boxes which animals have defecated Or by putting toys in their mouth which have been on the ground Hookworms Can penetrate the skin and gain entry into the human body Bare feet are a common route of entry Wearing shoes is one of the best ways to prevent parasites from entering your feet!!! Hydatid Disease After Humans consume the eggs passed by dogs the worms can form huge cysts in the body Toxoplasmosis How many have of you have heard that pregnant women shouldn’t clean cat litter boxes? That is because of the potential for them to contract Toxoplasmosis which can cause them to lose their unborn child. Toxoplasmosis Even though it is commonly associated with pregnancy and litter boxes, toxoplasmosis is more commonly transmitted through undercooked meat According to the CDC toxoplasmosis is the 3rd leading cause of foodborne related deaths Order your in the US food to be cooked all the way!! Contaminated Meat Meat can be contaminated with harmful bacteria and can also contain parasitic cysts which may infect people. Common Parasites Found in Meat – Toxoplasmosis – Trichinella – Taenia – Gnathostomosis Trichinosis & Taenia Both caused by eating cysts in undercooked pork or beef Incidence rate has decreased with better animal management and slaughter protocol Fully cook your meat! Cysticercosis If a person consumes Taenia eggs they can develop cysts in their brain! Gnathostomosis Similar to Taenia and Trichonosis, but gnathostomosis is found in raw fish What area do you think this disease is most common? Asia Cutaneus Larva Migrans (Creeping Eruption) Morphology of Gnathostoma spinigerum So How Can You Protect Yourself? Preventing Zoonotic Parasites Brainstorm some ways we can prevent them… – – – – – – Always wash your hands Keep sand boxes covered Wear shoes Pick up animal feces when possible Don’t drink untreated water Cook meat thoroughly Summary Zoonotic parasites have many routes of transmission to people – Vectors – Water – Fecal Contamination – Infected Meat References http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/DPDx/default.htm http://cal.vet.upenn.edu/projects/dxendopar/ index.html www.nih.gov www.nsf.gov www.floridahealthfinder.gov Thank you Terimakasih