* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nuclear Medicine - El Camino College
Center for Radiological Research wikipedia , lookup
Medical imaging wikipedia , lookup
Radiation burn wikipedia , lookup
Image-guided radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Radiosurgery wikipedia , lookup
Industrial radiography wikipedia , lookup
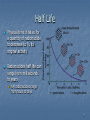
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear Medicine Spring 2009 FINAL NM Team Nuclear medicine MD Physicist Pharmacist Technologist Patient 2 Principles of NM Uses radiopharmaceuticals for diagnosis, therapy and medical research Small amounts of radioactive material used Sometimes no more than that received in CT or fluoroscopy Studies physiology Rather than structural appearance 3 Tracers Radioactive material that can be: Different tracers for different body parts Injected, ingested or inhaled organ-, tissue-, or even cell-specific They produce gamma-ray emissions from within organ being studied Gamma or scintillation camera transforms emissions into images Provides information about function 4 Modality Comparisons PET and SPECT for physiology X-ray measures structure, size and position of human anatomy CT creates cross sectional images of anatomy What do all of these modalities have in common? 5 Atom Components & Isotopes 6 Physical Principles of NM Radioactivity Radiation of energy from the nucleus of atom Can be in the form of alpha, beta particles or gamma rays from the nucleus 7 Basic Nuclear Physics Nuclide Radionuclide Atom with a particular arrangement of protons and neutrons in the nucleus Unstable nucleus that transmutes by way of nuclear decay (return to ground state) Decay Is the atoms attempt to regain stability By emission of alpha, beta and gamma radiation Different for each type of radionuclide 8 Half Life Physical time it takes for a quantity of radionuclide to decrease to ½ its original activity Radionuclides half life can range from milliseconds to years NM radionucldies range from hours to days 9 Nuclear Pharmacy Radiopharmaceutical Radionuclide Pharmaceutical Technetium -99 Short ½ life of 6.04 hours Low energy gamma photon 10 Radiation Safety Radiopharmaceuticals must be sterile Prep area must have isolated ventilation Protective measures when administering or handling Spills must be cleaned immediately Dosimetry devices Hands and badges 11 Modern Day Gamma Camera Scintillate means: to emit light Ionizing radiation causes certain materials to glow Scintillation detector Detects radiation by observing the emission of light photons emitted by the materials PMT detect and convert light photons emitted from the crystal into and electronic signal that amplifies the original photon signal It is then sent to be viewed 12 13 Detectors 14 Collimators Keep scattered rays from entering the scintillation crystal Resolution and sensitivity Absorbs scattered gamma rays Physical characteristics Made of material with high atomic number Lead 15 16 Crystals Sodium iodide Thallium Thick layer of crystals High energies Decreased resolution Thin layer of crystals Lower energies Increased resolution 17 Attached to the back of the crystals Detect and convert light photons into and electronic signal that amplifies the original photon signal Photomultiplier Tubes About 80-100 in a gamma camera Light pipe Like a focusing device 18 Put it all Together 19 Computer Acquires and processes data received from camera Post-processing In a time frame Adjust contrast and density Records Dosage Quality control 20 Types of Camera Systems Single detector Dual head Triple head 21 Single Head Detector 22 Dual Head Detector 23 Triple Head Detector 24 Imaging Methods Static Whole- Body Dynamic SPECT Co-registration PET 25 Static Single image of a particular structure Demonstrates radiopharmaceutical distribution Ex: lung scans, spot bone scans images, thyroid images Obtained in various orientations, anterior, posterior, and oblique Low activity levels Generally 30 seconds to five minutes 26 27 Whole Body Entire body or a large section of body Primarily used for Bone scans Tumor scans Abscess imaging Clinical and research applications 28 29 30 Dynamic Timed record of distribution of radiopharmaceutical Commonly used for Cardiac studies Hepatobiliary studies Gastric emptying studies 31 Dynamic Renogram 32 Dynamic Venogram 33 SPECT Images similar to CT & MRI 360 degree rotatator heads allows for: thin slices through a particular organ Coronal, planar and 3D imaging Ex: cardiac perfusion, brain, liver and bone studies 34 35 SPECT and CT combination Merges SPECT functional testing with CT anatomic landmark images Statistics show 25-30% change of treatment options from what would have been done with SPECT alone 36 37 38 PET Resolution is 2-10 better than SPECT Radiopharmaceuticals Minimal alteration in homeostasis Very small amounts used Co-registration being done with CT & MRI Almost all new machines are fused with a CT scanner 39 40 41