* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medical Imaging and Anatomy - Computer Graphics at Stanford
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
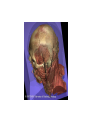
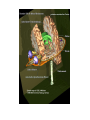
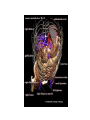
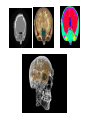
Medical Imaging and Anatomy Mike Houston, Anthony Sherbondy, Ruwen Hess Where do the pictures come from? • The imagination • Dissection • X-ray, CT, MRI, Cryosection, PET/SPECT, etc. X-Ray Transmission Imaging • Shoot x-rays through the patient onto detector film. • Different tissues absord and deflect x-rays to different degrees. The film is exposed less when xrays encounter higher density material like bone. • Low resolution. Hard to distinguish between blood vessals and tissue without an injection of iodine or barium Computed Tomography (CT) • Sort of a 3D x-ray. An x-ray emitter is rotated around the patient and a receiver measures the intensity of the transmitted rays from different angles • Uses an electronic receiver instead of film. • Became generally available in mid 1970's and have gotten MUCH better in resolution and accuracy. Still have problems with metal in the body... Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) • • • • • Subject body to strong magnetic field (0.08-4T) causing the nuclei of magnetic isotopes to align their orientation. This causes the nuclei to absorb energy and enter a higher energy state. When magnetic field is turned off, nuclei return to equilibrium state emitting energy. Each element has a unique energy signature that can then be measured. Getting more common and very cheap. Can now get a full body MRI scan for ~$500 Cryosection • Freeze specimen or embed in a plastic polymer • Cut specimen into as many slices as possible along an axis • Photograph each slice • Example: Visible Male and Visible Female Positron Emission Tomography (PET) • Inject a metabolically active tracer into subject with an affinity to a certain molecule. • 18F will accumulate in the brain where glucose is used as primary energy source. • The radioactive nuclei decay by positron emmission which collides with a free electron resulting in a gamma ray • Detectors pick up the events and the a reconstruction is computed Medical Imaging for Education Exploring the human body • The "Ancients" • Gray's Anatomy • Visible Human Project The Visible Human Project • • • • • • Create a digital image dataset of complete human male and female cadavers in MRI, CT and anatomical modes. MR –256x256 resolution at 4mm intervals, 12-bit/pixel CT –512x512 resolution at 1mm intervals, 12-bits/pixel Cryosection – Low res: 2048x1216 at 1mm intervals, 24bits/pixel – High res: 4096x2700 at 1mm intervals, 24bits/pixel 1871 slices per mode Note: specs are for visible male So what? • We now have a digitized model of an "average" male and female using the current major medical imaging techniques • We can now get views of the body that were previously difficult if not impossible • But, we know have LOTS of data and have to figure out how to visualize it effectively Lots of examples