* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory and Circulatory System1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
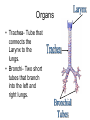
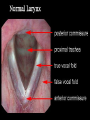
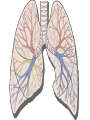
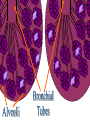
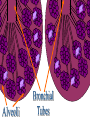
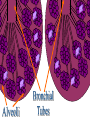
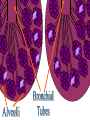
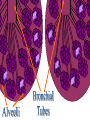
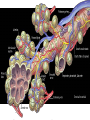
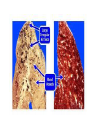
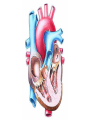
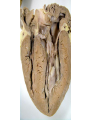
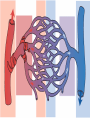
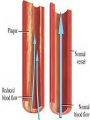
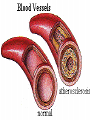
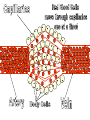
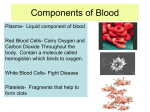
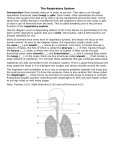
The Respiratory and Circulatory System What is Respiration? • The process in which the body brings in Oxygen and gets rid of Carbon Dioxide. Respiratory System • Includes: – The Pharynx – The Larynx – The Trachea – The Bronchi – The Lungs – The Diaphragm Organs • Pharynx- A tube-like passage used by food, liquid and air. • Larynx- Airway to which the vocal cords are attached. Organs • Trachea- Tube that connects the Larynx to the lungs. • Bronchi- Two short tubes that branch into the left and right lungs. Lungs • Organs that take in Oxygen and release Carbon Dioxide. • Contain Alveoli- Tiny grapelike clusters where Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide changes place. Organs • Diaphragm- Muscles beneath the lungs that contracts and relaxes every time you breath. – This helps to pump the lungs allowing Oxygen to enter and Carbon Dioxide to leave. Respiratory Disease • Lung Cancer- Smoking is the leading cause of Lung Cancer. • Bronchitis- Inflammation of the Bronchial Tubes. – Causes shortness of breath, wheezing and coughing to bring up mucus. • Emphysema- Damage to the Alveoli that results in breathing problems and coughing. Respiratory Disease • Asthma- Inflammation of the Respiratory System resulting in wheezing and shortness of breath. –Triggers- Allergens such as pollen, dust and cigarette smoke. What is Circulation? • The process by which nutrients and oxygen are taken to cells, and carbon dioxide and waste are taken from cells. Cardiovascular System • Includes: –The Heart –Blood Vessels –Blood The Heart • The Heart pumps blood throughout the body. • Atriums- The upper chambers of the heart. • Ventricles- The lower chambers of the heart. Types of Circulation • Coronary Circulation- Supplies the heart with blood. • Pulmonary Circulation- Supplies the lungs with blood. • Systemic Circulation- Supplies the body with blood. Vessels • Arteries- Carries blood away from the heart. • Veins- Carries blood towards the heart. • Capillaries- Where arteries and veins connect. –Capillaries are very thin so O2 and CO2 can diffuse into and out of the cells. What Makes up Blood? • Plasma- The liquid part of Blood- Mostly water. • Platelets- Cell fragments that helps blood clot. • Red Blood Cells- Transport O2 and CO2 throughout the body. – Contains Hemoglobin- Molecule that carries O2 and CO2. • White Blood Cells- Used to fight off infections. Function of Blood • Transports O2 and CO2 throughout the body. • Carries waste to the Kidneys. • Carries food nutrients to our cells. • Fight infections and heal wounds. Blood Types • • • • A B AB O Cardiovascular Diseases • Hemophilia- Disease that prevents people’s blood from clotting. • Anemia- Disease where not enough oxygen gets to the body cells. • Leukemia- Disease where the body makes too many white blood cells. • Arteriosclerosis- When fat deposits build up inside arteries. • Hypertension- When blood pressure is too high, making the heart work over-time. Preventing Cardiovascular Disease • Good diet, reduced stress, exercising and not smoking can reduce the chance of Cardiovascular Disease. Working Together • The Circulatory and Respiratory System work together to give Oxygen to all our body cells, and to get rid of Carbon Dioxide. Lymphatic System • Carries Lymph throughout the Lymph System and helps to fight off infections. • Lymph- Fluid from our tissue that has drained into the Lymphatic System. • Lymphocytes- Are White Blood Cells that help to fight off infections. • Lymph Nodes- Filter bacteria making it easier to fight them with White Blood Cells.