* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physiology, Health & Exercise
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
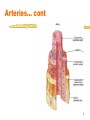
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
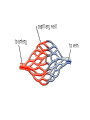
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
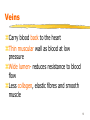
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
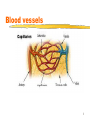
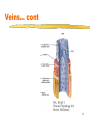
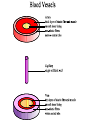
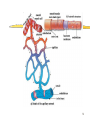
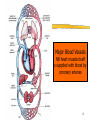
Lesson 2 Blood vessels Cardiac cycle Heart Sounds 1 Blood vessels There are three types of blood vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins 2 Blood vessels 3 Arteries Carry blood away from the heart Thick muscular wall to withstand high pressure of blood Narrow lumen Most collagen (tough fibrous protein)tough and durable Elastic fibres and smooth muscle- allows stretch & recoil 4 Arteries… cont No valves Branch into smaller and smaller vesselsarterioles Contraction of smooth muscle of arterioles allows blood to be diverted to different parts of the body e.g. fight or flight more blood to skeletal muscles and less to digestive system 5 Arteries… cont 6 Capillaries Tiny vessels- 1 cell thick wall 10mm in diameter Exchange of nutrients and waste with tissues occurs here Extensive branching network (capillary bed) throughout body tissues Only certain capillary beds open at one time to allow shunting of blood from one area to another 7 Capillaries… cont Most numerous type of blood vessel in the body Permeable walls Carry blood at low pressure and low flow rate Reduces fluid loss through permeable capillary walls Allows sufficient time for exchange of 8 materials Veins Carry blood back to the heart Thin muscular wall as blood at low pressure Wide lumen- reduces resistance to blood flow Less collagen, elastic fibres and smooth muscle 10 Veins… cont Have valves Blood at low pressure- return blood against gravity- so lie close to muscleswhen muscle contract they squeeze the veins to temporarily increase the blood pressure 11 Veins… cont 12 14 Describe three things that this graph shows. Major Blood Vessels NB heart muscle itself is supplied with blood by coronary arteries 16 Cardiac Cycle A pattern of contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) by heart in 1 heart beat Lasts about 0.8 seconds (based on heart rate of 75bpm) Chambers alternately contract and relax Blood always flows towards low pressure 17 Cardiac Cycle…cont 3 phases to the cycle: 1. Atrial systole 2. Ventricular systole 3. Diastole Decrease in volume Increase in pressure Blood forced out 18 Atrial systole Blood flows into LA and RA under low pressure LA & RA contract simultaneously AV (bicuspid & tricuspid) valves open Blood forced into LV & RV At this point LV & RV in diastole & SL valves closed 19 Ventricular systole 0.1 secs later AV (bicuspid & tricuspid) valves close Blood forced into LV & RV which contract & push blood through open SL valves to arteries High pressure in ventricles 20 Diastole Atria & ventricles relax Elastic recoil of relaxing heart walls lowers pressure in atria & ventricles Blood under high pressure in arteries drawn back into heart from veins 21 Heart Sounds Lub dub Lub- closing of AV valves Dub- closing of SL valves Human heart sounds Feline heart sounds 23