* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Physiology of Deep Water Running
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
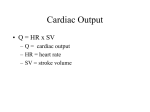
The Physiology of Deep Water Running Dr. Moran EXS 558 November 16, 2005 Lecture Outline Introduction What is the purpose? USES Research Interest 9,470 hits in Google Scholar for deep-water running Cardiorespiratory Responses to Water Immersion Blood Compartments Cardiovascular Lung Function Physiological Response Maximal exercise Sub-maximal exercise Longitudinal Studies “The Physiology of Deep Water Running” Journal of Sport Sciences Reilly et al. (2003) Uses Why deep-water running? Injury prevention – Decreased compressive forces on spine (Dowzer et al., 1998) – Decreased lower back injuries within a running population – Reduced musculoskeletal loading as compared to over-ground running – Rudzki & Cunningham (1999): with the introduction of deep-water running a total reduction of injury of 46.6% in military recruits Uses Recovery Recommended for accelerating the recovery rate in between soccer games (Cable, 2000) This has not been scientifically proven Reilly et al. (2001) Examined the role that deep-water running had on preventing delayed-onset-muscle-soreness (DOMS) Deep-water running (DWR) failed to prevent DOMS but appeared to speed the process of recovery for leg strength and perceived soreness Leg strength was reduced 20% 48hr post-activity w/o DWR but 7% with DWR Uses (con’t) Health-Related Exercises Recommended for people with orthopedic injuries Cardiovascular Training – Overweight People – Takeshima et al. (2002) Women aged 60-75 had improvements in: 1.) Knee extension strength 2.) Chest Press 3.) VO2 Max 4.) Vertical Jump 5.) Shoulder Press Uses (con’t) Ancillary Training Endurance athletes attempting to increase training volume without the associated pounding on musculoskeletal system Summary of Uses Population Purpose Benefit Injured Rehabilitation Prevents detraining Accelerates Rehab Soccer Players Recovery from DOMS Accelerates Recovery Pain-free exercise Runners Ancillary training Avoid overtraining NM training Untrained Aerobic/Strength Training Avoids injuries associated with over-land exercise Promotes muscular strength Physically Disabled Allows movement Freedom from risk of falling Overweight Aerobic Training Reduced load-bearing on joints (prevent injury) Cardiorespiratory Response Water Immersion Blood Compartments Hydrostatic Vascular Gradient – Contributes to increased central blood volume because of adjusted intrathoracic pressure relative to surrounding water – Pressure imbalance Between thoracic cavity and alveolar spaces Creates a 700ml redistribution of blood volume to the central circulation with the heart accepting about 200ml of that (Arborelius et al. 1972) The effect of graded immersion on heart volume, central venous pressure, pulmonary blood distribution, and heart rate in man. Risch et al. (1977) Cardiovascular Response Cardiac Output ↑ 30-35% when an individual at rest is immersed in water Obviously creates an improved end-diastolic volume (EDV) Peripheral Vascular Volume (PVV) Hydrostatic pressure of tissues causes transcapillary fluid shift leading to a ↓ in PVV Thus, an ↑ with thoracic blood volume stretch of heart walls Christie et al. (1990) left-ventricular end-systolic (30% ↑ ) and end-daistolic pressure greater in water than on land Cardiovascular Response (con’t) Stroke volume higher for any exercise intensity while submerged as opposed to on ground Possible reasons: Displacement of peripheral blood volume to central core area Does this affect O2 delivery? Left ventricular EDV is close to maximum at rest eliminating the chance for it increase with more intense exercise Cardiac filling time is reduced Cause of increased stroke volume Enhanced pre-load (Frank-Starling mechanism) NOT b/c of enhanced ventricle emptying Alterations of Lung Function Reduce action of inspiratory muscles – Because of hydrostatic pressure compressing the diaphragm Reduced lung capacity and vital capacity (def: the volume change of the lung between a full inspiration and a maximal expiration) 3-9% (Hong et al., 1967) The level of immersion will affect the amount of reduced pulmonary action – Functional residual capacity declines only slightly in immersion up to the hip, but 400ml when immersed to the xiphoid and another 400ml when immersed to the neck (Farhi et al., 1977) Physiological Response to DWR VO2 max Consistently reduced when DWR is compared to running on a treadmill Questionable methods Short duration of DWR protocols Rely on participants to increase exercise based on RPE Failure to reach true maximum? Dowzer et al. (1999) – Peak Oxygen Uptake Shallow Water Running (SWR) 83.7% VO2 Max DWR 75.3% VO2 Max – Peak Heart Rates SWR 94.1% of max HR DWR 87.2% of max HR Muscle Recruitment Changes? Michaud et al. (1995a) a greater % of work in water performed by upper extremity Upper arm action may be needed to aid in buoyancy This could explain the reduced VO2 max found from DWR Reduced HR During DWR No clear consensus on what causes a reduced HR while DWR Possible Mechanisms – Baroreflex-mediated decline in HR during rest in water temp below thermoneutrality – Enhanced venuous return and cardiac pre-load Cardiac Output = HR x SV – Reduced sympathetic neural outflow from an altered baroreceptor activation Respiratory Exchange Ratio RER = (volume of CO2)/(volume of O2) DeMaere and Ruby (1997) DWR induced a higher RER ration indicating an increased reliance of carbohydrate oxidation and decreased lipid (fat) utilization Summary of DWR Reilly et al. (2003) Longitudinal Studies