* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lesson 20 arteries and veins
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
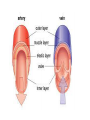
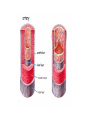
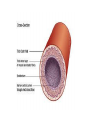
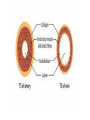
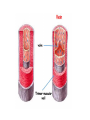
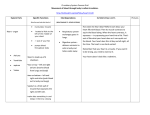
Arteries and Veins Learning Outcomes Arteries have an outer layer of connective tissue containing elastic fibres and a middle layer containing smooth muscle with more elastic fibres. The elastic walls of the arteries stretch and recoil to accommodate the surge of blood after each contraction of the heart. The smooth muscle can contract or relax causing vasoconstriction or vasodilation to control blood flow. Veins have an outer layer of connective tissue containing elastic fibres but a much thinner muscular wall than arteries. Function of valves. Structure and Function of Blood Vessels The central cavity of a blood vessel is called the lumen The lumen is lined with a thin layer of cells called the endothelium The composition of the vessel wall surrounding the endothelium is different in arteries, veins and capillaries Artery Arteries carry blood away from the heart Arteries have a thick middle layer of smooth muscle They have an inner and outer layer of elastic fibres Elastic fibres enable the artery wall to pulsate, stretch and recoil, thereby accommodating the surge of blood after each contraction of the heart Smooth Muscle Smooth muscle can contract or become relaxed This contraction or relaxation brings about vasodilation or vasoconstriction to control blood flow During strenuous exercise the arterioles leading to the muscles undergo vasodilation – the circular muscle in the arteriole wall is relaxed and the lumen is wide This allows an increased blood flow to the skeletal muscles the gut . . . . At the same time, the arterioles leading to the small intestine undergo vasoconstriction The circular muscles are contracted and the lumen is narrow As a result, this reduces the blood flow to the gut Veins Veins carry blood back to the heart The muscular layer and layers of elastic fibres in the vein wall are thinner than those in an artery because blood flows along a vein at low pressure The lumen of a vein is wider than that of an artery Valves are present in veins, to prevent the backflow of blood Following two slides compare an artery and vein Try these questions . . . 1. 2. 3. 4. Give two structural differences between an artery and a vein Give one functional difference Name the central cavity of a blood vessel What term is used when the circular muscle in a blood capillary is contracted and the central cavity is narrow? 5. Describe a blood capillary during vasodilation Answers . . . . 1. Wall of artery is thicker than that of vein and veins have valves 2. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, veins carry blood back to the heart 3. Lumen 4. Vasoconstriction 5. Circular muscle relaxed, lumen is wide 1. Give two structural differences between an artery and a vein Wall of artery is thicker than that of vein and veins have valves 2. Give one functional difference Arteries carry blood away from the heart, veins carry blood back to the heart 3. Name the central cavity of a blood vessel lumen 4. What term is used when the circular muscle in a blood capillary is contracted and the central cavity is narrow? vasoconstriction 5. Describe a blood capillary during vasodilation Circular muscle relaxed, lumen is wide