* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 1-7: Basic Constructions
Rule of marteloio wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Cardinal direction wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
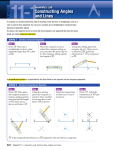
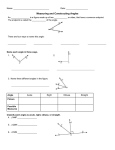
Section 1-7: Basic Constructions Objectives To use a compass and a straightedge to construct congruent segments and congruent angles. To use a compass and a straightedge to bisect segments and angles. Vocabulary Construction Straightedge Compass Perpendicular Lines Perpendicular Bisector Angle Bisector Construction In a construction you use a straightedge and a compass to draw a geometric figure. Straightedge A straightedge is a ruler with no markings on it. Compass A compass is a geometric tool used to draw circles and parts of circles called arcs. Construction #1: Constructing Congruent Segments Given: AB Construct: CD so that CD is congruent to AB Steps: Draw a ray with endpoint C. Open the compass to the length of AB. With the same compass setting, put the compass on C and draw an arc that intersects the ray. Label the intersection D. CD is congruent to AB Construction #2: Constructing Congruent Angles Given: RA Construct: RS so that RS is congruent to RA Steps: Draw a ray with endpoint S. With the compass on point A, draw an arc that intersects the sides of RA. Label the points of intersection B and C. With the same compass setting, put the compass point on S. Draw an arc and label its point of intersection with the ray as R. Open the compass to the length of BC. Keeping the same compass setting, put the compass on R. Draw an arc to locate point T. Draw ST. RS is congruent to RA Perpendicular Lines Perpendicular lines are two lines that intersect to form a right angle. Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector of a segment is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to a segment at its midpoint. It bisects the segment into two congruent segments. Construction #3: Constructing the Perpendicular Bisector Given: AB Construct: XY so that XY is perpendicular to AB at the midpoint M of AB. Steps: Put the compass point on point A and draw a long arc– be sure the opening is greater than half of AB. With the same compass setting, repeat step one, this time with the compass on point B. Label the two intersection points X and Y. Draw XY. Angle Bisector An angle bisector is a ray that divides an angle into two congruent coplanar angles. The ray “bisects” the angle. Construction #4: Constructing the Angle Bisector Given: RA Construct: AX, the bisector of RA. Steps: Put the compass point on vertex A. Draw an arc that intersects both sides of the angle. Label those points B and C. Put the compass point on C and draw an arc in the interior of the angle. Repeat step two, this time with the compass point on B. Label the intersection point of the two arcs X. Draw AX.














![PH_Geo_3-8_Constructing_parallel_lines[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001202465_1-91ca6e9d9e8948ba2229cefd106376ad-150x150.png)