* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
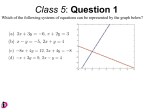
Algebra Chapter 7 Vocabulary System of linear equations- two or more linear equations in the same variables. Solution of a system of linear equations- an ordered pair (x, y) that satisfies each equation. Re-teach Solving a linear system using graph- and –check 1) Write the equation in a form so it is easy to graph. 2) Graph both equations. 3) Estimate the points (x,y) for intersection. 4) Check algebraically by substituting into each equation. Practice Graph the linear system, then decide if the ordered pair is a solution. 1. x + y = -2 (-3, 1) 2x – 3y = -9 2. –x + y = - 2 (4, -2) 2x + y = 10 3. x + 3y = 15 4x + y = 6 (3, -6) Re-teach Solving systems of equations by substitution 1) Solve one of the equations for one of its variables. 2) Substitute the revised Expression in for the other equation. 3) Solve the equation for the variable. 4) Substitute in the solution for one of the variables into the original equation. 5) Write the solution in an ordered pair. Re-teach Solving systems of equations by substitution -x + y = 1 2x + y = -2 1) Solve one of the equations for one of its variables. -x + y = 1 +x +x Y=x+1 2x + y = -2 Re-teach Solving systems of equations by substitution 2) Substitute the revised Expression in for the other equation. Y=x+1 2x + y = -2 2x + x + 1 = -2 Re-teach Solving systems of equations by substitution 3) Solve the equation for the variable. 2x + x + 1 = -2 3x + 1 = -2 3x = -3 X = -1 Re-teach Solving systems of equations by substitution 4) Substitute in the solution for one of the variables into the original equation. -x + y = 1 2x + y = -2 X = -1 2(-1) + y = -2 -2 + y = -2 Y=0 Re-teach Solving systems of equations by substitution 5) Write the solution in an ordered pair. X = -1 Y=0 (-1, 0) Practice 1) 2x + 2y = 3 x – 4y = -1 2) –x + y = 5 ½x + y = 8 3) 3x + y = 3 7x + 2y = 1 Vocabulary Linear Combination- an equation obtained by adding one of ht equations to the other equation. A linear combination is often known as solving systems of equations through elimination. Re-teach Solving linear systems by linear combinations 1) Arrange the equations with like terms in columns. 2) Multiply one or both of the equations to obtain an opposite variable. 3) Add/Subtract the terms from each column to get the value of the variable. 4) Substitute the value into the original equations. 5) Write the solution in an ordered pair. Re-teach Solving linear systems by linear combinations 1) Arrange the equations with like terms in columns. 3x + 2y = 44 5y + x = 11 3x + 2y = 44 X + 5y = 11 Re-teach Solving linear systems by linear combinations 2) Multiply one or both of the equations to obtain an opposite variable. 3x + 2y = 44 -3(X + 5y = 11) 3x + 2y = 44 -3x -15y = -33 Re-teach Solving linear systems by linear combinations 3) Add/Subtract then divide the terms from each column to get the value of one variable. 3x + 2y = 44 -3x -15y = -33 -11y = 11 Y = -1 Re-teach Solving linear systems by linear combinations 4) Substitute the value into the original equation. Y = -1 3x + 2y = 44 5y + x = 11 5(-1) + x = 11 -5 + x = 11 X = 16 Re-teach Solving linear systems by linear combinations 5) Write the solution as an ordered Pair. Y = -1 X = 16 (16, -1) Re-teach One solution (system will have perpendicular slopes) No solutions (system will have parallel slopes) Infinite solutions (system will be the same or equal 0 = 0) Practice Determine the type of results from each system. 1) 3x + y = -1 -9x – 3y = 3 2) X – 2y = 5 -2x + 4y = 2 3) 2x + y = 4 4x – 2y = 0 Vocabulary System of linear inequalities- two or more linear inequalities. Solution- ordered pair of the inequality in each system. Graph of linear inequalities- graph of all solutions of the system. Warm Up When is a line dotted? When is a line solid? How do we determine which way to shade a graph? Re-teach Triangular Solution y<2 x ≥ -1 y>x–2 1) Graph each system on the same plane. 2) The overlap is the intersection of the graphs. 3) After graphing pick a point, check to see if the point is a solution algebraically. Re-teach Solution between parallel lines Y<3 Y>1 1) Graph the equations. 2) Determine the overlapping shaded area. Re-teach Quadrilateral Solution Region x≥0 Y≥0 Y≤2 Y ≤ -½x + 3 1) Graph the system of linear inequalities. 2) Label each intersecting point. 3) Shade the region inside the intersecting points. Practice Graph and determine the types of solutions from each system. 1) 2x + y < 4 -2x + y ≤ 4 2) 2x + y ≥ -4 x – 2y < 4 3) 2x + y ≤ 4 2x + y ≥ - 4