* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.2 - People Server at UNCW
Survey
Document related concepts
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
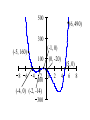
4.2 Polynomial Functions and Models A polynomial function is a function of the form Determine which of the following are polynomials. For those that are, state the degree. 2 (a) f ( x ) = 3x - 4 x + 5 Polynomial. (b) (c) Not a polynomial. Not a polynomial. If f is a polynomial function and r is a real number for which f(r)=0, then r is called a (real) zero of f, or root of f. If r is a (real) zero of f, then (a) r is an x-intercept of the graph of f. (b) (x-r) is a factor of f. Use the above to conclude that x = -1 and x = 4 are the real roots (zeroes) of f. 1 is a zero of multiplicity 2. -3 is a zero of multiplicity 1. -5 is a zero of multiplicity 5. If r is a Zero or Even Multiplicity If r is a Zero or Odd Multiplicity . Theorem If f is a polynomial function of degree n, then f has at most n-1 turning points. Theorem For large values of x, either positive or negative, the graph of the polynomial resembles the graph of the power function. For the polynomial (a) Find the x- and y-intercepts of the graph of f. (b) Determine whether the graph crosses or touches the x-axis at each x-intercept. (c) Find the power function that the graph of f resembles for large values of x. (d) Determine the maximum number of turning points on the graph of f. For the polynomial (e) Use the x-intercepts and test numbers to find the intervals on which the graph of f is above the x-axis and the intervals on which the graph is below the x-axis. (f) Put all the information together, and connect the points with a smooth, continuous curve to obtain the graph of f. (a) The x-intercepts are -4, -1, and 5. y-intercept: (b) -4 is a zero of multiplicity 1. (crosses) -1 is a zero of multiplicity 2. (touches) 5 is a zero of multiplicity 1. (crosses) (d) At most 3 turning points. Test number: f (-5) Graph of f: -5 160 Above x-axis Point on graph: (-5, 160) -4 < x <-1 Test number: -2 f (-2) -14 Graph of f: Below x-axis Point on graph: (-2, -14) -1 < x < 5 Test number: f (0) Graph of f: 0 -20 Below x-axis Point on graph: (0, -20) Test number: f (6) Graph of f: 6 490 Above x-axis Point on graph: (6, 490) 500 (6, 490) 300 (-1, 0) 100 (0, -20) (-5, 160) 8 6 4 2 100 (-4, 0) (-2, -14) 300 0 2 (5, 0) 4 6 8