* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
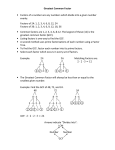
Chapter 13 Factoring Polynomials Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. 13.1 The Greatest Common Factor Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Factoring Polynomials When an integer is written as a product of integers, each of the integers in the product is a factor of the original number. The product is the factored form of the integer. When a polynomial is written as a product of polynomials, each of the polynomials in the product is a factor of the original polynomial. The product is the factored form of the polynomial. The process of writing a polynomial as a product is called factoring the polynomial. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 3 Greatest Common Factor Greatest common factor – largest quantity that is a factor of all the integers or polynomials involved. Finding the GCF of a List of Integers or Terms 1. Write each number or polynomial as a product of prime factors. 2. Identify common prime factors. 3. Take the product of all common prime factors. • If there are no common prime factors, GCF is 1. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 4 Example Find the GCF of each list of numbers. a. 12 and 8 12 = 2 · 2 · 3 8=2·2·2 So the GCF is 2 · 2 = 4. b. 7 and 20 7=1·7 20 = 2 · 2 · 5 There are no common prime factors so the GCF is 1. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 5 Example Find the GCF of each list of numbers. a. 6, 8 and 46 6=2·3 8=2·2·2 46 = 2 · 23 So the GCF is 2. b. 144, 256 and 300 144 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 · 3 · 3 256 = 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 · 2 300 = 2 · 2 · 3 · 5 · 5 So the GCF is 2 · 2 = 4. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 6 Example Find the GCF of each list of terms. a. x3 and x7 x3 = x · x · x x7 = x · x · x · x · x · x · x So the GCF is x · x · x = x3 b. 6x5 and 4x3 6x5 = 2 · 3 · x · x · x 4x3 = 2 · 2 · x · x · x So the GCF is 2 · x · x · x = 2x3 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 7 Example Find the GCF of the following list of terms. a3b2, a2b5 and a4b7 a3b2 = a · a · a · b · b a2b5 = a · a · b · b · b · b · b a4b7 = a · a · a · a · b · b · b · b · b · b · b So the GCF is a · a · b · b = a2b2 Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 8 Helpful Hint Remember that the GCF of a list of terms contains the smallest exponent on each common variable. smallest exponent on x smallest exponent on y The GCF of x3y5, x6y4, and x4y6is x3y4. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 9 Factoring Polynomials The first step in factoring a polynomial is to find the GCF of all its terms. Then we write the polynomial as a product by factoring out the GCF from all the terms. The remaining factors in each term will form a polynomial. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 10 Example Factor out the GCF in each of the following polynomials. a. 6x3 – 9x2 + 12x = 3 · x · 2 · x2 – 3 · x · 3 · x + 3 · x · 4 = 3x(2x2 – 3x + 4) b. 14x3y + 7x2y – 7xy = 7 · x · y · 2 · x2 + 7 · x · y · x – 7 · x · y · 1 = 7xy(2x2 + x – 1) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 11 Example Factor out the GCF in each of the following polynomials. a. 6(x + 2) – y(x + 2) = 6 · (x + 2) – y · (x + 2) = (x + 2)(6 – y) b. xy(y + 1) – (y + 1) = xy · (y + 1) – 1 · (y + 1) = (y + 1)(xy – 1) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 12 Factoring Remember that factoring out the GCF from the terms of a polynomial should always be the first step in factoring a polynomial. This will usually be followed by additional steps in the process. Example: Factor 90 + 15y2 – 18x – 3xy2. 90 + 15y2 – 18x – 3xy2 = 3(30 + 5y2 – 6x – xy2) = 3(5 · 6 + 5 · y2 – 6 · x – x · y2) = 3(5(6 + y2) – x (6 + y2)) = 3(6 + y2)(5 – x) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 13 Factoring by Grouping Step 1: Group the terms in two groups so that each group has a common factor. Step 2: Factor out the GCF from each group. Step 3: If there is a common binomial factor, factor it out. Step 4: If not, rearrange the terms and try these steps again. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 14 Example Factor by grouping. 21x3y2 – 9x2y + 14xy – 6 = (21x3y2 – 9x2y) + (14xy – 6) = 3x2y(7xy – 3) + 2(7xy – 3) = (7xy – 3)(3x2 + 2) Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall. Martin-Gay, Developmental Mathematics, 2e 15