* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Instrumentation and Resistor Circuits Physics 517/617 Experiment 1
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
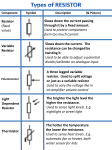
Physics 517/617 Experiment 1 Instrumentation and Resistor Circuits Basic Experiment - Physics 517/617 Study the operation of the oscilloscope, multimeter, power supplies, and wave generator. For the oscilloscope you should understand the function of all the knobs on the front panel. 1) Verfiy Ohms law by plotting voltage vs current. Use a resistor of your choice. Repeat the measurement with a resistor 100X higher than the previous resistor. Use a DC power supply. 2) Use a resistor divider network to measure the DC resistance of the multimeter (use voltage scale). 3) Repeat part 1 using a 100 Hz sine wave and a 50 KHz sine wave. Any frequency dependence for R? 4) Measure the input impedance of your oscilloscope. Determine the effective values of R and C and compare with the scopes spec sheet. You can use a resistor divider network to measure R, and a capacitor divider to measure C. 5) Design and build a circuit with the following specs: a) four or more resistors (all different) resistors in series and parallel b) circuit draws between 10 and 50 milliamps when connected to 5 V DC. Calculate and measure the voltage drop and current through each element in your circuit. 6) Use the oscilloscope to check the frequency calibration of your function generator. Start at about 10 Hz and go up to the highest frequency available. Plot the results. To have the results fit on one plot you must plot log(f 1 ) vs log(f 2 ) . Advanced Experiment - Physics 617 or optional 1) Build a Wheatstone bridge. You can use a resistor box to make life easier. 2) Measure the resistance of three resistors with your bridge. What limits the accuracy of your Wheatstone bridge?