* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RC Circuits
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Battery charger wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
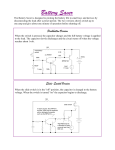
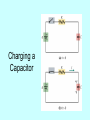
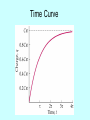
RC Circuits PH 203 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 14 Capacitance Remember that a capacitor stores charge: Q = C DV C = ke0A/d The potential across the capacitor can change with time The voltage across an uncharged capacitor is zero The voltage across a charged capacitor is equal to the applied potential VC = e Resistors and Capacitors If you connect a uncharged capacitor to a resistor and a battery the capacitor will go from 0 to maximum charge over some time The current in the circuit will start at a maximum and them go to zero as the capacitor charges A capacitor C paired with a resistor R has a charging time related to a time constant (t) t = RC This is the time to charge a capacitor to about 63% of the final value Charging a Capacitor Time Curve Charge Over Time If we charge a capacitor by connecting it to a battery of voltage e, the charge and voltage on the capacitor is: VC= e[1-e(-t/t)] Capacitor charges rapidly at first and then the rate of charge separation slows At about t = 4t the capacitor is nearly fully charged Discharging a Capacitor Energy in the capacitor is dissipated through the resistor QC = CVC VC= V0e(-t/t) where V0 is the initial voltage on the capacitor Using an Ammeter Must be placed in series Has low resistance Otherwise would decrease the current Using a Voltmeter Must be placed in parallel Has high resistance So only very little current flows through it Next Time Read 28.1-28.6 Problems: Ch 27, P: 47, 49, 56, Ch 28, P: 2, 12 Consider two identical light bulbs in series. If a third identical light bulb is added in series, what happens to the current through the battery and the power that flows from the battery? A) B) C) D) E) increase, increase increase, decrease decrease, decrease decrease, increase Both stay the same Consider two identical light bulbs in parallel. If a third identical light bulb is added in parallel, what happens to the current through the battery and the power that flows from the battery? A) B) C) D) E) increase, increase increase, decrease decrease, decrease decrease, increase Both stay the same















![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)