* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resistance of a wire - The Thomas Cowley High School
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
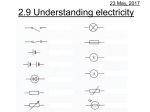
Electric Current 23 May 2017 + Remember: Copper atoms are much bigger than electrons and are packed together in the wire. Current In an electric c____, ircuit current is the flow of e_______. ore lectrons The bigger the current, the m___ electrons are flowing around the circuit. The w___ ires carry the electrons from one terminal erminal around the circuit to the other t______. lamps Ω Omega 23 May 2017 5.2 Resistance • Resistance is measured using an ammeter and a voltmeter. • Resistance = Voltage Current • This is called Ohm’s Law • Resistance is measured in Ohm’s (Ω) How many different words can you spell from the word resistance? Measuring Current Current is measured using an ammeter connected in series. What will the 3 ammeters read in this circuit? A 1 3 A 2 A Ammeter 1 = 0.15A, Ammeter 2 = ____, Ammeter 3 = ____ Measuring Current Current is measured using an ammeter connected in series. What will the 3 ammeters read in this circuit? A 1 3 A 2 A Ammeter 1 = 0.15A, Ammeter 2 = 0.15A, Ammeter 3 = 0.15A In a series circuit the current is always the same. Current in parallel In a parallel circuit the current can split depending on how difficult each route is. A1 The total current into and out of the supply is always the same. What are the missing currents? A1 = 0.6A A2 = _____? A3 = 0.2A A4 = _____? 23 May 2017 A4 A2 A3 Current in parallel In a parallel circuit the current can split depending on how difficult each route is. A1 The total current into and out of the supply is always the same. What are the missing currents? A1 = 0.6A A2 = 0.4A (A1-A3 = 0.6A-0.2A) A3 = 0.2A A4 = 0.6A (A1 = A4) A4 A2 A3 Measuring Voltage Voltage measures how energy changes around the circuit. It compares the energy in one part with another and shows the difference. Voltmeter V1 V2 V3 Voltage (V) 1.5 0.6 0.9 V1 NB Voltmeters are connected in parallel V2 V3 In series V1 = V2 +V3 Voltage in Parallel Voltage only changes when energy changes. In this circuit energy changes happen at the cell and the bulbs. V1 = V2 = V3 Voltmeter V1 V2 V3 Voltage (V) 1.5 1.5 1.5 V1 V2 V3 Measuring Resistance Set up the circuit as shown below: Resistance = Voltage Voltage (V) A V Slowly move the variable resistor and for each setting record the current in amps and the voltage in volts. Plot a graph of your results. 0 2 4 6 8 12 Current Current Resistance (A) (Ω) Correct type of graph Graphs Bar chart for categoric data Line graph for continuous data Current (Amps) Voltage against current through a resistor 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 Voltage (Volts) Points plotted correctly Suitable labels – Quantity (Units) Scale uniform ISA Answers 1. I was trying to find out if the current flowing through a resistor depends on the voltage across it. 2. Independent variable = Voltage Dependent variable = Current 3. Voltmeter or Ammeter 4. The smallest scale division was 0.01V or 0.01A 5. Smaller scale division means more precise measurements 6. Use the same resistor Different resistance values change the current 8. As the Voltage increases the current increases Section 2 10. As temperature increases the resistance falls 11. Range 0º C to 150ºC No. 150ºC too high for room temperatures. 12. At these temperatures resistance only changes very slightly. 13. 50ºC circled. Not anomalous. More likely to be 25ºC 14. Thermistor tested might not be typical between 50 and 200 (5 to 20%) 15. Results would be more reliable 16. Have smaller intervals between readings 17. Company was changing the results. Avoiding bad publicity. Would damage the companies reputation. 18. Improves the reliability 19. They have had a scale marked on them A range either side of the expected value that is considered acceptable 5% Testing the effect of current on a wire Circuit Results Voltage Current Resistance (V) (A) (Ohms) 2 A Test Wire 4 6 8 12 Ω Omega 23 May 2017 5.2 Resistance • Resistance is measured using an ammeter and a voltmeter. • Resistance = Voltage Current • This is called Ohm’s Law • Resistance is measured in Ohm’s (Ω) How many different words can you spell from the word resistance? Resistance of a wire (ISA) 23 May 2017 • To investigate which factors change the resistance of a wire. Apparatus: Resistance wire, Voltmeter, Ammeter, Power supply, Leads, Crocodile clips, metre ruler, Variable resistor. A Test Wire V