* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 09 Instruments
Peak programme meter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Automatic test equipment wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electronic musical instrument wikipedia , lookup
Music technology wikipedia , lookup
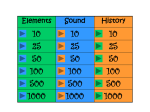
Unit 9 Measuring Instruments • • • • • Objectives: Discuss the operation of a d’Arsonval meter movement. Connect a voltmeter to a circuit. Read an analog multimeter. Connect an ammeter. Measure resistance using an ohmmeter. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Analog meters are characterized by the fact that they use a pointer and scale to indicate their value. • One of the common types of meters uses the d’Arsonval type of meter movement. • Analog meters use a moving coil placed between the poles of a magnet. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Basic d’Arsonval meter movement. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Basic d’Arsonval meter movement with rectifier to change AC voltage to DC voltage. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments The voltmeter is designed to be connected directly across the source of power. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Reading an analog meter is similar to reading a speedometer or fuel gauge. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments The ammeter is used to measure current and must be connected in series with the load to permit the load to limit the current flow. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments A shunt is used to set the value of the ammeter. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Many electricians use the clamp-on type of AC ammeter. Please note the clamp-on ammeter reads only one conductor at a time. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments • • • • Ohmmeters The ohmmeter is used to measure resistance. There are two basic types: analog or digital. The common VOM (volt-ohm-milliammeter) contains an ohmmeter. An ohmmeter should always be readjusted to zero when the scale is changed. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Digital Ohmmeters • Digital ohmmeters display the resistance in figures instead of using a meter movement. • They operate by measuring the voltage drop across a resistor. • The ohmmeter, whether digital or analog, must never be connected to a circuit when the power is turned on! Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Digital Ohmmeter Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Digital Voltmeter Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Low-impedance Voltage Tester The low-impedance voltage tester has a very large current draw compared to other types of voltmeters and should never be used to test low-power circuits. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Low-impedance Voltage Tester This tester has an impedance of 5000 Ω and can generally be used to measure voltages as high as 600 V. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Low-impedance Voltage Tester This is also known as a solenoid type tester. This tester is not susceptible to giving the misleading voltage readings caused by highimpedance ground paths or feedback voltages. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Low-impedance Voltage Tester High-impedance ground paths can produce misleading voltage readings. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Low-impedance Voltage Tester Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Reading a Digital Meter Many digital meters are auto-ranging, which means that they select the range scale automatically. This type will display a notation beside the numerical digits to indicate the meter scale. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Review: 1. The d’Arsonval movement is one of the common types of meters. 2. The d’Arsonval movement operates only on DC currents or rectified AC current. 3. Voltmeters have a high resistance and are designed to be connected directly across the power line. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Review: 4. Ammeters have a low resistance and must be connected in series with a load. 5. Shunts are used to change the value of DC ammeters. 6. Clamp-on ammeters read only one conductor at a time. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Review: 7. Ohmmeters are used to measure the resistance in a circuit. 8. There are two basic types of Ohmmeters: analog and digital. 9. Ohmmeters must never be connected to a circuit that has power applied to it. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Review: 10. Digital multimeters display their value in digits instead of using a meter movement. 11. Digital ohmmeters measure resistance by measuring the voltage drop across an unknown resistor when a known amount of current flows through it. Unit 9 Measuring Instruments Review: 12. Low-impedance voltage testers (solenoid type) are not susceptible to indicating a negligible voltage caused by a highimpedance ground or feedback.