* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lec6-elec
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
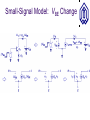
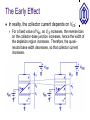
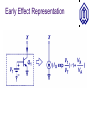
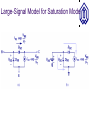
BJT (cont’d) OUTLINE –Transconductance –Small-signal model –The Early effect –BJT operation in saturation mode Reading: Chapter 4.4.3-4.5 Notes on PN Junctions Typically, pn junctions in IC devices are formed by counter-doping. The equations provided in class (and in the textbook) can be readily applied to such diodes if NA net acceptor doping on p-side (NA-ND)p-side ND net donor doping on n-side (ND-NA)n-side I D I S (e qVD kT 1) Dn Dp I S Aqni L N L N n A p D 2 ID (A) VD (V) Transconductance, gm The transconductance (gm) of a transistor is a measure of how well it converts a voltage signal into a current signal. It will be shown later that gm is one of the most important parameters in integrated circuit design. dI C d VBE I S exp gm dVBE dVBE VT 1 VBE g m I S exp VT VT IC gm VT Visualization of Transconductance gm can be visualized as the slope of the IC vs. VBE curve. The slope (hence gm) increases with IC. Transconductance and IC For a given VBE swing (DV), the resulting current swing about IC2 is larger than it is about IC1. This is because gm is larger when VBE = VB2. Transconductance and Emitter Area When the BJT emitter area is increased by a factor n, IS increases by the factor n. For a fixed value of VBE, IC and hence gm increase by a factor of n. Derivation of Small-Signal Model The BJT small-signal model is derived by perturbing the voltage difference between two terminals while fixing the voltage on the third terminal, and analyzing the resultant changes in terminal currents. This is done for each of the three terminals as the one with fixed voltage. We model the current change by a controlled source or resistor. Small-Signal Model: VBE Change Small-Signal Model: VCE Change Ideally, VCE has no effect on the collector current. Thus, it will not contribute to the small-signal model. It can be shown that VCB ideally has no effect on the small-signal model, either. Small-Signal Model: Example 1 The small-signal model parameters are calculated for the DC operating point, and are used to determine the change in IC due to a change in VBE. IC 1 gm VT 3.75 r gm 375 Small-Signal Model: Example 2 In this example, a resistor is placed between the power supply and collector, to obtain an output voltage signal. Since the power supply voltage does not vary with time, it is regarded as ground (reference potential) in smallsignal analysis. The Early Effect In reality, the collector current depends on VCE: For a fixed value of VBE, as VCE increases, the reverse bias on the collector-base junction increases, hence the width of the depletion region increases. Therefore, the quasineutral base width decreases, so that collector current increases. Early Effect: Impact on BJT I-V Due to the Early effect, collector current increases with increasing VCE, for a fixed value of VBE. Early Effect Representation Early Effect and Large-Signal Model The Early effect can be accounted for, by simply multiplying the collector current by a correction factor. The base current does not change significantly. Early Effect and Small-Signal Model DVCE VA VA ro VBE I C DI C I S exp VT Summary of BJT Concepts BJT in Saturation Mode When the collector voltage drops below the base voltage, the collector-base junction is forward biased. Base current increases, so that the current gain (IC/IB) decreases. Large-Signal Model for Saturation Mode BJT Output Characteristics The operating speed of the BJT also drops in saturation. Example: Acceptable VCC Range In order to prevent the BJT from entering very deeply into saturation, the collector voltage must not fall below the base voltage by more than 400 mV. VCC I C RC (VBE 400mV ) Deep Saturation In deep saturation, the BJT does not behave as a voltage-controlled current source. VCE is ~constant.