* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lect 4
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
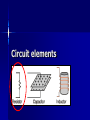
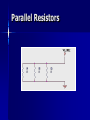
Circuit elements Resistors Resistance The electrical resistance of a circuit component or device is defined as the ratio of the voltage applied to the electric current whichflows through it: If the resistance is constant over a considerable range of voltage, then Ohm's law ,I = V/R, can be used to predict the behavior of the material. The resistivity, and thus the resistance, is temperature dependent Resistivity and Conductivity The electrical resistance of a wire would be expected to be greater for a longer wire, less for a wire of larger cross sectional area, and would be expected to depend upon the material out of which the wire is made The resistance of a wire can be expressed as Resistance = resistivity x length/area The factor in the resistance which takes into account the nature of the material is the resistivity ρ . The inverse of resistivity is called conductivity. There are contexts where the use of conductivity is more convenient. Electrical conductivity = σ = 1/ρ Resistor Combinations The combination rules for any number of resistors in series or parallel can be derived with the use of Ohm's Law, the voltage law, and the current law. Series Resistors Series Resistors Parallel Resistors Parallel Resistors Parallel resistors Two R’s More than 2R’s For I Then R DC Electric Power Remember: Ohm's Law For many conductors of electricity I is directly proportional to V applied to them. The ratio of V/I is called the resistance and if the ratio is constant over a wide range of voltages, the material is said to be an "ohmic" material. If the material can be characterized by such a resistance, then the current can be predicted from the relationship: DC Electric Power The electric power in watts associated with a complete electric circuit or a circuit component represents the rate at which energy is converted from the electrical energy of the moving charges to some other form, e.g., heat, mechanical energy, or energy stored in electric fields or magnetic fields. For a resistor in a DC circuit the power is given by the product of applied voltage and the electric current: Power = Voltage x Current P = VI Power Power is the rate energy is “used” (actually converted to heat or another form). Power is measured in watts (or kilowatts). Notice that rate always involves time. One watt = one joule/second Three equations for power in circuits that are collectively known as Watt’s law are: P IV PI R 2 2 V P R Power Dissipated in Resistor Convenient expressions for the power dissipated in a resistor can be obtained by the use of Ohm's Law. Power What power is dissipated in a 27 W resistor is the current is 0.135 A? Given that you know the resistance and current, substitute the values into P =I 2R. P I 2R (0.135 A) 2 27 W 0.49 W Power What power is dissipated by a heater that draws 12 A of current from a 120 V supply? The most direct solution is to substitute into P = IV. P IV 12 A 120 V 1440 W Power What power is dissipated in a 100 W resistor with 5 V across it? V2 The most direct solution is to substitute into P . R 2 V P Small resistors operating in low R 5 V 2 100 W 0.25 W voltage systems need to be sized for the anticipated power. 1n Energy Energy, W, is the ability to do work and is measured in joules. One joule is the work done when a force of one newton is applied through a distance of one meter. The symbol for energy, W, represents work, but should not be confused with the unit for power, the watt, W. 1m Energy The kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a much larger unit of energy than the joule. There are 3.6 x 106 J in a kWh. The kWh is convenient for electrical appliances. What is the energy used in operating a 1200 W heater for 20 minutes? 1200 W = 1.2 kW 20 min = 1/3 h 1.2 kW X 1/3 h =0.4 kWh