* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
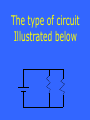
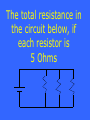
Circuits Electricity & Magnetism Motors, Speakers, Etc. 1 pt 1 pt 1pt 1 pt 2 pt 2 pt 2pt 2pt 2 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 4 pt 4 pt 4pt 4 pt 4pt 5pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt Static Electricity Ohm’s Law and Power 1pt This type of material allows electrons to flow through it What is a conductor? It is what happens when you get shocked What is excess electrons jump from you to the object (or vice versa) to even out the charge? It is what happens when a charged object is held next to a neutral one What is the neutral object becomes polarized (by induction)? The direction of the force between a piece of wool and styrofoam after rubbing them together What is attraction? The reason a charged object can attract a neutral one What is “the neutral object becomes polarized, so the charged object attracts the near side more than it repels the far side (since it is farther away)? The “I” in Ohm’s Law, and its units What is current, amperes? The current flowing through a 220 Ohm light plugged into the wall (110 V) What is .5 A? The number of 1.5 V batteries you need to push a current of 1 A through a 15 Ohm resistor What is 10? The power used by a 5 A hairdryer plugged into the wall (110 V) What is 550 Watts? The resistance of a bulb which consumes 55 W of power from a 110 V wall What is 220 Ohms? The meaning of the symbol What is a resistance (or resistor)? The type of circuit Illustrated below What is parallel? The total resistance in the circuit below, if each resistor is 5 Ohms What is 15 Ohms? A circuit breaker in your house is wired in this way What is in series with the sockets it protects? The total resistance in the circuit below, if each resistor is 5 Ohms What is 5/3 Ohms? This can be created by moving charges What is a magnetic field? Moving magnets will create this What is an electric field? The magnetic field near a straight currentcarrying wire looks like this What is circular (around the wire)? Where the magnetic poles of a coiled wire with an electric current are located. What is on the top and bottom? The direction of the force on a currentcarrying wire, relative to the direction of the current and magnetic field lines What is perpendicular? It converts electrical energy into kinetic What is a electric motor? In a speaker the motion of the cone is caused by this What is the varying force between the permanent magnet and electromagnet? How does the force on the coil change if the current changes direction What is it reverses? A speaker can also be used as this, which produces electrical energy What is a microphone? The reason our motors only rotate in one direction What is “the unsanded part of the coil prevents current from flowing when it would cause a force in the opposite direction”