* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2010
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Wave interference wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
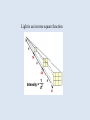
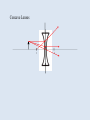
Physics Final 2010 Know: Opposite charges attract When you give something an electric charge, Electrons are moving from one thing to another The Force between electric charges depends on the square of the distance An electron has a charge of -1.6 x 10-19 C. If an object has a charge of 8 x 10-19 C, describe what causes the charge Know Units: C A V coulombs charge amperes current voltage potential difference J joules All energy W ohms resistance Definition of potential difference, resistance, and current Ohm’s Law V=IR What things change the resistance of a wire, and how For resistors in series and parallel, know what stays the same across all, and what is the sum Calculate equivalent resistance ?10 W ?5 W V I 4 A ? A R ? W 10 eq. res. 4W 12 W 24 V 6W A Equivalent Resistance? 24 W 2W Voltage in 6 W resistor? V = IR = 6V Current in circuit? 1 A Current in 6 W resistor? 1 A Power dissipated by 6 W resistor? P = IDV = 6 W Magnetic field lines go from the north pole to the south pole Right hand rules Waves are the transfer of energy Definitions: wavelength frequency period amplitude period? frequency? period = 1/frequency velocity maximum? restoring force maximum? acceleration maximum? For a pendulum: l T 2 period g length gravitational acceleration If you increase l, what happens to T? If you decrease g, what happens to T? 10 m 2m f = 4 Hz l?5m amplitude? 2 m wave speed? v = f l = 20 m/s Transverse Wave wavelength? frequency? amplitude? Longitudinal Wave wavelength? frequency? amplitude? Sound Longitudinal Wave Needs a medium to travel through Pitch is how high or low a sound sounds Pitch is a measure of frequency The Doppler Effect Mirrors and Lenses Images are described in terms of: real or virtual upright or inverted magnification Light is an inverse square function Plane Mirrors image is virtual, upright, magnification = 1 object distance = image distance angle of incidence = angle of reflection Concave Mirrors between C andinverted, f…real, inverted, outside at C…real, inside f…virtual, C….real, inverted, upright, mag =bigger smaller 1 bigger C f Convex Mirrors Always form virtual, upright, smaller images Concave Lenses f f Index of Refraction n…a ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum with the speed of light in a material Know how light bends when it goes from one “n” to another