* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning about AC signals
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
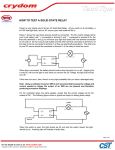
Learning about Electrical Components ES 110 Basic Components Function generator LED Relay Speaker Pot Ohm’s Law Drawing the circuit Schematic capture: http://phet.colorado.edu/simulations/sims.php?sim= Circuit_Construction_Kit_ACDC Relay A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet to operate a switching mechanism mechanically, but other operating principles are also used. Different Types of Relays An SPST relay (Single Pole Single Throw) simply opens or closes a signal path. This relay is typically normally open when power is removed, and the relay needs to be energized in order to connect the signal path. A DPST relay (Double pole Single Throw) is in essence two SPST relays but energized from the same coil. A SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) relay has one normally open and one normally closed path and a DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw) relay is in essence two SPDT relays which are energized from the same coil. Part I: Connecting a Relay 1. What is the minimum voltage required to turn on the relay? Part 2: Photoresistor A photoresistor is a sensor whose resistance varies with light intensity. Most decrease in resistance as the light intensity increases. Light Condition Resistance Completely Dark A little Dark! Room Condition Flash Light Fixed Resistance V(Out) Input Voltage (5V) Part 2: Photoresistor Using Excel plot Voltage vs. Resistance of the photo resistor. Is it linear? Using MSWord draw your circuit (as shown below) Include the table in your report What are the potential applications of a photoresistor? Redraw the following circuit and explain what it does. Part 3: Make the following measurements: Adjust the generator so you see a 2V peak-to-peak square wave signal with frequency of 8.5 KHz. DON’T forget UNITS! Take a snapshot of the signal (your snapshot must contain at least 2 cycles of the signal)- Use the figure in the previous slide. On you snapshot indicate how you measure Vpp, DC voltage (also called the offset), and the period (as shown the previous slide). Watch the video for more information. Use MSWord Equations to calculate the frequency of the signal from your plot. Show all your work. What is Vp of this signal? Take another snapshot of the signal. This time make sure you set the voltage cursers to show the Vpp. Part 4: Connect Photo Resistor to the Relay and Turn on the Siren! GND 1 5V