* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Uses of a Potential Divider
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
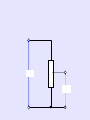
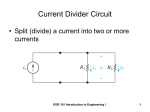
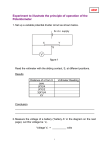
The Potential Divider Electricity Lesson 10 Learning Objectives To know what a potential divider is. To derive and know how to use the potential divider equation. To know that the load affects the output of a potential divider To know the applications of potential dividers; to detect temperature or light levels. Definition What is potential divider? A potential divider consists of two or more resistors connected in series with each other and a source of fixed potential difference. Draw a circuit diagram for this arrangement. Circuit Diagram What is the pd across each resistor? We can use potential difference between points A and B as a supply for another component. 6V 50 100 A B Uses of a Potential Divider To supply a fixed pd between any value between zero and the source pd. To supply a variable pd from a fixed one. To supply a pd that varies with physical changes e.g. position, temperature or light level Another Example R2 V2 VS R1 V1 Supplying a fixed pd The total resistance of the circuit = R1 + R2 The current through the resistors = V0/(R1 + R2) V V 1 IR1 V2 IR2 R1 V1 R1 R2 0 V0 R2 V2 R1 R2 Deriving Potential divider equation For an unloaded potential divider the current is the same through both resistors So the voltage is proportional to the resistance V IR V IR 1 1 2 2 V R V R 1 1 2 2 Potential divider equation If R1 >> R2 then V1 is more or less the supply voltage If R1 << R2 then V1 is close to 0 V. V0 as an input to the potential divider and V1 as an output. The circuit itself provides a way to tap off a voltage between 0 V and V0. Confused? So what’s the difference between a variable resistor and a potential divider? Confused? When a variable resistor is used the total resistance of the circuit is being altered. Also, the pd is not being taken across the variable resistor. VINV V out Using potential dividers Use as a volume, brightness or contrast control. Making and designing a circuit to use as a temperature sensor Making and designing a circuit to use as a light sensor Controlling logic devices Effect of different resistive loads Output voltage is affected by load resistance Connecting a resistor across the output reduces the output voltage Shorting out across a bulb reduces the total resistance of the bulb – the wire is in parallel with the bulb Questions A series circuit is connected as shown in the diagram. 1. What is the potential difference between A and B? 2. An additional resistor of 100 W is connected between the 50 W resistor and the cells. What is the potential difference between A and B now? 3. The additional 100 W resistor is now connected in parallel with the first 100 W resistor. What is the potential difference between A and B now? Question How do we get a variable supply voltage from a fixed one? How can we measure physical changes in position, temperature or light level etc. Answer A potential divider is one way of producing a variable p.d. A combination of a suitable sensor (angle / position sensor, thermistor or LDR) and a potential divider enables measurement / monitoring / control of physical changes. Alternative formula The potential divider equation can be derived by rearranging the ratios above to give: V output = R1 / (R1+R2) V input.