* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AC Circuits - Cedarville University
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
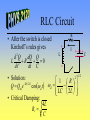
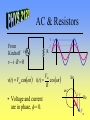
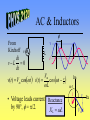
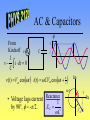
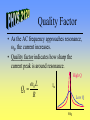
AC Circuits See online explanation at http://www.physclips.unsw.edu.au/jw/AC.html Total Energy • Total energy of the system is the sum of the electric and magnetic field energy. ++++ E L ---- 2 m Q 2 UC cos t 2C LI m2 UL sin 2 t 2 Qm2 LI m2 U UC U L 2C 2 C I L B C RLC Circuit R • After the switch is closed Kirchoff’s rules gives 2 d Q dQ Q L 2 R 0 dt dt C • Solution: Q Qm e - Rt / 2 L cos d t • Critical Damping: 4L Rc C + I L ++++C ---- - 1 R d - LC 2 L 2 1/ 2 AC Source • The voltage of the power Vm v supply follows that of a cosine function. • Represent the source as a -V m vector rotating in the complex plane. • Real component of vector is the instantaneous voltage. t Im t v Vm Re v(t ) Vm cost AC & Resistors v i From Kirchoff v R v -i R 0 v(t ) Vm cost Vm i (t ) cost R • Voltage and current are in phase, f = 0. Im t iv Re Vm Power • Power used by a resistor is 2 m V 2 P(t ) v i cos t R • Average power is 2 Vm Vm I m P 2R 2 • Effective voltage and current are Vrms Vm 2 I rms Im 2 P Vrms I rms AC & Inductors f From Kirchoff v di v-L 0 dt v(t ) Vm cost v L i Vm Im i (t ) cost - p2 L t • Voltage leads current Reactance by 90°, f = p/2. X L L i v Re Vm AC & Capacitors f From Kirchoff v v C i 1 v - i dt 0 C v(t ) Vm cost i(t ) CVm cost p2 Im t • Voltage lags current Reactance 1 XC by 90°, f = -p/2. C i Vm v Re LRC Circuits & AC • In a series circuit current is the same everywhere, so add voltages as phasors. • Phasors are rotating vectors in the complex plane. R v L Im C vL • Assume we are at t = 0s. v vR jvL - jvC vC i vR Re Impedance • Express voltage as current times impedance. v iR j iX L - j iX C v iR j X L - X C iZ Z R X L - X C 2 X L - XC f tan R -1 2 f vC Im vS f vL vR Re ELI the ICE man • At resonance, 0, XL=XC and f = 0. 0 1 LC X L - XC f tan R -1 • For <0, the circuit is capacitive and current leads voltage. Also f < 0. • For >0, the circuit is inductive and voltage leads current. Also f > 0. Quality Factor • As the AC frequency approaches resonance, 0, the current increases. • Quality factor indicates how sharp the current peak is around resonance. Q0 0L High Q Im R Low Q 0 Transformers • A transformer consists of two sets of coils which share the same magnetic flux. • AC current through the primary generates a changing magnetic flux, which generates a changing voltage on the secondary. NS VS VP NP VS I S VP I P Primary v Secondary RL Power Lines • Ex. How much power is lost if 120V is delivered through a 10W transmission line to a 10W load? Compare that to transmission at 12,000 V and then stepped down to 120V at the load. RT RT 120V RL 12,000V 120V RL Power Transmission Less resistive loss Through Town: at low current. 20 kV To Home: 240 V Long Distance: 230 kV