* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download mythology intro
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
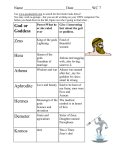
Mythology Objectives LEARNING GOALS: Using Edith Hamilton’s Mythology, the student will •Know the purpose of myths •Know the requirements of myths •Know the types of myths •Know characteristics of Greek gods •Know key Greek gods and mythology related terms •Greek streaming music Edith Hamilton’s Mythology Purpose of Myths: 1. Explain origin(s) of world/man 2. Explain nature 3. Explain ways of gods to man 4. Entertainment Temple of Apollo Requirements for a myth: 1. Narrative 2. Imaginative, clever, inventive (may explain an event that wasn’t understood or a “scientific principle) 3. 4. 5. 6. Involves super-human beings Usually improbable or absurd Often has a moral Part of the past of a group or race of people Types of myths: 1. Historical: Built around an event that actually or supposedly happened (ex. Trojan Wars). 2. Religious: Told about a god or goddess to explain a religious practice 3. Explanatory: Explain things/events that are not understood; most myths fall into this group 4. Amusing: Told “just for fun;” aesthetic myths. 5. Allegorical: “symbolic;” things may represent vices and virtues; reader is to put himself in the place of the person in the myth. •Gods and Heroes in the Greek World (01:12) •Discovery Channel School. 2004. Discovery Education. 4 January 2009 <http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com/> Title of the Myth:__________________________________ Summary of the Myth: Characters: •Gods/Goddesses? •Demigods? •Mortals? •Mythological Creatures? Type of Myth: Explanatory? _____ Amusing? _____Etc?_____ If explanatory, what does it explain? ____________________ Does it have a moral?_____________________________ Greek myths: Man is at the center of the universe. However, not as dark a picture as previous religions (pagan, nature) with horrors—human sacrifices Greek gods in man’s image, yet mortal with extra powers—traces of magic witches, demons, ghosts, astrology as before •Greek Mythology and the Role of the Gods in Human Destiny (01:46) Greek Mythology and the Role of the Gods in Human Destiny. Discovery Channel School. 1997. Discovery Education. 4 January 2009 <http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com/> Titans are the giant sons and daughters of Uranus and Gaia (Earth). Twelve Titan Gods and Goddesses: Oceanus and Tethys, Hyperion and Theia, Coeus and Phoebe, Cronus and Rhea—parents of Zeus Mnemosyne, Themis, Crius, Iapetus (Heaven) Children of Hyperion: Eos, Helios, Selene Daughters of Coeus: Leto and Asteria Sons of Iapetus: Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus, Menoetius The 12 Titans gods, also known as the elder gods, who ruled the Earth before the Olympians overthrew them. The ruler of the Titans was Cronus who was dethroned by his son Zeus. Most of the Titans fought with Cronus against Zeus and were punished by being banished to Tartarus. •Some Common Figures from Greek Mythology (01:03) Some Common Figures from Greek Mythology. Aims Multimedia. 1990 Discovery Education. 4 January 2009 <http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com/> Edith Hamilton’s Mythology The Twelve Olympians The Twelve Olympians Greek/Roman Names Zeus/Jupiter Poseidon/Neptune Hera/Juno Hades/Pluto Hestia/Vesta Ares/Mars Athena/Minerva Hermes/Mercury Apollo/Phoebus Apollo Artemis/Diana Hephaestus/Vulcan Aphrodite/Venus 25 Fascinating Things You Probably Didn't Know About Greek Gods https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_ZHK_hJmiCg Zeus/Jupiter…God of Gods • • • • • • • • • • • • Roman name: Jupiter Chief of the Olympians god of. . . -. . .the sky -. . .justice, law and order -. . .strangers and travelers Other facts: Symbols - Eagle, thunderbolts Son of Cronus and Rhea; brother of Hades+Poseidon Wrathful, lustful, not “all-knowing” Married to Hera, ungodly marital behavior Many children mostly out of wedlock Rhea hid him from Cronus to keep from being eaten; he overthrew Cronus; constantly unfaithful to Hera • YOUTUBE Zeus • The stone itself (which may have been a copy) has a carving of a knotted net covering its surface, and has a hollow centre, which widens towards its base (illustrated, to the right). • The Omphalos at Delphi came to be identified as the stone which Rhea wrapped in swaddling clothes, pretending it was Zeus. This was to deceive Cronus, his father, who swallowed his children so they could not grow up and depose him as he had deposed his own father, Uranus. • Omphalos stones were said to allow direct communication with the gods. • Christian destroyed the site in the 4th century at the order of Emperors Theodosius and Arcadius Poseidon/Neptune - God of the Sea • Roman name: Neptune • Zeus’s brother of Zeus and Hades/Son of Cronus & Rhea • Cranky and ill tempered • Powerful, secretive • Vengeful, usually argumentative with other gods • god of. . . • -. . .the sea (trident is symbol) • -. . .earthquakes • -. . .represents bulls and horses • YOUTUBE Poseidon Hades/Pluto God of the Underworld • god of. . . • -. . .the underworld • Son of Cronus & Rhea; brother of Zeus+Poseidon (drew the short straw) • He is not death. He does not kill anyone. He simply watches over the dead. • He carried wife, Persephone, away and made her queen of the underworld • dark bearded, crown, scepter, key, helmet of invisibility, chariot • Rarely worshipped Hera/Juno Goddess of Marriage Protector of Married Women • • • • • • • • • Roman name: Juno Wife and sister of Zeus goddess of. . . -. . .motherhood -. . .wives Peacock, cow, pomegranate Powerful, bold, terribly jealous Daughter of Cronus & Rhea Avenged infidelity often Hestia/Vesta Goddess of Home and Hearth • • • • • Hearth fire Good-natured, loving Does not appear in myths at all…symbolic herself Daughter of Cronus & Rhea Seven Vestal Virgins oversee her fire Ares/Mars God of War • • • • • • • • Roman name: Mars •4 horses: Terror, Son of Zeus and Hera Fire, Flame, Trouble Terrorized mortals Spear, vulture, dog •Relatives: Deimos(fear), Boastful, loud, cruel Phobos(terror), god of. . . Eris(discord) -. . .mindless war Not as important to Greeks as the Romans Athena/Minerva Goddess of the City, Wisdom, Handicrafts, War & Agriculture • • • • • • • • • Roman name: Minerva Daughter of Zeus & Metis Owl (wisdom) is her symbol Created olive tree goddess of. . . -. . .wisdom -. . .intelligent warfare Wise, even-tempered, fierce in battle Zeus’s daughter (but not Hera’s) Sprung from his head fully armed; his favorite • Athens is her city • Parthenon is her temple Hermes/Mercury God of Travelers, Thieves & Shepherds • • • • • • • • • Roman name: Mercury Son of Zeus & Maia Chief messenger, not the most honest god Tricky and sneaky/cunning Messenger of the gods god of. . . -. . .thieves and deceivers Winged sandals and hat, caduceus Witty, happy, clever, friendly, helpful Apollo God of Light & Purity • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Roman name: Phoebus Apollo Son of Zeus and Leto Twin brother of Artemis Mouse, sun dial, lyre Cheerful, sometimes jealous Perpetually young, handsome, wise Teaches moderation god of. . . -. . .light/truth -. . .prophecy -. . .music (lyre) -. . .medicine -. . .archery YOUTUBE Apollo Artemis/Diana Goddess of the Hunt & Moon • • • • • • • • • Roman name: Diana Daughter of Zeus & Leto Twin sister of Apollo Cypress tree, wild animals, deer Aloof, majestic, nature-loving, quick to anger, athletic Skilled archer, lived among virgin nymphs goddess of. . . -. . .the hunt (deer sacred to her) -. . .chastity Hephaestus/Vulcan God of Fire & Forge • Roman name: Vulcan • Son of Zeus & Hera’s crippled son; only ugly/lame god • Married to Aphrodite • Blacksmith of the gods/god of fire • Vulcan-Birmingham • Fire, quail • Modest, helpful, prone to laughter • Helped by Cyclopes in underground forges • Taught men to use fire • • • • • • • • • Aphrodite/Venus Goddess of Love Roman name: Venus Married to Hephaestus goddess of. . . -. . .love/beauty -. . .desire Sprung from foam and sea Dove, rose, apple Seductive, irresistible, sometimes treacherous Hephaestus won her hand, not heart, she’s in love with Ares • Led Paris to Helen The Rock of Aphrodite is a few kilometres to the west of Pissouri village, Cyprus. Legend has it that Aphrodite, goddess of love and beauty, rose from the waves in this spot. Blown by the wind, Aphrodite's first stop was on the island of Cythera, but this was such a tiny island that Aphrodite kept moving and eventually got to Cyprus, where she began living in Paphos. Hestia • Roman name: Vesta • Daughter of Zeus and Hera • Goddess of the hearth, of the right ordering of domesticity and the family • Each city had a public hearth sacred to her; where the fire never went out • In Rome, fire cared for by six virgin priestess called Vestals. Other gods! Eros • Roman name: Cupid • Son of Aphrodite • Helps people fall in love with each other Persephone • • • • • Roman name: Proserpine Daughter of Zeus and Demeter Becomes the queen of the underworld goddess of. . . -. . .Spring Pan • • • • • Roman name: Pan Associated with Dionysus Has goat ears and legs god of. . . -. . .shepherds and flocks • YouTube Pan Dance The Myths God Teachers, Quests, Cycles, Metamorphoses, Losses of Innocence, Creation Prometheus pro ME thee us • Kind, clever, longsuffering • An original Titan • Benefactor of Mankind • stole fire from Zeus and gave it to the primitive mortals • Punished for thousands of years Demeter and Persephone • Demeter goddess of Agriculture • Loving but moody • Daughter Persephone kidnapped by Hades • Neglect of the Earth • Pomegranate seeds • Spring vs. Winter Dionysus dy o NY sis • God of the Vine • Grapes, panther, goat, dolphin • Joyful, pleasure-loving, dangerous when opposed • Son of Zeus & Semele • Turned kidnapping sailors into dolphins • Bacchantes ecstasy dancing Cupid and Psyche CUE pid and SY key • Cupid (Eros) Archer of Love • Psyche Greek Heroine • Punished for challenging Aphrodite (Eros’ mother) • Accidental love • Jealous sisters urge disobedience • Oil drip wakes Eros • Vengeful tasks of Aphrodite • Forgiveness and marriage Athena and Arachne a THEE nah and a RAK nee • Athena challenged Arachne • Arachne’s weaving was better • She hung herself after being beaten • Athena turned her into a spider Pygmalion and Galatea pig MAIL yon and gal ah TAY ah • • • • • King of Cyprus Sculpted a woman Prayed to Aphrodite Live statue Love and marriage Apollo and Daphne ah PAWL oh and DAF nee • Huntress, independent, no interest in love or marriage • Apollo taunts her, chasing her deep into the woods • Pursuit and plea for help • Daphne - Laurel tree transformation • Vow of fidelity – Apollo tells her that he will use her laurel branches “whenever songs are sung and stories told.” Orpheus and Eurydice • Son of a Muse & a Thracian Prince (Thracians were great musicians) • Mother gave him the gift of music • No on “could resist him” • Sailed with Jason on the Argo • Saved heroes from the Sirens • Married Eurydice (referred to as a “bud”) • Goes to rescue her from Hades • Wife doesn’t make it out of the cavern (her last words are “farewell”). • Maenads come upon him and kill him – limb by limb • Buried in a tomb at Mt. Olympus Phaeton FAY tohn • Childish son of Apollo (Helios) • Proof of parentage • Wish granted to fly the chariot • Out of control flight • Zeus puts an end to it Pyramus and Thisbe PEER ah muss and THIZ bee • Fairest and Handsomest in Babylonia • Forbidden love • Plan to meet at Tomb of Ninus • Thisbe’s cape soiled with blood by a lioness • Pyramus stabbed himself over her assumed death • Thisbe returned to him and stabbed herself also Icarus and Daedalus ICK ar uss and DAY dah luss • Jealous of his nephew Talus, killed him and moved to Crete • King Minos’ wife fell in love and had a child with a bull (Minotaur) • Daedalus built the labyrinth and a way to escape • Warnings of high and low flying to Icarus • Melting wax, falling Icarus Narcissus nar SISS uss • • • • • Hera’s sentence of silence for Echo the nymph Narcissus is vain, Echo loved him “Is anyone here?” “Here, here!” Echo ignored by Narcissus faded to only a voice Finally saw himself and died looking at it Baucis and Philemon BA kiss and FILL ah min • • • • • • Zeus & son Hermes Test of Hospitality Ever-full wine bowl Flood Hut to Temple Oak and Linden trees Pyrrah and Deucalion PEER ah and doo CAL yon • The Greek Noah, son of Prometheus (who warned him) • Zeus floods Earth • Ran aground on Parnassus • Loneliness in a cave (Delphi Oracle) • “Throw the bones of your mother over your shoulders.” • Rocks turn to people • Parents of Pandora Jason JAY son • Jason sent away to avoid death by uncle • Bargain for thrown with uncle (golden fleece) • Argonauts set out • Bargains with Medea’s father • Plowed the fields of the fire breathing bull, attained fleece, and distracted Medea’s father with her help. • Married Medea, later grew tired of her and she killed their children Theseus THEE see us • Aegeus buried sandals and sword under heavy rock • Theseus lifted it at 16 yrs. • Slayed the Minotaur (labyrinth) for Minos • Ariadne loved Theseus and asked Daedalus for help (thread idea) • Returning to Aegeus, wrong sails displayed Hercules HER cue leez • Hearty, good-natured, prone to rages • 12 Labors • Nemean Lion, Hydra, Thrace’s flesh-eating horses, Cerebrus, etc • Made a god upon his death Perseus PER see uss • King Acresias and Danae • Polydectes loved Danae, Perseus protects by offering Medusa’s head • Athena’s shield, nymph’s invisibility helmet, winged sandals, and magic pouch, Hermes’ knife • He succeeds • Pegasus born • Saved Andromeda, froze her family for deceit • Also froze Polydectes for hassling Danae The Parthenon is the most important and characteristic monument of the ancient Greek civilization and still remains its international symbol. It was dedicated to Athena Parthenos, the patron goddess of Athens. It was built between 447 and 438 BC. and its sculptural decoration was completed in 432 BC. Terms to know: Mt. Olympus: home of the gods •Mount Olympus and the Gods of Greek Mythology (02:20) Mount Olympus and the Gods of Greek Mythology. Discovery Channel School. 1997. Discovery Education. 4 January 2009 <http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com/> Elysian Fields:or sometimes Elysian plains, were the final resting place of the souls of the heroic and the virtuous. Elysium, also known as the Elysian Fields, in Greek mythology was a pre-Hellenic paradise, a land of perfect peace and happiness. In the works of Homer, Elysium was a land at the farthest and westernmost edge of the world to which the great heroes were carried, body and soul, and made immortal. Charon: and boatman ferries souls of dead across water to gate to Tartarus He only accepts the dead which are buried or burned with the proper rites, and if they pay him an obolus (coin) for their passage. For that reason a corpse had always an obolus 1 placed under the tongue. • Charon, Athenian red figure lekythos C5th B.C., Rhode Island School of Design Tartarus—Underworld; lower region of the dead. Tartarus is the lowest region of the world, as far below earth as earth is from heaven. According to the Greek poet Hesiod, a bronze anvil falling from heaven would take nine days and nights to reach earth, and an object would take the same amount of time to fall from earth into Tartarus. Tartarus is described as a dank, gloomy pit, surrounded by a wall of bronze, and beyond that a three-fold layer of night. While Hades is the main realm of the dead in Greek mythology, Tartarus also contains a number of characters. In early stories, it is primarily the prison for defeated gods; the Titans were condemned to Tartarus after losing their battle against the Olympian gods. However, in later myths Tartarus becomes a place of punishment for sinners. It resembles Hell and is the opposite of Elysium, the afterlife for the blessed. When the hero Aeneas visits the underworld, he looks into Tartarus and sees the torments inflicted on characters such as the Titans, Tityos, Otus and Ephialtes, and the Lapiths. Rhadymanthus (and, in some versions, his brother Minos) judges the dead and assigns punishment. Cerberus: Three headed dragon tailed dog who permits all spirits to ENTER but none to return. He was overcome several times: Hercules' final labour was to capture Cerberus, which he did by wrestling it into submission. Orpheus used his musical skills to lull Cerberus to sleep. Hermes put him to sleep with water from the river Lethe. In Roman mythology, the Sybil of Cumae lulled Cerberus to sleep with drugged honeycakes in order to permit Aeneas fuller entry to the underworld. In a Greek tale, Psyche also lulled Cerberus to sleep with drugged honeycakes. In The Inferno, Cerberus punishes the gluttons and is passed by Virgil and Dante due to Virgil throwing him a body part of one of Cerberus' victims. Heracles and threatened Cerberus, Attic black-figure neck-amphora, ca. 540 BC Styx river: river which separates underworld from the world above; Styx it is said winds around Hades (hell or the underworld are other names) nine times. Its name comes from the Greek word stugein which means hate. This river was so respected by the gods of Greek mythology that they would take life binding oaths just by mentioning its name. If a god gave his oath upon the river Styx and failed to keep his word, Zeus forced that god to drink from the river itself. The water is said to be so foul that the god would lose his/her voice for nine years. It is thought that Charon, the old ferry man who ferries the dead onto the underworld, crosses the river Styx, but this is a misconception. Charon crosses the river Acheron where also Cerebus stands his eternal guard. Thetis dipping Achilles in the Styx River, Daumier 1842 Where is the REAL river Styx? • There are five rivers that separate Hades from the world of the living, they are: • Acheron - the river of woe; • Cocytus - the river of lamentation; • Phlegethon - the river of fire; • Lethe - the river of forgetfulness; • Styx - the river of hate. Delphi: Delphi was the site of the Delphic oracle, most important oracle in the classical Greek world, and it was a major site for the worship of the god Apollo. People came from all over Greece and beyond to have their questions about the future answered by the Pythia, the priestess of Apollo. And her answers, usually cryptic, could determine the course of everything from when a farmer planted his seedlings, to when an empire declared war. Arguments over the correct interpretation of an oracle were common, but the oracle was always happy to give another prophecy if more gold was provided. A good example is the famous incident before the Battle of Salamis when the Pythia first predicted doom and later predicted that a 'wooden wall' (interpreted by the Athenians to mean their ships) would save them. Julian the Apostate (331/332– - 26 June 363), a Roman emperor, tried to revive classical Greek culture in the mid 4th century AD. He is said to have consulted the Oracle of Delphi. The Pythia responded with the following oracle: Tell to the king that the carven hall is fallen in decay; Apollo has no chapel left, no prophesying bay, No talking spring. The stream is dry that had so much to say. This was probably the last advice from the Oracle of Delphi. The Oracle said that the time to revive classical Greek culture has passed, Apollo is dead. Some say that the reason for this answer was that there was no “narcotic” gas coming anymore from the ground in Delphi that was used to set the Pythia in trance. Today scientists believe that the gas contained ethylene that in low concentrations produce trancelike states. Plutarch said that the pneuma smelled like sweet perfume. He also describes how in his times the emission was weak and irregular, the cause, in his opinion, of the weakening influence of the Delphic oracle in world affairs. He suggested that either the vital essence had run out or that heavy rains had diluted it or a earthquake four centuries earlier had partially blocked its vent.