* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Myths of the twelve Olympians
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
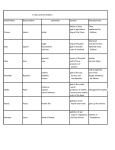
Introduction to Greek Mythology 1 Introduction to Greek Mythology Prepare yourself for a spectacular and scandalous journey filled with: 2 Unit Objectives Students will be able to… define mythology and explain its purpose. identify mythological vocabulary and its relevance in today’s world. identify the gods and goddesses and explain their relevance to today’s world. identify the archetypes of mythology and explain their relevance to today’s world. read and analyze stories from Greek Mythology to make connections between these classic stories and modern society. 3 Why We Study Greek Mythology It provides insight into the human condition (human nature). It grants us a glimpse at an ancient people trying to make sense of phenomena they could not explain. 4 Big Ideas of the Unit Greek Mythology has provided the foundation of our modern vocabulary. The plots, themes, and characters of classical literature still resonate today because they illustrate human nature. Archetypes are symbols used in literature to effectively communicate their ideas. 5 What is a myth? Myth comes from the Greek “mythos” which meant “speech” or “discourse” and now means “fable” or “legend.” A myth is “a story of forgotten or vague origin, basically religious or supernatural in nature, which seeks to explain or rationalize one or more aspects of the world or a society.” Pantheon.org 6 In the same way, Greek Myths… Were used to explain: ~ the creation of the earth, ~ death and the afterlife, and human experiences: love, ~ jealousy, revenge, & war. *They were also used as entertainment and were only told orally because most people could not read. Gods & Goddesses Greek Myths include gods & goddesses. A god or goddess is immortal. This means that they can never die but they had human emotions. Mortals are men and women that lived on earth. The gods often interacted with them. Polytheistic – They had more than just one god Ajax - Greek warrior in the Trojan War, who "cleaned up" in battle; Ajax is the name of a popular household cleanser. Amazon - Race of warrior women; amazon.com - huge online bookstore. There is also the Amazon Health Care. Ambrosia - In ancient Greek mythology, ambrosia is sometimes the food, sometimes the drink, of the Greek gods. There is Ambrosia Natural Foods, Ambrosia Software, the famous Ambrosia Salad, and a ton of cafes, banquet halls and restaurants named Ambrosia. Atlas - Was doomed to support the heavens on his shoulders; a modern moving company (Atlas Van Lines); also, Atlas Travel is a popular name for travel agencies all over the globe. Atlas Railroad Company, Atlas Snowshoes, and even Atlas Games. Juno - Roman name for Hera, wife of Zeus; Juno is a popular web-hosting company (www.juno.com), specializing in free 9 web pages and custom e-mail. MYTHS OF THE TWELVE OLYMPIANS English I Twelve Olympians Zeus (Jupiter) • Hera (Juno) Poseidon (Neptune) • Hades (Pluto) Pallas Athena (Minerva) Apollo Artemis (Diana) Hermes (Mercury) Ares (Mars) Hephaestus (Vulcan and Mulciber) Hestia (Vesta) Aphrodite (Venus)_ Came after the Titans. Called Olympians because Olympus was their home. Mt. Olympus Place of perfect peace Not the same as Heaven Where the 12 Olympians live Eat ambrosia Drink nectar Zeus (Jupiter) Supreme ruler-Lord of the Sky, the Rain-god and the Cloudgatherer Had the greatest power, but was NOT omnipotent (all-knowing) he could be deceived. Thunderbolt Married to Hera, but often cheated on her – a womanizer Breastplate-aegis (“eejis” armor plate that protects the chest) Bird-eagle Tree-oak Oracle-Dodona in the land of oak trees Zeus (Jupiter) Jupiter is so named because it is so big – it is the “King of Planets” Zeus Hera Zeus’s wife and sister Protector of marriage and married women Considered one of the most beautiful Cow and peacock sacred to her Argos was her favorite city Shows her anger in punishing the many women Zeus fell in love with, even if when they yielded only because he coerced or tricked them A very important role in Trojan War Hera No planet, but there is an asteroid named after her plus a city in Alaska Poseidon (Neptune) Ruler of the sea His wife – Amphitrite (grandaughter of the Titan, Ocean) Gave the first horse to man Storm and calm were under his control Shown carrying his trident, a threepronged spear Called the “earth shaker” Poseidon Neptune is so named because the blue looks like water Hades (Pluto) Son of Cronos and Rhea Not necessarily evil Underworld and ruler over the dead Also called “Pluto, the God of Wealth, of the precious metals hidden in earth” Wife Persephone (Proserpine) whom he carried from the earth and made Queen of the Lower World King of the dead Hades (Pluto) Pallas Athena (Minerva) Daughter of Zeus-sprang from his head (no mother) Daughter of Zeus and Metis (titan) – she popped out of his head after he swallowed the pregnant Metis Virgin goddess Goddess of the City, the protector of civilized life, of handicrafts (weaving) and agriculture, Goddess of war, goddess of wisdom Inventor of bridle (a harness fitted around a horse’s head to restrain or guide an animal) who first tamed horses for men to use Zeus’ favorite child – she would carry his thunderbolt Temple Parthenon Athens her special city Olive created by her; was her tree Pallas Athena (Minerva) Phoebus Apollo Son of Zeus and Leto (Latona) Master of musicians who delights Olympus as he plays the golden lyre Lord of the “silver bow” Archer-god The Healer (first taught men the healing art) God of Light God of Truth No false words ever comes out of his mouth Oracle was at Delphi-direct link between the gods and men Laurel was his tree Dolphin and crow sacred to him God of sun, music, and medicine “Phoebus” means brilliant or shining Apollo Artemis (Diana) The goddess of wilderness, the hunt and wild animals Apollo’s twin sister, daughter of Zeus and Leto Cypress was sacred to her and wild animals especially the deer In some stories she is fierce and revengeful She is the moon goddess sometimes Virgin goddess As Diana, she is also a goddess of light Artemis Aphrodite (Venus) The Goddess of Love and Beauty laughter-loving goddess Often in a mocking manner Daughter of Zeus and Dione in The Iliad Myrtle was her tree The dove her bird—sometimes to the sparrow and the swan In some stories, known as the wife of Hephaestus Aphrodite (Venus) •Born from the foam in the sea caused by the attack of Cronos/ Saturn on Ouranus/Uranus. “Aphros” is foam in Greek Venus is so named because it is a beautiful planet and can be easily seen with just the eye Hermes (Merury) Son of Zeus and Maia (daughter of Atlas) On his feet winged sandals; wings were on his low-crowned hat too and on his magic wand, the Caduceus Shrewdest and most cunning of all gods Made the lyre out of tortoise shell God of Commerce and the Market, protector of traders Guide of the dead, the Divine Herald who led the souls down to their last home Messenger of gods Hermes Mercury revolves around the sun so fast, it was named for the messenger god. One year is faster than one day on Mercury Ares (Mars) God of War Son of Zeus and Hera Supposedly both detested their son His bird was the vulture Dog wronged by being chosen as his animal Ares Hephaestus (Vulcan) God of Fire Considered unattractive Also lame because he was thrown off Mt. Olympus for interfering with a fight between Hera and Zeus Kindly peace-loving god popular on earth and heaven Protector of the blacksmiths—patron of handicrafts Wife is Aphrodite Some poets said Vulcan's forge was under volcanoes and caused smoke and fire to come from them during an eruption. Hephaestus Hestia (Vesta) Zeus’ sister Virgin goddess Goddess of the hearth, symbol of home, around which newborn children must be carried before they could be received into the family. Every meal began and ended with a prayer to her Each city had a public hearth to Hestia where the fire was never allowed to go out. Hestia