* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT - ICGEB
Process management (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Windows NT startup process wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Linux kernel wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Caldera OpenLinux wikipedia , lookup
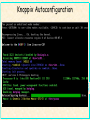
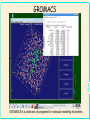
Linux OverView NCBI Chuong Huynh NIH/NLM/NCBI New Delhi, India Sept 28, 2004 [email protected] What is UNIX? •A family of operating systems •Multitasking IRIX •Multiuser Runs more than one program at SOLARIS the same time. •Networked Many different people can use BSD NCBI thebusy A system system at the cansame be running time. LINUX It is designed to be several hundred or linked even to other computers and to at allow thousands of programs the Digital UNIX people to work over a network. same time. HP-UX The network IS the computer. ... Linux History NCBI • Linux was written by Linus Torvalds while he was a grad student at the University of Helsinki. • He received a new 386, and he found the existing DOS and UNIX too expensive and inadequate. • In those days, a UNIX-like tiny, free OS called Minix was extensively used for academic purposes. Since its source code was available, Linus decided to take Minix as a model. Unix/Linux Basic Architecture SHELL Utility Kernel Hardware NCBI • Unix is a layered operating system • Unix is a multi-user, multi-tasking operating system Linux kernel NCBI • Linux is the kernel or core of a free computer operating system that runs on many different Central Processing Units (CPUs). • It is constantly being updated and improved; and new versions can appear daily, several times a day, or every other day. . Linux Distribution NCBI • Linux, combined with thousands of other free software packages—especially those from the Free Software Foundation and The XFree86 Project, Inc.—becomes a Linux distribution. • There are hundreds of different Linux distributions (distrowatch.com), but the most popular are Red Hat (Fedora); SuSE from SuSE, Inc.; Debian (named after Ian Murdock and his girlfriend, Deb) from The Debian Project; Slackware from the Slackware Linux Project; and Mandrake from MandrakeSoft. Linux and Open Source NCBI • Linux and most of its accompanying software is free and distributed with source code. • The source code is distributed under a unique "copyleft" license named the GNU General Public License (GPL), which ensures that the software will forever be free and available in source form. • There are many different software licenses used for software included with a Linux distribution • And some Linux distributions include proprietary software as value-added purchase incentives. Linux Support NCBI • If you want support for Linux, you can pay for such support, hire a consultant, or learn more about Linux on your own. • There is plenty of information about Linux available on the Internet. • You can purchase various support options from vendors such as Red Hat, Inc. • One of the best and cheapest ways to get help is to join a Linux Users Group, or LUG. • Or search the search engines, especially in the newsgroup, someone is bound to have already asked the same question. • Every experienced Linux user starts out as a beginner, but with the help of newly found friends and practice, a new Linux user (known as a newbie) can learn a lot faster. Installing Linux? NCBI • Linux may be installed from optical media; by floppy disk; via a local network or over the Internet using FTP, HTTP, or NFS; from a hard drive partition; via a parallel-port cable or null-modem cable and serial interface; from a USB Zip drive; or by other methods. • You don't even have to install Linux in order to run Linux because it does not require a hard drive in order to run, and you can run Linux on your PC without installing by using a "live filesystem" CD-ROM, such as one in distribution from KNOPPIX or SuSE's evaluation CD. • You can download, burn, and boot from such a CD directly to a Linux session with a graphical desktop. Linux and Internet Connection NCBI • Linux can be used to connect with many different Internet Service Providers (ISPs). • Most Linux dial-up (modem) users connect to an ISP by using the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), which is readily supported. Linux cable modem users can usually connect by using the Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP). Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) users connect by using PPP-over-Ethernet (PPPoE) because Linux supports PPP, DHCP, and PPPoE. • Millions of Linux user to connect to the Internet every day, and browse the Web, download and upload files, and send and receive electronic mail—along with many other types of common Internet-related activities. Linux at the Enterprise Level NCBI • Linux is used by enterprise-level companies, such as those in the Fortune 500, many governments on various levels, academia, small businesses, Small Office Home Office (SOHO) users, and millions of users around the world. • Linux is destined to host more than half of the server computers connected to the Internet, but gauging exactly how many Linux users exist can be hard because Linux is free. Where do I find more information about Linux? NCBI http://www.linux.org A definitive Linux portal for all kinds of information http://www.tldp.org The Linux documentation project http://www.unix-vs-nt.org/kirch/ An impartial comparison of UNIX / NT http://www.tir.com/~sorceror/mdlug/mdlug.zip A HTML slideshow onLinux http://www.oreilly.com/catalog/opensources/book/toc.html Open-source essays http://www.cuug.ab.ca/~leblancj/nt_to_unix.html It’s good to migrate to Linux http://www.linuxmall.com/resources/nlm Newbies Linux manual http://www.cs.helsinki.fi/~torvalds/ Linus Torvalds’ home page http://www.ssc.com/lj/index.html Linux Journal is a nice Linux periodical http://www.gnu.org/ Official GNU web-site news://comp.os.linux The Linux USENET newsgroup • • • • • • • • Networked with other computers Multiple asynchronous task Unique profile for each user’s environment Protecting info stored from another user on the same system WWW uses Unix prevalently; most web servers run under Unix. Unix used extensively in universities where software was originally developed for bioinformatics began Until the mid 1990’s the only workstation capable for bioinformatics of visualizing protein structure data in real time were SGI and Sun Unix Workstation Command line richness with a graphical user interface – provides options and possibilities Many pre-built software prepackaged with various Linux distribution from word processing to web servers. NCBI • Why use Unix for bioinformatics? Then why use Linux? NCBI • Free Unix clone for personal computers with full multitasking, X Window system, TCP/IP networking, etc. • Cost effective • Runs all of the bioinformatics programs effectively • Samba software suite – Linux acts as a Windows file/print server • Linux is a free Unix clone Fedora Core 2 Linux NCBI Why use Cygwin? NCBI • Provides a Unix like environment on top of Microsoft Windows operating system. Cygwin is not an operating system, but an Application Programming Interface on top of an existing operating system. • Ease the transition of learning Unix/Linux for those familiar with Microsoft Windows Cygwin CD Installation Exercise NCBI • Install cygwin CD on your MS Windows machine • Ask the instructor or the Teaching Assistant to login as an administrator to allow you to have administrative privilege to install cygwin • All the documentation required is in the index.html in the cygwin CD • There are many packages which one? • KDE for cygwin? Why Use Live Linux CD distro? NCBI • Non-destructive method to demo Linux for any Intel/AMD based PC • Linux operating systems residing on the CD • Boots and autoconfigures itself without user interaction • The CD is the primary boot device and needs a lot of RAM. Anything save in memory is temporary. Generally more memory = better. • Save to hard drive • Autoconfiguration process identifies hardware and selects the best configuration for the hardware it finds. What is Knoppix? NCBI • Knoppix is an example of a Live Linux CD distribution • Knoppix is created by Klaus Knopper • Excellent hardware detection and autoconfiguration abilities • The packages and OS structure are based on the Debian distribution, but the hardware-discovery process uses kudzu, Redhat's hardware probing utility Knoppix Hardware Requirements? NCBI • Knoppix has fairly standard hardware requirements. • It needs an Intel-compatible CPU (i486 or later) and 20MB of RAM for text mode, with at least 96MB for graphics mode with KDE. • 128MB of RAM is recommended when using applications as resource-hungry as OpenOffice.org. • It requires a bootable CD-ROM drive, or a boot floppy and standard drive CD-ROM (IDE/ATAPI or SCSI). • Finally, it also requires a standard SVGAcompatible graphics card and a serial, PS/2 standard, or IMPS/2-compatible USB mouse. How Knoppix Works? Put Knoppix CD in a bootable CD-ROM Reboot computer Wait Done NCBI • • • • Knoppix Booting NCBI Knoppix Autoconfiguration NCBI How Knoppix Works (1)? NCBI • The boot process resembles a standard CD distribution, but uses virtual drives in RAM. • It can boot into either text or graphics mode (KDE Graphical User Interface desktop environment), requiring more memory in graphics mode. • The OS file system is a single, compressed, read-only file that uncompresses applications and utilities as required. This allows 2GB of binaries to be stored on a 700 MB CD. • The rest of the CD contains documentation and the boot kernel. • Boot time can be anywhere from 30 seconds to two minutes, depending on your hardware. How Knoppix Works (2)? NCBI • The CD's bootloader offers you the opportunity to add kernel commands. These "cheat codes" control everything from device discovery to desktops and local language selection. • You can view the options yourself by pressing F2 at boot-up time. • The default booting process chooses a KDE GUI desktop environment. • As the boot process continues, it creates the RAM disk, which is followed by the "hotplug" autoconfiguration process. • Shell scripts automatically put in the correct settings for the services once the hardware has been identified. • DHCP support is enabled. So why use Knoppix Live Linux CD for the course? NCBI • The focus of the course is on data interpretation. Ideally, you would want your own bioinformatics workstation with the operating system installed to the hard drive (much faster and larger). • And when you return home, you can easily demo the same programs you learned here for review Vigyaan biochemical software workbench • One example of a Knoppix based “bioinformatics” distribution – Vigyaan CD or BioKnoppix NCBI Pymol on vigyaancd NCBI PyMOL is a biomolecular structure visualizer with high-quality image output. GROMACS NCBI GROMACS is a collection of programs for molecular modeling of proteins.