* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Computers: Tools for an Information Age
Berkeley Software Distribution wikipedia , lookup
Windows Phone 8.1 wikipedia , lookup
Library (computing) wikipedia , lookup
Plan 9 from Bell Labs wikipedia , lookup
Burroughs MCP wikipedia , lookup
Windows NT startup process wikipedia , lookup
Distributed operating system wikipedia , lookup
Copland (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Mobile operating system wikipedia , lookup
Spring (operating system) wikipedia , lookup
Windows NT 3.1 wikipedia , lookup
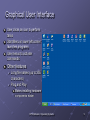
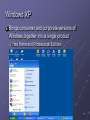
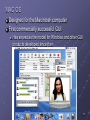
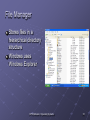
Module 9: Operating Systems Objective What is an operating system (OS)? OS kernel, and basic functions OS Examples: MS-DOS, MS Windows, Mac OS Unix/Linux Features of modern OS Graphical operating system Multiple users, secure, stable Support networks The main issues that an OS deals with Resource allocation, CPU time, memory management Multiprocessing, time-sharing, multiprogramming Utility programs Copyright © 2003 by Prentice Hall 1 Systems Software and Application Software Software are classified into categories according to their functions: system software, application software System software are programs related to coordinating computer operations, E.g. Operating systems Language translators Convert program code to machine-readable form Utility programs are those application programs performing secondary chores CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 2 What is an Operating System ? A set of programs that lies between applications software and the hardware Manages computer’s resources (CPU, memory, peripheral devices) Establishes a user interface Determines how user interacts with operating system Provides and executes services for application software CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 3 Kernel The core of an OS is called kernel, which Is loaded from hard drive into memory when computer is booted and stays as long as the computer is running Booting refers to starting the computer Manages the operating system Loads other operating system programs from disk storage as needed Other programs referred to as nonresident CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 4 Examples of Operating Systems Platform: combination of computer hardware and operating system software Common Platforms PC with MS DOS (disk operating system), Windows MAC OS PC and Unix/Linux CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 5 MS-DOS Uses a command-line interface Screen provides prompts for user. User types commands. Five basic commands: dir, mkdir, cd, copy, del. Largely replaced by graphical user interfaces Not user-friendly It is still there ( demo ) CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 6 Microsoft Windows Began as an operating environment for MS-DOS Not a full-blown operating system; required MSDOS Uses a graphical user interface Users can use DOS commands and interface Now a complete family of operating systems CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 7 Brief history of Windows OS Microsoft Windows 1.0, 1985 Microsoft Windows 2.0, 1987 Microsoft Windows 3.0, 1990 Windows 3.1, 1992 Windows 95, 1995 sells more than 1 Million copies within 4 days. Windows 98 Microsoft Windows 2000 Microsoft Windows XP, 2001 Other MS Windows OS product lines Windows NT, Windows Servers, Windows CE CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 8 Graphical User Interface User clicks an icon to perform tasks Start Menu in lower left corner launches programs Use menus to activate commands Other features Long file names (up to 255 characters) Plug and Play Makes installing hardware components easier CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 9 Windows NT Windows 98 and early is for single user Windows NT was designed for corporate networked environments Be able to handle many users Engineered for scalability Stronger security CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 10 Windows 2000 The generation of Windows NT One computer “serves” many users You identify yourself and the system knows your preferences You get “your” desktop and files, regardless of which PC you use to log into the network CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 11 Windows XP Brings consumer and corporate versions of Windows together into a single product Has Home and Professional Editions CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 12 Windows XP Enhancements Improved user interface Much clearer and uncluttered desktop More icons on redesigned Start Menu Improved multimedia support More personalization Multiple user support User can log off, leaving programs running, and allow another user to log on Set up limited accounts for children to use; i.e., no inappropriate games or no Internet access Internet support and protection CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 13 Windows CE Scaled-back version of Windows 9x Designed to work on machines with small screens and little, if any, storage Used in Pocket PCs Used in mobile phone Used in embedded systems Computer devices integrated into other products; i.e., robots CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 14 MAC OS Designed for the Macintosh computer First commercially successful GUI Has served as the model for Windows and other GUI products developed since then CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 15 UNIX Developed in 1971 for use on the DEC minicomputer Not tied to any family of processors Runs on just about every type of system Run on most main frame, supercomputers, Sun workstations, PC Primary operating system in use on Internet servers E.g. main web server of WLU is running Unix Features Very reliable, secure, stable system. Character-based system with command-line interface, now comes with several graphic user interface Handles many simultaneous users easily Multiple tasks CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 16 Linux Similar to Unix, but in open source domain Uses command-line interface Many companies have created a GUI to work with Linux Open-source concept Source code is free Users can download, change, and distribute the software More stable than Windows Applications relatively scarce CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 17 Simple Unix/Linux Commands ls, ls –l, ls -a mkdir cd, cd .. pwd mv cp rm rmdir cat, less, tail grep who chmod Network commands: telnet, ftp, ssh CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 18 Operating Systems for Networks Network operating system (NOS) Handles network functions Make resources appear as though they were running from client computers Common systems Functions Sharing resources (hard disks and printers) Data security Administrative control CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 19 Examples of Network Operating Systems Windows NT Server Windows 2000 Server Novell Netware Unix Linux CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 20 The Main Task of an Operating Systems Resource allocation: assigning and computer resources to certain programs and processes for their use This problem was raised when people designed the OS for large computers with multiple users. It is also a fundamental problem for modern OS for PC. Main issues related to resource allocation Sharing the Central Processing Unit Sharing memory Sharing storage resources Sharing printing resources CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 21 Sharing the CPU Multiprogramming Two or more programs executed concurrently Programs take turns using the CPU Event-driven An interrupt suspends processing to allow another program to run After the second program runs, the operating system returns the CPU to another program Time-Sharing Programs take turns using the CPU Time-driven Each user is given a slice of time (fraction of a second) CPU works only on that user’s tasks during its time slice Response time: the time between typed request and computer’s reply Typically used in applications with many users CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 22 Multiprocessing The use of a powerful computer with multiple CPUs Supper computers usually have many processors Personal computers will soon have multiple processors Multiple programs run simultaneously Each runs on its own processor CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 23 Sharing Memory Memory management Divides memory into separate partitions Allocates memory to programs Keeps programs separate from one another Sharing memory Divides memory into foreground and background Uses virtual storage Also called virtual memory CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 24 Foreground and Background Foreground: for programs with high priority that will receive more CPU time Background: for programs with lower priority that will receive less CPU time Programs waiting to run are kept in queues based on their priority CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 25 Virtual Storage Programs currently executed are stored on disk Portions of program brought into memory as needed Minimizes the amount of memory needed Can be implemented by paging Divide memory into small, fixed-size pages Page table keeps track of memory locations CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 26 Sharing Storage Resources Keeps track of location of files Responds to commands to manipulate files Keeps track of input and output requests for files Processes them in the order received CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 27 Sharing Printing Resources Spooling: program writes a line to a disk file rather than sending directly to a printer When file is completed, placed in queue File printed when printer becomes available Allows program to complete execution much more quickly Writing to disk much quicker than writing to printer CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 28 Utility Programs Perform secondary chores Examples File manager File compression Others CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 29 File Manager Stores files in a hierarchical directory structure Windows uses Windows Explorer CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 30 File Compression Reduces amount of space a file requires Makes file take up less space on disk Takes less time to transmit across communication lines CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 31 Other Utility Programs Backup and Restore Backup: make copies of disks and store in a safe place Restore: restore files from backups Disk defragmenter: reorganizes disk so all files are stored in contiguous locations Device driver: handles commands for devices, such as printers and storage devices CP102 Module 9: Operating Systems 32