* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint Notes on The Middle Ages
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 13th century wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
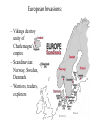
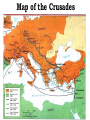
The Middle Ages (476-1300) What is so different about Europe? Do Now: Review ~ Post-476 1. What happened to Western Europe after the “fall of Rome?” 2. What happened to the eastern portion of the Roman Empire? 3. What was going on in the Middle East shortly after Rome fell? Post–“Fall of Rome” (476 A.D.) 1. W. Europe is isolated; “Dark Ages” begin – Germanic invasions: divided into small Christian kingdoms (400-700) – No centralized government 2. Byzantine Empire: – Eastern Orthodox Christianity – Age of Justinian; Golden Age 3. Islam emerges (Arabia, 7th C) – New religion & empire; Golden Age – Armies in Africa, Europe & Asia Task: • You are living in Western Europe after 476 A.D., how would you find protection? • How would you find safety/order when no government exists? Create a list of ideas. 1. Why did the man visit the Godfather? 2. What was the result of their visit? In order to attain order in Europe post-fall of Rome (476) FEUDALISM developed. A political/social system where land is exchanged for loyalty. “And we will provide you with support and soldiers” “I will give you land (manor) to rule and govern” Feudalism: L O Y L LORDS/ Nobles N A D L T Y A SERFS Do Now: 1. Explain this system? 2. Why was this system created? Task: • You are living in Western Europe after 476 A.D., what would you look for in a ruler? (characteristics, traits, qualities, beliefs) – What advice would you give him/her about the state [condition] of Western & Eastern Europe? – What changes would you want him/her to pursue? Why? Why was feudalism brought to Western Europe? • Need for security and stability! • No centralized government (post-fall of Rome!) • European Invasions! What ideal is the cartoon portraying? CHIVALRY! Why did the Church have so much power? 1. Controls Spiritual life – Decides who gets sacraments (controls salvation) – Refusal to obey Church law punished by excommunication • Banned from the Church – Cannot obtain sacracments, cannot obtain salvation – Penalty of interdict: faced by nobles; exclusion of an entire town from receiving sacraments! -Leaders give into Church pressure! 2. Controls Secular life – Pope (head of RCC) has power over secular rulers • Added order & stability to Europe – Tithe: tax (1/10th of income); required ALL Christians to pay – Religion linked to social life; church becomes social center • Cathedral schools, lead to universities Evidence of ____________Power: Medieval ________________ Romanesque (early ma) Gothic (late ma) St. Filibert, France 10th Century German Cathedral (8th – 11th) Romanesque Floor Plan CATHEDRAL AT REIMS GOTHIC CATHEDRALS 5th C – 12th C “Flying Buttress” St. Etienne, Bourges, 12th Century “FLYING BUTTRESSES” Do Now: Why was the Church so powerful during the MA? Roman Catholic Church & Persecution ANTISEMITISM: Prejudice against Jews • How were the Jews persecuted? • Why were they persecuted? Reflection: 1. How and Why were the Jews persecuted? 2. What is your reaction to this persecution? Explain. The Age of Charlemagne (768-814) “Charles the Great” • Western Europe enjoys period of Christian unity • Successful conqueror • Pope proclaims Charlemagne ‘emperor’ (800) – Widens the divide between Eastern & Western Europe European Invasions: – Vikings destroy unity of Charlemagne’s empire – Scandinavian: Norway, Sweden, Denmark – Warriors, traders, explorers Do Now: 1. Western Europe 2. Middle East 3. Eastern Europe During the early Middle Ages, what do you think relationships were like between these THREE parts of the world? How do you know? Do Now: How can government convince people to join the army? Task: • Your task is to create a propaganda poster that aims to recruit soldiers to join the Crusades. – Ideas MUST pertain to Pope Urban’s speech – Your poster MUST be set in the Middle Ages • The information must focus on the values of Medieval Europe. • Your grade is based on the following: 1. Effectiveness/Allure – 3 points a. Includes HEADLINE & IMAGE 2. Accuracy – 2 points (of historical information) THE CRUSADES a series of wars fought between the Christian and Muslim world for the “holy land” “Deus lo volt!” – God wills it! The First Crusade • Council of Clermont (1095) – Pope Urban II calls for a crusade to free “Holy Land” from Turk invaders. • Christians capture Jerusalem (1099) • Massacre Muslim/Jewish residents. • More crusades launched • Muslims are victorious Do Now: Questions: 1. What was the goal of the Crusades? 2. Who was Pope Urban? 3. Why would people want to fight in the Crusades? 4. Who fought in the Crusades? Do Now: Questions: 1. Who won the Crusades? Why? 2. How was Europe affected by the Crusades? Saladin • Muslim leader • Conquers Jerusalem in 1187 • By 1291, Muslims conquer last Christian territory (entire Holy Land) • Massacre Christians Map of the Crusades “The Greatest Failure in History” Impact of the Crusades 1. Cultural Diffusion: Euro contact Eastern cultures - Muslim/Byzantine goods & ideas 2. Revival of learning – Greek/Roman (Byzantines) & Muslim advances 3. Increased demand led to increased trade New markets New wealth Rise of a middle class (bourgeoisie) Growth of new cities High Middle Ages: The Black Death 1. Who: (was affected) 2. What: (happened) 3. Where: (did this happen) 4. When: (did this happen) 5. Why: (did this happen) 6. How: (did this happen) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The High Middle Ages: How did life change? (use Guided Reading to help) Agricultural production/Population increase Rise of trade - wealth, new goods Rise of cities Rise of a business economy Rise of a middle class - Decline of feudalism - Power of Kings increase (centralize) Rise of Guilds The High Middle Ages: How did life change? 7. Criticisms against the church a. Wealth • Leads to future problems b. Worldly: devotion to family over Church duties • SOLUTION: marriage outlawed for priests c. Simony & Corruption: selling of Church positions – SOLUTIONS: outlawed simony; Church ONLY chooses Church officials (not kings/nobles) Church v. State France, 13/14th Century • Sequence of Events: – Philip IV: taxes French clergy – Pope Boniface IV: forbids Philip to tax without papal consent • Punishment: excommunication – Philip IV: threatens to arrest clergy that refuses to pay; sends troops to seize Boniface • French elect Pope • Papacy moved to France (from Rome) – – Babylonian Captivity – lasts for 70 years) • (14th century) Rome responds by electing their own pope! Two popes? Why did Philip move the papacy? How did this decision affect the pope’s power? “It was the best of times, it was the worst of times” Homework: Create a list of reasons explaining why the period of the Middle Ages may be considered the “best” and “worst” of times! (2 lists total!) “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: School Teacher Student pencil smartboard notes suspension laughing cutting study “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: Early Middle Ages “Dark Ages” Manorialism Feudalism Charlemagne Roman Catholic Church Chivalry Fief tithe “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: Early Middle Ages 476 Vikings invasions Gothic Byzantine Empire excommunication salvation Battle of Tours Islamic Empire “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: Early Middle Ages Loyalty serfs interdict Inquisition Roman Catholic Church Chivalry Anti-Semitism tithe Eastern Orthodox “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: Crusades Jerusalem Pope Urban Turks Muslims Saladin “Greatest Failure” Trade Cities Cultural Diffusion “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: High (Late) Middle Ages Middle Class opportunity Babylonian Captivity Centralized Government simony Bubonic Plague Education commerce worldly “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: Anything Middle Ages Loyalty serfs interdict Inquisition Chivalry manorialism Anti-Semitism Black Death Eastern Orthodox “Talk A Mile a Minute” Topic: Anything Middle Ages knight manor Roman Catholic usury Chivalry Crusades Anti-Semitism Babylonian Captivity heresy