* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download High Middle Ages
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
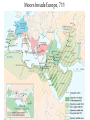
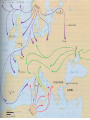
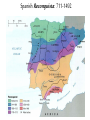
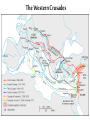
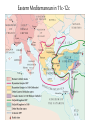
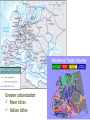
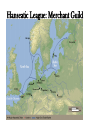
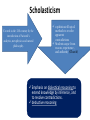
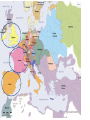
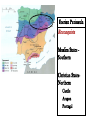
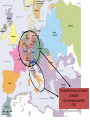
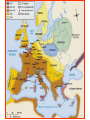
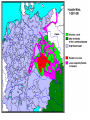
Post Classical Age: 1200-1450 Reorganization of the Post Classical World Continuity and Change European Interests turned outward Organization, Consolidation and Migration of Eurasian Steppe people Reading Quiz 1. Identify two regions taken by the Mongol conquests of the 13th C. 2. Identify one factor that contributed to the decline of Pax Mongolica? 3. How did the development of commerce and money challenge the feudal system of exchange? 4. Why is the formation of Parliaments and the Magna Carta important in understanding the development of the West? 5. What changes were taking place specifically in Italy in the late Middle Age and why? Western Europe High Middle Ages Moors Invade Europe, 711 Feudal Europe, c. 1200 Spanish Reconquista: 711-1492 Seljuk Turks (Seljuk Sultanate) • Migrated into Near East 10th Century • Established role of Sultan as protector of Abbasid Caliph • Origins of Ottoman Turks Pope Urban II Calls the 1st Crusade: 1095 The Western Crusades Eastern Mediterranean in 11c-12c Impact of the Crusades History’s most successful failure… Trade Increased Demand for goods- economic growth Development of business opportunities Agricultural & commercial revolution Increased contact Exposure to goods & ideas Reawakening of Classical Age Scientific Knowledge - Universities Changing Social & Political Structure Breakdown of Feudalism – rise of middle class Political Consolidation – challenge to the church Economy of the Medieval World • After 1000… Agricultural Revolution: iron plows, horse collar and horse shoes, cleared lands, crop rotation, new crops, warmer climate Population Increases… Increased production & Specialization New Business Practices Partnerships, Credit, Banking trade & commercial opportunities new urban areas Mediterranean trade North & Baltic sea trade (Hanseatic League) Greater urbanization River cities Italian cities Hanseatic League: Merchant Guild New Goods, New Ideas Or in many cases… old ideas? How was this new information received by the educated? Medieval Universities Major Contributors St Thomas Aquinas Albertus Magnus William of Ockham Scholasticism Created in the 13th century by the introduction of Aristotle's analytics, metaphysics and natural philosophy. sophisticated logical methods to resolve apparent contradictions Students argue from reason, experience, and authority (Church) Emphasis on dialectical reasoning to extend knowledge by inference, and to resolve contradictions. deductive reasoning Medieval Masterpieces In the vernacular The Divine Comedy, 1321 Dante Alighieri The Canterbury Tales end of 14th c , Geoffrey Chaucer Architecture, Literature & Art Gothic Cathedrals Notre Dame Chartres Reims Cologne Santa Maria del Fiore Forerunners of the Renaissance Emergence of the… “The Artist” Giotto Artistic Development High Middle Age Creation of Modern political Europe Centralization of power New Monarchies Political Developments England France Norman Dukes (descendants 987- death of last Carolingian of Charlemagne) Hugh Capet Elected Battle of Hastings 1066 invasion William the Conqueror Domesday Book 1215: Magna Carta Parliament Lord with possessions around Paris Capetian Kings Early 1300s centralized French Territories Hundred Years War: increased power for both monarchies 100 Years War Succession crisis over French Throne Valois (French) - cousin Plantagenet (English)- nephew Intermittent fighting in France Long bow Use of Canon- gunpowder Joan of Arc Outcome Further Centralization of power – England & France (Tudors AND Valois) Iberian Peninsula Reconquista Muslim States Southern Christian StatesNorthern Castile Aragon Portugal FRAGMENTATION CONTINUES GERMANY (HOLY ROMAN EMPIRE) ITALY Political Developments Holy Roman Empire 962 German Princes ELECT Otto of Saxony Holy Roman Emperor Expansion & centralization prevented by Papal influence Investiture Controversy papal/monarch conflict Italy BALANCE OF POWER City States Venice, Florence, Milan, Naples Papal Influence Mediterranean Trade Prosperity -More Urban Middle Ages (600-1450) Germanic Invasions & Kingdoms 476: Fall of Rome 9th Century Invasions, Feudalism 800: Charlemagne crowned Holy Roman Emperor High Middle Ages 1095: Pope Urban II launches 1st Crusade CHANGES… Growth of Nation-States and Monarchies Breakdown of political Feudal System Growing Economic complexity Changing Social Structure Cultural Development Intellectual Curiosity Characteristics of the High Middle Age Increased economic opportunities (commercial revolution), New Monarchs and the development of nation-states supported breakdown of feudal social structure by … • Granting charters and encouraging a merchant class (mercantilism) • Staffing government-paid bureaucratic jobs with new middle class to undercut power of nobles • Providing protections and opportunities for peasants no longer tied to land (end of serfdom) What roadblocks will Western Europe experience in their quest towards recovery? What Impact will these changes have on the power and prestige of the Church? Black Death Environmental Conditions – the Great Famine Catholic Church in the High Middle Ages Environmental Factors Little Ice Age & The Great Famine The Black Death- Bubonic Plague Hunters in the Snow by Pieter Breughel. Hans Holbein: Dance of Death The Plague: Black Death 1/3rd of European Population decimated Outbreaks: 1348, 1361, 1368, 1371, 1375, 1390, 1405 ---18th Century The victims ate lunch with their friends and dinner with their ancestors Boccaccio The Decameron Economic and Social challenges: Cities worst-off, villages abandoned rise in Anti-Semitism social unrest - rebellion • Continued agricultural revolution: forced diversification of agriculture & development of new technologies • Continued trade with greater demand for luxury goods Positive Consequences? • Fewer laborers, more land: Lessening power of numerous noble aristocrats • Greater need for centralized power/Monarch and services • Religious Fanaticism (mystics, flagellants)- failure of Church Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse Albrecht Durer 1378 to 1417: The Great Western Schism Papal Complex at Avignon Gallican Church Late Medieval Church • Corruption – Worldliness, – simony, pluralism – sale of indulgences • Calls for reform – John Wycliff (Lollards) – Jan Huss (Hussites) – Conciliarism How does the development of the Western European Nation-state compare to the prosperous empires of the West African Sudanic Empires? By 1450, Western Europe was set search out new opportunities to grow and expand… Monarchs directing purposeful growth of its nation-states(mercantilism) Economic prosperity (agriculture, manufacturing, trade) New Middle Class with excess capital for investment Rise of the West