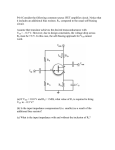
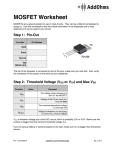
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MOSFET
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
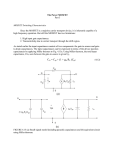
Lecture – 19 Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 1 MOSFET • Construction & operation of Depletion type MOSFET •Plotting transfer characteristic curve Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 2 MOSFETs Basics • MOSFETs (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors) have been used in power electronics applications since thee early 80's due to their appreciable current carrying and offstate voltage blocking capability with low onstate voltage drop. • They have managed to replace BJTs in many applications due to their simpler gate drive requirements and higher positive temperature coefficient which allows devices to be paralleled for higher current capabilities. Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 3 MOSFET Types •N-channel enhancement type MOSFETS are the most popular for use in power switching circuits and applications. Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 4 Depletion Type MOSFET • Depletion type MOSFET has characteristic similar to those of a JFET between cut off and saturation at IDSS but then has the added feature of characteristics that extend into the region opposite polarity for VGS. • It is also known as IGFET (Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor). Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 5 Basic Construction: n-channel depletion type MOSFET • A slab of p-type material is formed from Si base and is referred to as Substrate. • Source (S) and Drain (D) terminals are connected through metallic contacts to n-doped region linked by nchannel. • The gate is also connected to a metal contact surface but remains insulated from n-channel by a very thin SiO2 layer. • SiO2 is a particular type of insulator referred to as a dielectric that sets up opposing electric fields within dielectric when exposed to an externally applied field. • It is the insulating layer of SiO2 in the MOSFET construction that for the very desirable high input impedance of the device. Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 6 Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 7 Basic Operation and Characteristics When VGS=0V • VGS=0V is done by direct connection from one terminal to other and VDS is applied across the drain-to-source terminal. • The result is an attraction of the positive potential at the drain by the free electrons of n-channel and a current ID=IS=IDSS will flow. Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 8 When VGS is negative: n-channel • When VGS is negative, the SiO2 negative potential at the gate will layer tend to pressure electrons toward p-type substrate (like charges repel) and attracts holes from ptype substrate (opposite charges attract) . G• Depending on magnitude of –ve bias established by VGS, a level of recombination between electrons and holes will occur that will Metal reduce the number of free Contact electrons in the n-channel available for conduction. The resulting level of drain current is therefore reduced with increasing negative bias for VGS. Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 e + e + e + e + e + e p-material substrate + e + e + e + 9 Transfer Characteristic curve for n-channel depletion type MOSFET ID mA ID mA VGS = +1V VGS Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 10 When VGS = +ve • For positive values of VGS, the positive gate will draw addition electrons (free carriers) from ptype substrate due to reverse leakage current and establish new carriers through the collisions resulting between accelerating particles. • As VGS continues to increase in the positive direction, ID will also increase at a rapid rate. • Due to the rapid rate, the user must be aware of maximum drain current rating since it could be exceeded with a positive gate voltage. Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 11 • The application of the +ve VGS has “enhanced” the level of free electrons in the channel compared to that encountered with VGS=0V. • For this reason, the region of +ve gate voltages on drain or transfer characteristic is called enhancement region, with the region between cut-off and saturation level of IDSS referred to as the depletion region. • Shockley’s equation is applicable for depletion type MOSFET. I D I DSS (1 Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 VGS VP ) 2 12 Example: Sketch the transfer characteristics for an nchannel depletion type MOSFET with IDSS=mA and VP=-V Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 13 P-channel depletion type MOSFET • The construction of p-channel depletion type MOSFET is exactly the reverse of that of n-channel. • It has n-channel substrate and p-type channel. • The terminals remains the same, but all the voltage polarities and the current directions are reversed. • Drain characteristic would exactly the same pattern but with VDS having –ve , ID having +ve and VGS having opposite polarities. Farzana R. Zaki CSE 177/ EEE 177 14