* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TTL Logic Family
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of the transistor wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
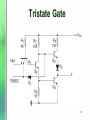
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
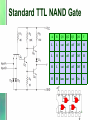
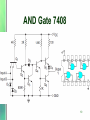
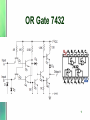
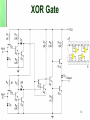
TTL Logic Family 1 Introduction • Uses bipolar technology including NPN transistors, diodes and resistors. • The NAND gate is the basic building block • Contains different subfamilies with varying characteristics such as speed and power consumption 2 Standard TTL NAND Gate A B Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Y L L sat off off Off H L H sat off off Off H H L sat off off Off H H H iam sat sat On L 3 NAND Output Current Sinking & Sourcing 4 Sinking Sourcing What is a totem pole? In art and history…. Totem poles are carved and painted vertical logs, constructed by many northwest coast native American Indian people. The poles display mythological images, animal spirits whose significance is their association with the lineage. 5 Totem pole in TTL ? • What is totem pole? – addition of an active pull up circuit in the output of a gate is called totem pole. Using Q3 and Q4 to achieve this purpose • Why totem pole? – To increase the switching speed of the gate which is limited due to the parasitic capacitance at the output. 6 7 NOT Gate 7404 8 NOR Gate 7402 9 AND Gate 7408 10 OR Gate 7432 11 XOR Gate 12 Open Collector Output 13 Tristate Gate 14 Low Power TTL (74L) Same as standard TTL Except that the value of the resistance is increased to lower power dissipation. However, this is at the expense of reduced speed. 15 High Speed High Power TTL (74H) Reduced Resistors increase power dissipation. Removed output diode and added a Darlington pair transistor to reduce output resistance 16 Shottky Diode 17 Standard TTL Transistor Switching Problem • Trs are driven into deep saturation to fully conduct, or cutoff to switch off. • The result of deep saturation is that the two junctions are now forward biased. • The forward biasing of the BC junction forces a large number of minority carriers to the collector region. • When the Tr switches off, these minority carriers needs to be removed. This takes a finite amount of time called the storage time (major component of the propagation delay) and thus increases the switch off time. 18 Solution 1 • Prevent the Tr from going deep in saturation. This accomplished by preventing the BC junction from becoming forward biased. • The Shottky diode is used to do the above by placing it across the BC junction. Because of its lower barrier potential, it will conduct current from the base directly to the collector before the BC is forward biased. Thus less carriers are stored in the collector area and the switching becomes much faster. 19 SOLUTION 2 Normal Transistor in saturation Transistor with Shottky diode in saturation 20 Schottky TTL (74S) 21 Low Power Shottky 74LS 22 23 Advanced Low Power Shottky 74ALS • All saturating transistors are clamped by using Schottky diodes. • Inputs and outputs are clamped by Schottky diodes • New manufacturing and materials reduce stray capacitance to increase speed. • active turn-off of the LOW-level output transistor, producing a better HIGH-level output voltage and thus a higher HIGH24 level noise immunity. 74ALS00 25