* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congruent angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
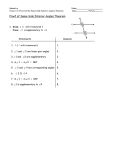
LESSON 3-2: PROPERTIES OF PARALLEL LINES When a transversal intersects parallel lines, special congruent and supplementary angle pairs are formed. Refer to the diagram below for the following postulates and theorems. l || m Congruent angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines: • Postulate 3-1: Corresponding Angles Postulate – If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then corresponding angles are congruent. 1 5 2 6 4 7 3 8 • Theorem 3-1: Alternate Interior Angles Theorem – If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then alternate interior angles are congruent. 4 6 3 5 • Theorem 3-3: Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem – If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then alternate exterior angles are congruent. 1 8 2 7 Supplementary angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines: • Theorem 3-2: Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem – If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then same-side interior angles are supplementary. m4 + m5 = 180 m3 + m6 = 180 EXAMPLES/PRACTICE: Identify all the numbered angles congruent to the given angle and identify all the numbered angles supplementary to the given angle. Explain. 1. 2. 3. Prentice Hall Geometry • Teaching Resources (Edited) You can use the special angle pairs formed by parallel lines and a transversal to find missing angle measures. EXAMPLES/PRACTICE: Find the measure of each numbered angle. 4. 5. EXAMPLE: What are the measures of the angles in the figure? (2x + 10) + (3x 5) = 180 Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem 5x + 5 = 180 Combine like terms. 5x = 175 Subtract 5 from each side. x = 35 Divide each side by 5. Find the measure of these angles by substitution. 2x + 10 = 2(35) + 10 = 80 3x 5 = 3(35) 5 = 100 2x 20 = 2(35) 20 = 50 To find m1, use the Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem: 50 + m1 = 180, so m1 = 130 Exercises: 6. Find the value of x. Then find the measure of each labeled angle. 7. 8. Prentice Hall Geometry • Teaching Resources