* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 - Humble ISD
Criticism of the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Imamate (Twelver doctrine) wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
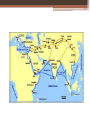
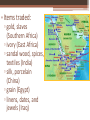
Chapter 6 The Rise of Islam Geography • Lived in the Arabian Peninsula ▫ desert lands lacked rivers and lakes ▫ nomadic ▫ moved constantly to find water and food for their animals The Arabs • Organized tribes • Sheikh: chosen leader of a tribe • Farmers and sheep herders • Lived on rain-fed and oasis areas The Arabs • Most were polytheistic • Traced their ancestors to Abraham and his son Ishmael, who were believed to have built at Makkah (Mecca) the Kaaba, a house of worship • Recognized Allah as the supreme god The Life of Muhammad No representation of Muhammad is in any Islamic art • Married rich widow = Khadija • Was troubled by growing gap between rich and poor • Went to meditate and was believed to have received revelations from God through the angel Gabriel The Life of Muhammad • Believed that Allah had already revealed himself through Moses (Judaism) and Jesus (Christianity) • Final revelations were through Muhammad Cave of Hira, site of 1st revelation The Life of Muhammad • Qur’an - holy book of Islam • Islam - peace through submission to the will of Allah • Contains ethical guidelines and laws to follow • Islam has only one God, Allah, and Muhammad is God’s prophet Oldest manuscript 9 c. – only 1/3 survives The Life of Muhammad • Tried to convince people of Mecca but, was persecuted • He and his 30 followers moved to Medina (“city of the prophet”) ▫ Journey known as Hijrah The Life of Muhammad • Won support from the Bedouins, of Medina • Formed 1st community of practicing Muslims • Muslims saw no separation between political and religious authority The Life of Muhammad • Muhammad becomes political, religious, and military leader • In 630, takes force of 10,000 soldiers to conquer Mecca (place of persecution) Muhammad and his companions advancing on Mecca (angels also shown) The Teachings of Muhammad • Monotheistic • Allah is the allpowerful Creator • Gives salvation and hope of an afterlife • Muhammad was the prophet of Allah The Five Pillars of Islam One God Prayer Alms Fasting • Believing Allah is the only God and Muhammad is his messenger • Pray 5 times a day to Allah • Give alms to the poor and unfortunate • Fast during the month of Ramadan Pilgrimage • Make a pilgrimage to Makkah once in a lifetime (hajj) Sharia: Code of Laws • provides believers with a set of practical laws • applies teachings of the Quran to daily life • does not separate religion from politics • The Hadith warns against imitating God by creating pictures of living things • Muslims can NOT eat pork, drink alcoholic beverages, gamble or engage in dishonest behavior Islamic Civilization & Culture Sections 3 & 4 Prosperity in the Islamic World • Prosperity based on extensive trade by ship and camel ▫ Camel caravans went from Morocco (Northwest Africa) to the Caspian Sea • Items traded: ▫ gold, slaves (Southern Africa) ▫ ivory (East Africa) ▫ sandal wood, spices, textiles (India) ▫ silk, porcelain (China) ▫ grain (Egypt) ▫ linens, dates, and jewels (Iraq) “The Emerald City” • Large, magnificent cities ▫ Baghdad, Cairo, Damascus, Córdoba • Palaces & mosques • Public buildings w/fountains, baths, and marketplaces (bazaars: covered market) Islamic Society • Islam claims that all people are equal in the eyes of Allah • However, in the Arab Empire, there was a well-defined class system ▫ Upper Class: ruling families, wealthy merchants, and elites ▫ Lower Class: Peasants and slaves ▫ Slaves: captives of war from Africa & Asia; most served as soldiers; women slaves were domestic servants Islamic Society • Women Women voting for the 1st time in Iraq (2005) ▫ Quran granted spiritual and social equality w/men ▫ Women could own and inherit land ▫ Still dominated by men Male guardian Secluded at home Kept from social contacts with men outside their families Islamic Society • Parents arranged marriages • Men could have up to four wives • Women had a right to divorce, however, the right was extended only to men • Women cover much of their body (traditional Arab practice) Science • Observatory: scientists studied and named many stars • Astrolabe: helped sailors determine their location by observing the position of the stars • Medicine: Ibn Sina wrote a medical encyclopedia; showed that unsanitary conditions contributed to the spread of contagious diseases Literature • Muslims believed the Qur’an was their greatest work of literature • The Arabian Nights: collection of folktales, fables, and romances ▫ Story of Aladdin, Sinbad the Sailor and Ali Baba and the forty thieves (“Open Sesame”) Ali Baba and the 40 Thieves Art & Architecture • The Great Mosque of Samarra (Iraq) ▫ Minaret: tower from which the crier, muezzin, calls the faithful to prayer 5 times a day ▫ Example 90 feet high Damascus “Forest of Trees” – hundreds of columns Art & Architecture •Arabesques: repeated Arabic letters, plants, abstract figures, and geometric patterns