* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
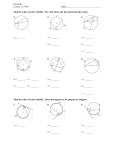
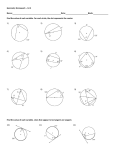
Geometry is the branch of mathematics which deals with the properties and relations of line, angles, surfaces and solids. The word geometry is divided from two Greek words; geo meaning ‘the earth’ and metron meaning ‘to measure’. In ancient times, people needed to measure earth or land so that they could bye or sell it. Just as arithmetic deals with numbers, geometry deals with figures, points and lines. A point is usually represented by a small dot and is named by a single capital letter of he alphabet. A point has a position and we can ascertain its location. However it has no magnitude i.e. it has no length, breadth or thickness. You can not draw an actual point on paper, no matter how sharp a pencil you see. A line is straight and extends indefinitely on both sides. It has no end points and its length can not be measured. Since a line extends indefinitely on both sides you can not show a line on a paper its totally. You can only show a part of it. A plane is a flat surface that extends indefinitely in all directions. Its dimensions can not e measured. Justas we can not draw a a whole line on paper, we cannot a whole plane either. We can only show a portion of it. A table top, or the surface of walls of a room are examples of portions of planes. The figure shows two rays OA and OB starting from the same initial point O. the figure that they form is known angle. The common initial point O is called the vertex of the angle. The two rays OA and OB are called the arms of the angle. An angle is formed by two rays starting from the same initial point. A triangle is a three-sided closed figure, formed by three line segments. These three line segments intersect in pairs. ABC is a triangle formed the line segments AB , BC and CA. AB and BC intersect in B. AC and BC intersect in C and AC and AB intersect in A . The length of the perpendicular from the vertical angle to the base is called the altitude of the triangle. It is a measure of the height of the triangle. The line segments joining the vertices to the mid-points of the opposite sides of a triangle are known as medians. A quadrilateral is a four-sided figure . ‘Quadri’ means four, and ‘lateral’ means many sides. HERE is a quadrilateral ABCD . It is formed from the line segments AB, BC, CD and DA. These line segments meet at their end points. The quadrilateral ABCD has : a) Four vertices A, B, C and D. b) Four sides AB, BC, CD and DA. ADJACENT SIDES : Two sides of a quadrilateral which has a common vertex are called its adjacent sides. OPPOSITE SIDES : Two sides of a quadrilateral which do not has a common vertex, are called its opposite sides. ADJACENT ANGLES : Two angles of a quadrilateral which have a common side are called its adjacent angles. OPPOSITE ANGLES : Two angles of a quadrilateral which do not have a common side are called its opposite angles. A circle is a set of points on a plane which are at the same distance from a fixed point. The fixed point O is called the centre of the circle and the constant distance (OA, OB, OC, OD) is known as the radius of the circle.