* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download crct review - GHTEACHERS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
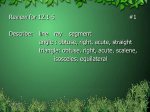
CRCT REVIEW MATH You are going to do great!!! PLACE VALUE ORDERED PAIR (1,2) A pair of numbers used to locate a point on a coordinate plane; the first number tells how far to move horizontally and the second number tells how far to move vertically relation • A set of ordered pairs Example: (5,1) (10,2) (15,3) (20,4) (25,5) GREATEST COMMON FACTOR • The greatest factor that two or more numbers have in common Example: 18: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18 30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30 6 is the GCF of 18 and 30. MULTIPLES • multiple • The product of a given whole number and another wholeExample: number percent • The ratio of a number to 100; percent means "per hundred measure of central tendency • A measure used to describe data; the mean, median, and mode are measures of central tendency. mean • The number found by dividing the sum of a set of numbers by the number of addends; see also average Example: 74, 91, 63, 92, 85 mode • The numbers or items that occur most often in a set of data Example: The mode of 1, 3, 4, 4, and 6 is 4. median • The middle number or the average of the two middle numbers in an ordered set of data Example: The median of 1, 3, 4, 6, and 7 is 4. range • The difference between the greatest and least numbers in a set of data Example: The greatest temperature is 83°F. The least temperature is 80°F. Since 83 - 80 = 3, the range is 3°F. number line • A line with equally spaced tick marks named by numbers (POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE INTEGERS) • Example: A number written as the product of all its prime factors prime number • A whole number greater than 1 whose only factors are 1 and itself • Example 1,2, 3, 5, • Not prime 4, 8, 12, composite number • A whole number that has more than two factors 21: 1, 3, 7, 21 • Example: 4: 1, 2, 4 • Example: parallel lines • Lines in a plane that never intersect perpendicular lines • Two lines that intersect to form four right angles congruent Having the same size and shape Example: The triangles are congruent. line of symmetry A line that divides a figure into two congruent parts similar figures Figures with the same shape but not necessarily the same size Name Sides Angles Triangle 3 3 Quadrilateral 4 4 Pentagon 5 5 Hexagon 6 6 Heptagon 7 7 Octagon 8 8 Nonagon 9 9 Decagon 10 10 FACE • A polygon that is a flat surface of a solid figure Right Triangle • A RIGHT triangle has ONE right angle. obtuse triangle A triangle that has one obtuse angle Example: Acute Triangle • An ACUTE triangle has THREE acute angles. • The ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter circumference The distance around a circle Example: Diameters • A DIAMETER of a circle is a chord that contains the center of the circle. Diameter CV, diameter DT, diameter GH, diameter EU, etc..... Radius • • • • • • • A line segment with one endpoint at the center of a circle and the other endpoint on the circle • acute angle • An angle that has a measure less than a right angle (less than 90°) Example: Straight Angle • A STRAIGHT ANGLE is one whose measure is EXACTLY 180 DEGREES. A straight angle is made up of two opposite rays. Another important fact is that a straight angle forms a straight line. Obtuse Angle • An OBTUSE ANGLE is one whose measure is GREATER THAN 90 AND LESS THAN 180 DEGREES. Right Angle • A RIGHT ANGLE is an angle whose measure is EXACTLY 90 DEGRRES. Right angles are denoted by a small square in its interior. VERTEX • The common point for both rays is called the Vertex. Identify the Triangles • Triangles are also classified according to their length. • Scalene Triangle- no congruent sides • Isosceles Triangle- two congruent sides • Equilateral Triangle- three congruent sides area The number of square units needed to cover a surface Example: The area is 9 square units. Perimeter • The distance • around a figure • 2 cm + 3 cm + 3 cm • = 8 cm The perimeter of this figure is 8 centimeters VOLUME • The measure of the amount of space a solid figure occupies The volume of this figure is 24 cubic units PRISM • A solid figure that has two congruent, polygon-shaped bases, and other faces that are all rectangles pyramid • A solid figure with a polygon base and all other faces triangles that meet at a common vertex Associative Property • The property that states that the way addends are grouped or factors are grouped does not change the sum or the product 12 + (5 + 9) = (12 + 5) + 9 (9 x 8) x 3 = 9 x (8 x 3) Commutative Property • The property that states that when the order of addends or factors is changed, the sum or product is the same 9+4=4+9 6x3=3x6 greater than (>) A symbol used to compare two numbers, with the greater number given first Example: 8>6 8 is greater than 6. FRACTION • A number that names a part of a whole or a part of a group