* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
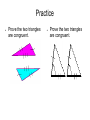
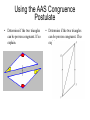
Chapter 4a: Congruent Triangles By: Nate Hungate, Gary Russell, J.P. Lawrence, Kyle Stegman 4.1 Triangles and Angles ● Triangle- A shape formed by three segments joining three non collinear points. ● Vertex- The three points that join the sides of a triangle. ● Adjacent Sides- Two sides that share a common vertex. ● Legs- Sides that form the right angle of a triangle. ● Hypotenuse- The side opposite of the right angle. ● Base- In an isosceles with two congruent sides, the third side is the base. ● Interior Angles- The three angles inside a triangle. ● Exterior Angles- Angles outside of a triangle. ● Corollary- A corollary to a theorem is a statement that is easily proven using the theorem. Names of Triangles ● ● ● ● Classification by sides Three congruent sides= equilateral Two congruent sides= isosceles No congruent sides= scalene ● ● ● ● ● Classification by angles Three acute angles= acute Three congruent angles= equiangular One right angle= right One obtuse angle= obtuse Classifying Triangles ● If triangle ABC has one obtuse angle and two congruent sides, then it is a ________________. ● If triangle DEF has three congruent angles and three congruent sides, then it is a ________________. Theorems ● ● Theorem 4.1: Triangle Sum Theorem= The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180. Corollary to the Triangle theorem: The acute angles of a right triangle are complementary ● Theorem 4.2: Exterior Angle Theorem= the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles. Finding Angle Measures ● Classify the triangle by its angles and by its sides: ● Find the measure of the exterior angle shown: 30 (3x+12) 4.2 Congruence and Triangles ● ● ● Congruent- Two figures are congruent if they are the same size and shape. Corresponding Angles- When two figures are congruent, the corresponding angles are in corresponding positions and are congruent. Corresponding Sides- When two figures are congruent, the corresponding sides are the sides that are in corresponding positions, and they are congruent Naming Congruent Parts of a Triangle ● Identify all pairs of congruent corresponding parts: Theorems ● ● Theorem 4.3: Third Angles Theorem= If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the third angles are also congruent. Theorem 4.4: Properties of Congruent Triangles: Reflexive Property of Congruent Triangles- Every triangle is congruent to itself. Symmetric Property of Congruent Triangles- If triangle ABC is congruent to triangle DEF, then triangle DEF is congruent to triangle ABC. Transitive Property of Congruent Triangles- If triangle ABC is congruent to triangle DEF and triangle DEF is congruent to triangle JKL, then triangle ABC is congruent to triangle JKL. 4.3 Proving Triangles are Congruent: SSS and SAS ● SSS- If three sides of one triangle are congruent to three sides of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. ● SAS- If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. Using the SSS Congruence Postulate ● The marks on the triangle show that segment NM is congruent to segment OL, segment NO is congruent to segment ML, and segment MO is congruent to MO (reflexive property). So by SSS triangle NMO is congruent to triangle LOM. Using the SAS Congruence Postulate ● The marks on the triangles show that segment AB is congruent to DE, angle B is congruent to angle E, and that segment BC is congruent to EF. So by SAS triangle ABC is congruent to triangle DEF. E A F D F B C Practice ● Prove the two triangles are congruent. A B ● Prove the two triangles are congruent. 4.4 Proving Triangles are Congruent: ASA and AAS • ASA- If two angles and • AAS- If two angles and the side the included side a non-included side of of one triangle are one triangle are congruent to two angles congruent to two angles and the included side of and the corresponding a second triangle, then non-included side of a the two triangles are second triangle, then the congruent. two triangles are congruent. Using the ASA Congruence Postulate • Determine if the two triangles can be proven congruent. If so explain. • Determine if the two triangles can be proven congruent. If so explain. Using the AAS Congruence Postulate • Determine if the two triangles can be proven congruent. If so explain. • Determine if the two triangles can be proven congruent. If so explain.