* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Amniotic fluid embolism “ Anaphlactoid Syndrome of pregnancy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
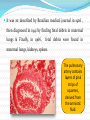
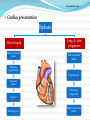
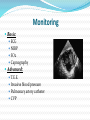
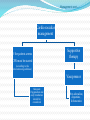
Prof. Dr. Bahaa Ewiss Professor of Ansthesia & Intensive Care Unit Ain Shams university Introduction Amniotic fluid embolism is pure unpreventable, unpredictable & incompletely understood syndrome with potentially lethal complication ( mortality rate up to 85%). So since it is rapid , progressive & with lethal complication, so the diagnosis is very difficult & by exclusion. It was 1st described by Brazilian medical journal in 1926 , then diagnosed in 1941 by finding fetal debris in maternal lungs & Finally, in 1966, fetal debris were found in maternal lungs, kidneys, spleen. The pulmonary artery contains layers of pink strips of squames, derived from the amniotic fluid. Pathophysiology Amniotic fluid + fetal debris Genesis of the syndrome Utero placental membrane leakage Maternal circulation Leukotriens & PGs Predisposing factors Age: > 35 years old Medical induction of labor Amniocentesis Instrumentation Artificial rupture of Multiparicicty membrane Cervical ulceration C.S. Eclampsia Fetal macrosomia Fetal distress Placenta previa Polyhydramnios Uterine rupture Presentation In case of vaginal delivery or C.S. under spinal anesthesia: Acute unexplained hypotension Desaturation , hypoxia , bronchospasm, …. In case of C.S. under G.A. : Unexplained hypotension, hypoxia , coagulopathy Presentation cont…. Cardiac presentation Biphasic Short & rapid Right ventricular failure Long & slow progressive Left ventricular failure Pulmonary hypertension Hypotension Pumonary edema Hypoxia Mortality 50 % Pumonary congestion Right ventricular failure Morbidity of the condition DIC Heart failure Renal failure Neurological ( convulsion) Post arrest complications Monitoring Basic: ECG NIBP SO2 Capnography Advanced: T.E.E. Invasive blood pressure Pulmonary artery catheter CVP Investigations “ non specific “ CBC : there is a marked decrease in the platelet levels Fibrinogen: there is a decrease in the level FDPs: there is an significant increase in the level D.dimer : ???? Management Delivery may increase the survival of both the baby & his mother Management cont….. According to CPR guideline of pregnant women Oxygenation E.T.T Mechanical ventialtion Management cont….. Cardio vascular management If the patient arrests CPR must be started Supportive therapy (according to the international guidelines) Vasopressor Adequate Oxygenation and early intubation should be considered Nor adrenaline, dopamine , dobutamine Other line of management Haemofiltration Plasma exchange ECMO Cell salvage Management of DIC Ventilator assisted devices Frequently asked questions Q1 :What about the role of heparin single dose?? Q2: What about corticosteroid IV?? Conclusion As it is rapid , progressive with lethal complications so we should be minded about amniotic fluid embolism & rapid interference. Good monitoring of the patient during labor , C.S. or in the recovery is mandatory. Amniotic fluid embolism should be considered in case of rapid progressive hypotension, desaturation & hypoxia. Rapid delivery of the baby. CPR as soon as possible.