* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecosystems & Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
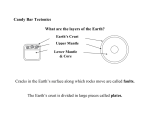
Ecology & Energy ECOLOGY • Study of living organisms and their interactions with the non/ living environment History Made up of Biotic Things: Living • Ernst Haeckel, 1800’s • Eco = “house” • ology = “study of” And Abiotic Things: Not Living Case Study: Easter Island 1) List all of the env. Problems 2) What are the lessons learned? Areas of Ecology • Organisms • Populations • Communities • Ecosystems • Biosphere Organism POPULATION POPULATION POPULATION Community Ecosystem Inhabitants of Ecosystems • Orgs adapted to a specific set environmental conditions, through evolution (natural selection) Charles Darwin Peppered Moths of England Chesapeake Bay Ecosystem • Where Potomac River meets Atlantic Ocean. • 1 Ecosystem, 3 Communities Chesapeake Bay Watershed Chesapeake Communities 1) Potomac River = orgs adapted to fresh water, very low salinity Bull Shark in Potomac River Chesapeake Communities 2) Estuary (place where salt and fresh water meet) • Brackish (salt marsh): orgs adapted to low salinity (salt concentration) Chesapeake Estuary Chesapeake Communities 3) Atlantic Ocean: Salt Water, high salinity All Ecosystems Need Energy! • Comes from the Sun! • Energy: ability to do work! Potential vs. Kinetic Energy • Stored energy • Ex: Water behind a dam Hoover Dam • Energy due to motion • Ex: Light, ball rolling Thermodynamics: the Study of Energy Transformations 1st Law of Thermodynamics • Energy cannot be created nor destroyed • May change from one form to another Ex: Solar Energy Chemical Energy 2nd Law of Thermodynamics • No rxn is 100% efficient lose energy • Systems spontaneously increase entropy (disorder) Gaia Hypothesis • James Lovelock!! • All orgs and non-living factors on Earth are connected. • Self-regulating system which strives to maintain homeostasis Earth’s Layers • Crust: Top layer. • 2 types: Oceanic & Continental • Oceanic crust: thickness of 4-7 km. • At bottom of ocean. • Formed by magma leaks. Continental Crust • Continental crust: 20-40 km thick • Less dense (lighter) than oceanic crust. • We live on it! Mantle • Mantle: below crust • Rocks are a bendable solid (hot). • Where magma comes from. • Never drilled there. Lava Core • Made of Nickel and Iron • HOT! • Gives earth magnetic poles. • Inner core: solid metal. • Outer core: surrounds inner, is liquid metal. Core’s Magnetic Field Alfred Wegener • German Alfred Wegener noticed world continents fit together like a puzzle. • Called puzzle Pangaea. • Said that continents had moved over time. 1st Phase: Pangaea 2nd Phase: Laurasia and Gondwana Lithosphere: AKA Crust • Lithosphere: Crust and top part of mantle • Is broken into parts plates. • Move 1-16 cm/yr, move in all directions. • Plates: convergent, divergent, transform Plate Boundaries in Yellow Plate Tectonics (Plate Handout) • Movement of plates (2-20 cm per yr) • Divergent plates: 2 plates moving apart from each other forms new plates, volcanoes • Convergent plates: 2 plates moving toward each other forms mountains • Transform plates: 2 plates slide past each other makes earthquakes