* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
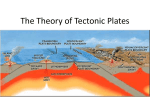
Sea Floor Spreading & Plate Tectonics Ch. 2 part 2 Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. The basics of plate tectonics Convergent vs. divergent boundaries Diagram the geological provinces Active vs. passive continental margins Sea Floor Spreading • Huge pieces of oceanic crust are separating at the mid ocean ridge • Rifts are created: – Cracks in the crust • Releases pressure from mantle • Magma pushes up • Animation • Paper/desk demo with numbers Plate Tectonics • What is the general idea behind plate tectonics? – Earth’s lithoshpere broken into plates – Plates all moving in different directions Plate Tectonics • What is the lithosphere? – The crust and top part of mantle – Lithospheric plates float on asthenosphere • 100km or 60 mi thick Plate Tectonic Boundaries • Three types • Draw them Movement • Plates moving in different directions • This is continental drift • What happens when plates separate (we looked at this already) or collide? Sea Floor Spreading: Divergent Boundaries • I’ll draw this on board--you copy • Forms mid-ocean ridges • Move 2 cm -18 cm per year – Fingernails grow 6 cm year • New lithosphere is created • What happens to old lithosphere? • Destroyed in trenches • Otherwise . . . • . . .earth would be continually expanding Subduction: Convergent Boundaries • Subduction: – Downward movement of lithospheric plate into mantle – Causes earthquakes, volcanoes, and trenches • Three types – Oceanic --> <-- Oceanic – Oceanic --> <-- Continental – Continental --> <-- Continental • Animations Subduction • Oceanic-Continental • Which plate always descends into the other? • Oceanic --> denser. What does this cause? Oceanic --> <--Continental • • • • I’ll draw on board---you copy Trenches volcanoes Mountain ranges Oceanic--> <--Oceanic • Trenches • Volcanoes • Forms island arcs: I draw on board--you copy – Curved chain of volcanic islands along a trench – Examples: • Aleutian and Mariana Islands Older, colder plate becomes denser than underlying hot, weak asthenopshere. Upper sediments become melted --> magma forms --> heads towards surface The Curve • Why are trenches and island arcs curved? – Due to the earth’s spherical shape – Notice Aleutian islands and Mariana trench • What do they call this “ring” in the Pacific? Aleutian Islands Cleveland Volcano, Aleutians Mt. Saint Helens Erupts: 1980 • Play Mt. Saint Helens video clip Ring of Fire (Play Ring of Fire clip) Hot Spots and the HI islands • What are hot spots? (play Hot Spot video clip and Typical Hawaii Eruption clip) • When will Lo'ihi break the surface? Continental--> <-- Continental • I draw on board---you copy • No subduction • Continental plates light, resist downward motion • Rocks buckle and fold and are “welded” together • Mountain range formed • What example is in this picture? • The Himalayas Himalayas from space Himalayan Collision Transform or Shear Boundary • Draw diagram below • Plates slide past each other • What is a classic, local example of this? Quiz a partner • What are the three types of plate tectonic boundaries? Give examples of each and the result of each – Convergent • Oceanic-oceanic (trenches, volcanoes, earthquakes & island arcs) • Oceanic-continental (trenches, volcanoes, mt. ranges) • continent-continent (earthquakes, mountain ranges) – Divergent • Sea floor spreading forms mid ocean ridges – transform • earthquakes Plate Overview Vid Clip Fault lines in the Bay Area Yes, there is more than just one . . . San Andreas Fault • Map and Pic of 1906 quake 1906 Quake Quake of 1989 Hayward Fault • Let’s look at this fault through Google Earth (in demo section—stop at UCB football stadium) • Covers some of the densest urban terrain in CA • Article on Hayward Fault Formation of a New Ocean in Africa? • 3 plates pulling apart from each other at the Afar Triangle (shaded part) – Arabian plate and two parts of the African plate (splitting along East African Rift Zone) – Rift: 36 mi long, 26 ft wide • Red triangles are volcanoes • More on Ethiopia's Afar region Afar Triangle video clip What Causes the Motion of Plates? • Slab Pull: – Lithosphere cools --> denser – Sinks into mantle --> pulls rest of plate with it Convection (heat from core causing mantle to swirl) was original hypothesis Satellite View • Let's zoom in Continental Drift Continental Drift • The continents once united in a supercontinent called Pangaea about 180 mya. • They have since been moving into their present locations • What about before 180 mya? 750 mya to present BBC Interactive Timeline Plate Tectonics 500 million years in the future? • If the plates continue to move in the directions they move today for another 500 million years, propose a configuration of oceans and continents at the end of that time. Constantly Changing Earth • • • • Constantly changing SST and Sea Level More ice --> lower sea level Last ice age about 18,000 years ago There will be more on this later in the year, but here is a quick clip . . . If the sea level rises . . . Geological Provinces • Two main regions in the sea floor: 1. Continental Margin 2. Abyssal plain Continental Margin 1. Continental Shelf: • Submerged; almost flat (400-600 ft) 2. Continental Slope • Steep; edge of continent (10,000-16,500 ft) 3. Continental Rise: • Formed by sediments building up at base of slope Deep Sea Fan • Sediment accumulating at canyon’s base CA Continental Margin (Monterey Bay) Active vs. Passive Margins • Active Margin: – Shelf colliding with another plate – Little or no shelf; steep – earthquakes, volcanoes • Passive Margin: – Trailing edge – Little activity Width of margin: East vs. West coast of South America Hydrothermal vents • What are plates doing at center of ridges? – Pulling apart • Water seeps down cracks, heats up, and emerges • How hot? – Up to 650º F!! • Does anything live down there? Black Smokers • Water dissolves many minerals as it seeps into crust • Emerges hot--> rapidly cools and solidifies • Forms a chimney-like structure • Show Hydro Vents movie clip (5 minutes) Question #1 p. 39 • How can you tell which way the plates are moving? • Trenches indicate plates colliding • Mid-ocean ridge indicates plates separating