* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11venus4s
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Life on Titan wikipedia , lookup
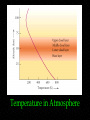
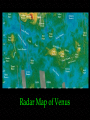
Venus Astronomy 311 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 11 Venus -- The Goddess of Beauty Romans named it Venus for its beauty symbol for Venus is a mirror Venus from Earth sometimes called the morning or evening “star” Venus is covered with clouds clouds reflect ~75% of sunlight Venus Facts Size: 95% Earth Orbit: 0.7 AU Description: Earth-sized, hot, thick atmosphere (Earth’s evil twin) Venus’s Retrograde Rotation When viewed from above the north pole of the Earth, most of the planets: revolve around the Sun counterclockwise It is upside down Why is Venus upside down? We have no evidence of this, however Retrograde Rotation Rotation Rate Venus revolves around the Sun with a period of 225 days Reason is unclear impact altered its rotation rate? Venus from Pioneer Venus’s Atmosphere Composition: Pressure: 90 atmospheres (equal to being 1 km underwater on Earth) Temperature: 750 K (hottest planet in solar system) Chemicals in Atmosphere Forms many sulfur compounds including sulfuric acid (H2SO4) Sulfuric acid has vapor point such that it boils on the surface but condenses in the atmosphere to form clouds Also, hydrofluoric acid (HF), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and other corrosive compounds Temperature in Atmosphere Formation of Atmosphere 1) 2) Water produces greenhouse effect, boils oceans 3) 4) With no water, CO2 cannot be removed from atmosphere, thick CO2 atmosphere forms 5) 6) Volcanoes outgas sulfur, forms sulfuric acid clouds The Surface of Venus Clouds block blue light so surface appears red, but surface is actually gray Chemical analysis indicates that surface rocks are similar to basalt, a volcanic rock Interlude Planetary Configurations Magellan Maps Venus Probes and landers saw only bits and pieces of it Used radar to penetrate the clouds and map the surface with a resolution of 100 meters Radar Map of Venus Global Surface of Venus Two large highlands or continents (Aphrodite Terra and Ishtar Terra) The entire surface is the same age Venus re-surfaces itself Surface features named after women Volcanism on Venus Evidence for Volcanism: sulfur in atmosphere filled craters Note that volcanoes are not active now The Interior of Venus With so much volcanism, part of Venus must be molten, but: the crust is not broken up into moving plates Why no plate tectonics? too hot or too dry? Venus probably has a molten core Next Time Read Chapter 7 Summary Earth-Sized, hot, thick atmosphere (Earth’s evil twin) Rotates slowly and upside-down Studied by Venera landers and Magellan radar mapper Summary: Atmosphere Composed of CO2 with sulfuric acid clouds Thick (90 atmospheres) : No water to wash out CO2 Hot (750 K): Powerful greenhouse effect Summary: Surface Volcanism shapes surface and outgases sulfur See volcanoes and lava flow channels Surface mostly flat with a few highlands Nature of core is unknown