* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
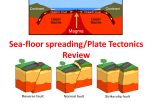
KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME VOCABULARY PLATE TECTONICS 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. Gravity and motions in the asthenosphere move tectonic plates over Earth’s surface. VOCABULARY continental drift Pangaea mid-ocean ridge convection convection current theory of plate tectonics Earth’s tectonic plates. Arrows indicate the direction of movement. CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. •Plates move at very slow rates—from about one to ten centimeters per year. VOCABULARY continental drift Pangaea •At one time in geologic history the continents were joined together in one large landmass called Pangaea. mid-ocean ridge convection convection current •As the plates continued to move and split apart, oceans were formed, landmasses collided and split apart until Earth’s landmasses came to be in the positions they are now. theory of plate tectonics CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. •Evidence of these landmass collisions and splits comes from fossils, landform shape, features, and rock structures, along with climate change. VOCABULARY continental drift Pangaea mid-ocean ridge •Landmass changes can occur at hot spots within lithospheric plates. convection convection current theory of plate tectonics •Earth’s landmasses will continue to move and change during the geologic time of the future. CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. VOCABULARY continental drift continental drift The hypothesis that Earth’s continents move on Earth’s surface. Pangaea mid-ocean ridge convection convection current theory of plate tectonics CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. VOCABULARY continental drift Pangaea A hypothetical supercontinent that included all of the landmasses on Earth. It began breaking apart about 200 million years ago. Pangaea mid-ocean ridge convection convection current theory of plate tectonics CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. VOCABULARY continental drift mid-ocean ridge A long line of sea-floor mountains where new ocean crust is formed by volcanic activity along a divergent boundary. Pangaea mid-ocean ridge convection convection current theory of plate tectonics CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. VOCABULARY continental drift convection A process by which energy is transferred in gases and liquids, occurring when a warmer, less dense area of gas or liquid is pushed up by a cooler, more dense area of the gas or liquid. Pangaea mid-ocean ridge convection convection current theory of plate tectonics CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. VOCABULARY continental drift convection current A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continuous loop. Pangaea mid-ocean ridge convection convection current theory of plate tectonics CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. VOCABULARY continental drift theory of plate tectonics A theory stating that Earth’s lithosphere is broken into huge plates that move and change in size over time. Pangaea mid-ocean ridge convection convection current theory of plate tectonics CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. New crust is formed at divergent boundaries. Features include: • mid-ocean ridges VOCABULARY divergent boundary convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. New crust is formed at divergent boundaries. Features include: • mid-ocean ridges • records of magnetic reversals VOCABULARY divergent boundary convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. New crust is formed at divergent boundaries. Features include: • mid-ocean ridges • records of magnetic reversals • rift valleys VOCABULARY divergent boundary convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. New crust is formed at divergent boundaries. Features include: • mid-ocean ridges • records of magnetic reversals • rift valleys VOCABULARY divergent boundary convergent boundary transform boundary VISUALIZATION CLASSZONE.COM Explore what happens along plate boundaries. rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. VOCABULARY divergent boundary divergent boundary •Where two plates are moving apart. •Most are located along the midoceanic ridge (sea-floor spreading). convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley •New crust forms because magma pushes up and hardens between separating plates. •Characterized by either a mid-ocean ridge or a continental rift valley. magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. VOCABULARY divergent boundary convergent boundary • • • Where two plates come together and collide. Activity depends upon the types of crust that meet. A more dense oceanic plate slides under a less dense continental plate or another oceanic plate—this is called a subduction zone, and some crust is destroyed during this type of activity. convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. VOCABULARY divergent boundary transform boundary •Where two plates slide past each other. •Crust is neither created or destroyed at this type of boundary. •Earthquakes occur frequently along this type of boundary. convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. VOCABULARY divergent boundary rift valley A deep valley formed as tectonic plates move apart, such as along a mid-ocean ridge. convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. VOCABULARY divergent boundary magnetic reversal A switch in the direction of Earth’s magnetic field so that the magnetic north pole becomes the magnetic south pole and the magnetic south pole becomes the magnetic north pole. convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. VOCABULARY divergent boundary hot spot An area where a column of hot material rises from deep within a planet’s mantle and heats the lithosphere above it, often causing volcanic activity at the surface. convergent boundary transform boundary rift valley magnetic reversal hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.4 CHAPTER HOME KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. Crust is destroyed or folded at convergent boundaries. • Subduction boundaries form island arcs, deepocean trenches, and coastal mountains. • Collision boundaries can form mountains. VOCABULARY subduction continentalcontinental collision oceanic-oceanic subduction oceaniccontinental subduction CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE 1.4 CHAPTER HOME KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. Crust is destroyed or folded at convergent boundaries. • Subduction boundaries form island arcs, deepocean trenches, and coastal mountains. • Collision boundaries can form mountains. Crust is neither formed nor destroyed at transform boundaries. VOCABULARY subduction continentalcontinental collision oceanic-oceanic subduction oceaniccontinental subduction CHAPTER RESOURCES SECTION OUTLINE 1.4 CHAPTER HOME KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. VOCABULARY subduction subduction The process by which an oceanic tectonic plate sinks under another plate into Earth’s mantle. continentalcontinental collision oceanic-oceanic subduction oceaniccontinental subduction CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.4 CHAPTER HOME KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. VOCABULARY subduction continental-continental collision A boundary along which two plates carrying continental crust push together. continentalcontinental collision oceanic-oceanic subduction oceaniccontinental subduction CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.4 CHAPTER HOME KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. VOCABULARY subduction oceanic-oceanic subduction A boundary along which a plate carrying oceanic crust sinks beneath another plate with oceanic crust. continentalcontinental collision oceanic-oceanic subduction oceaniccontinental subduction CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.4 CHAPTER HOME KEY CONCEPT Plates converge or scrape past each other. VOCABULARY subduction oceanic-continental subduction A boundary along which a plate carrying oceanic crust sinks beneath a plate with continental crust. continentalcontinental collision oceanic-oceanic subduction oceaniccontinental subduction CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.5 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME The landforms of Earth can be changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces. •http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/tectoni cs/# •http://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/ani mations/volcanoes/index.html VOCABULARY vocanic eruptions mountainbuilding forces stresses normal fault reverse fault strike-slip fault CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.5 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME The landforms of Earth can be changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces. Volcanic Eruptions: •Volcanic eruptions are constructive in that they add new rock to existing land and form new islands. •Magma from the mantle rises to Earth’s surface and flows out an opening called a vent. •Magma that reaches Earth’s surface is known as lava. •The vent as well as the mountain that forms around is from the cooled lava, ash, cinders, and rock is called a volcano. •Most volcanoes occur along plate boundaries; •An area in the Pacific Ocean where volcanoes are common is called the Ring of Fire. VOCABULARY vocanic eruptions mountainbuilding forces stresses normal fault reverse fault strike-slip fault CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.5 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME The landforms of Earth can be changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces. Mountain-Building Forces •Forces or stresses (for example, tension and compression) on rocks in the lithosphere can cause them to bend and stretch. •This bending and stretching can produce mountain ranges. •If pressure is applied slowly, folded mountains form. •Fast pressure=high peak mountains (The Himalayan Mountains) •Slow pressure=folded mountains (they look like a hood of a car after a wreck, and an example are the Appalachian Mountains. VOCABULARY vocanic eruptions mountainbuilding forces stresses normal fault reverse fault strike-slip fault CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.5 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME The landforms of Earth can be changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces. VOCABULARY Stresses: oForces or stresses (for example, tension, compression, or shearing) great enough to cause rocks to break can create faults. oThere are three types of faults. vocanic eruptions mountainbuilding forces stresses normal fault reverse fault strike-slip fault CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.5 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME The landforms of Earth can be changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces. VOCABULARY Normal Faults: •Caused by tension forces. •Happen where the lithosphere is being stretched. •Usually occur at divergent boundaries. •If normal faults uplift a block of rock, a fault-block mountain forms. vocanic eruptions mountainbuilding forces stresses normal fault reverse fault strike-slip fault CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.5 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME The landforms of Earth can be changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces. VOCABULARY Reverse Faults: •Caused by compression forces. •Causes shortening of the crust. •Occurs most frequently at convergent boundaries. vocanic eruptions mountainbuilding forces stresses normal fault reverse fault strike-slip fault CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.5 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME The landforms of Earth can be changed by volcanic eruptions and mountain-building forces. VOCABULARY Strike-Slip Faults: •Caused by shearing forces. •Occur most often at transform boundaries. •Example of fault: the San Andreas Fault •http://www.iris.edu/gifs/anim ations/faults.htm vocanic eruptions mountainbuilding forces stresses normal fault reverse fault strike-slip fault CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.1 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Earth has several layers. I. Earth has several layers. A. Earth is made up of materials with different densities. B. Earth’s layers have different properties. 1. Core, Mantle, Crust C. The lithosphere is made up of many plates. VOCABULARY inner core outer core mantle crust lithosphere asthenosphere tectonic plate CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.2 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Continents change position over time. II. Continents change position over time. VOCABULARY continental drift A. Continents join together and split apart. Pangaea 1. Evidence for Continental Drift mid-ocean ridge 2. Pangaea and Continental Drift convection B. The theory of plate tectonics explains how plates and their continents move. 1. Evidence from the Sea Floor convection current theory of plate tectonics 2. Causes of Plate Movement 3. Putting the Theory Together CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.3 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates move apart. III. Plates move apart. A. Tectonic plates have different boundaries. B. The sea floor spreads apart at divergent boundaries. VOCABULARY divergent boundary convergent boundary 1. Mid-Ocean Ridges and Rift Valleys transform boundary 2. Sea-Floor Rock and Magnetic Reversals rift valley C. Continents split apart at divergent boundaries. magnetic reversal D. Hot spots can be used to track plate movements. hot spot CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY 1.4 KEY CONCEPT CHAPTER HOME Plates converge or scrape past each other. IV. Plates converge or scrape past each other. A. Tectonic plates push together at convergent boundaries. 1. Continental-Continental Collision 2. Oceanic-Oceanic Subduction 3. Oceanic-Continental Subduction B. Tectonic plates scrape past each other at transform boundaries. VOCABULARY subduction continentalcontinental collision oceanic-oceanic subduction oceaniccontinental subduction C. The theory of plate tectonics helps geologists today. CHAPTER RESOURCES KEY CONCEPT SUMMARY CHAPTER HOME Chapter Resources Image Gallery Review Game Animations Click here to review chapter images and animations Play a fun interactive review game Link to all the McDougal Littell Science animations Click on the items below to access resources on Audio Readings Resource Centers Hear chapter audio readings Get more information on select science topics Content Review Standardized Test Practice Review key concepts and vocabulary 4 % CE 7 1 0 2 6 5 4 3 9 8 3 2 . Math Tutorial M+ M– M CC ON/C 5 1 CLASSZONE.COM Review math concepts BACK TO CHAPTER Practice state standardized tests