* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Units 1 & 2 Geography
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
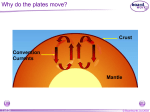
Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher’s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 1 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Constructive plate boundary At a constructive plate boundary, two plates move apart. As the two plates move apart, magma rises up to fill the gap. This causes volcanoes. However, since the magma can escape easily at the surface the volcano does not erupt with much force. Earthquakes are also found at constructive boundaries. An example of a constructive boundary is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. 2 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Constructive plate boundary 3 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 How fast do plates move? Tectonic plates move at different rates. The Nazca and Pacific plates are moving apart at a rate of 18cm per year while the Eurasian and North American plates are moving apart at a rate of 3cm per year. To the nearest metre, how far will the Nazca and Pacific plates have moved over the next 200 years? 6 metres 4 of 31 36 metres 200 metres 928 metres © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Constructive plate boundaries mid-ocean ridge B A ocean mantle Where would you find older rocks – at A or at B? 5 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Destructive plate boundary A destructive plate boundary is found where a continental plate meets an oceanic plate. The oceanic plate descends under the continental plate because it is denser. As the plate descends it starts to melt due to the friction caused by the movement between the plates. This melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock forms a volcano. 6 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Destructive plate boundary 7 of 31 © Boardworks Ltd 2005 Destructive plate boundary Match the labels to the letters. F E A B D 1.oceanic plate 2. The oceanic crust sinks under the less dense continental crust. 4. continental crust 8 of 31 C 5. explosive volcanoes 3. The oceanic crust melts and rises. 6. mantle © Boardworks Ltd 2005